“Smartly incorporating ChatGPT into education could actually benefit students and teachers.” Big Think.
Once students master the basics of math, they are allowed to use calculators. The same should be true of writing and ChatGPT.

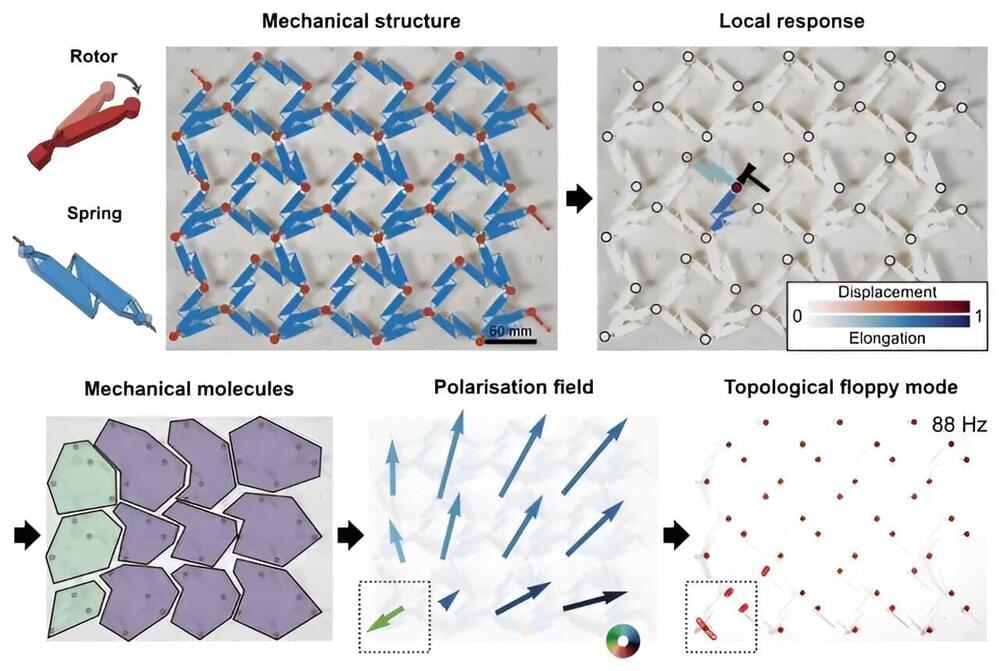
The branch of mathematics known as topology has become a cornerstone of modern physics thanks to the remarkable—and above all reliable—properties it can impart to a material or system. Unfortunately, identifying topological systems, or even designing new ones, is generally a tedious process that requires exactly matching the physical system to a mathematical model.
Researchers at the University of Amsterdam and the École Normale Supérieure of Lyon have demonstrated a model-free method for identifying topology, enabling the discovery of new topological materials using a purely experimental approach. The research is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Topology encompasses the properties of a system that cannot be changed by any “smooth deformation.” As you might be able to tell from this rather formal and abstract description, topology began its life as a branch of mathematics. However, over the last few decades physicists have demonstrated that the mathematics underlying topology can have very real consequences. Topological effects can be found in a wide range of physical systems, from individual electrons to large-scale ocean currents.

It wasn’t until Albert Einstein that we developed a more sophisticated mathematical understanding of time and space that allowed physicists to probe deeper into the connections between them. In their endeavors, physicists also discovered that seeking the origin of time forces us to confront the origins of the universe itself.
What exactly is time, and how did it come into being? Did the dimension of time exist from the moment of the Big Bang, or did time emerge as the universe evolved? Recent theories about the quantum nature of gravity provide some unique and fantastic answers to these millennia-old questions.

Cryptocurrency is usually “mined” through the blockchain by asking a computer to perform a complicated mathematical problem in exchange for tokens of cryptocurrency. But in research appearing in the journal Chem a team of chemists has repurposed this process, asking computers to instead generate the largest network ever created of chemical reactions which may have given rise to prebiotic molecules on early Earth.
This work indicates that at least some primitive forms of metabolism might have emerged without the involvement of enzymes, and it shows the potential to use blockchain to solve problems outside the financial sector that would otherwise require the use of expensive, hard to access supercomputers.
“At this point we can say we exhaustively looked for every possible combination of chemical reactivity that scientists believe to had been operative on primitive Earth,” says senior author Bartosz A. Grzybowski of the Korea Institute for Basic Science and the Polish Academy of Sciences.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency launched a second iteration of its Tools Competition to discover artificial intelligence-enabled technologies that can aid data science and other forms of adult learning.
The agency said Monday that the new program aims to upskill and reskill adults in science, technology, engineering and mathematics and similarly complex areas, preparing them for the 21st century labor landscape.
The opportunity is open to digital learning platform experts, technologists, researchers, students and educators who can propose AI tools that can provide feature tutoring and self-directed learning. The resulting platform may leverage AI or large language models.
With the insertion of a little math, Sandia National Laboratories researchers have shown that neuromorphic computers, which synthetically replicate the brain’s logic, can solve more complex problems than those posed by artificial intelligence and may even earn a place in high-performance computing.
The findings, detailed in a recent article in the journal Nature Electronics, show that neuromorphic simulations employing the statistical method called random walks can track X-rays passing through bone and soft tissue, disease passing through a population, information flowing through social networks and the movements of financial markets, among other uses, said Sandia theoretical neuroscientist and lead researcher James Bradley Aimone.
“Basically, we have shown that neuromorphic hardware can yield computational advantages relevant to many applications, not just artificial intelligence to which it’s obviously kin,” said Aimone. “Newly discovered applications range from radiation transport and molecular simulations to computational finance, biology modeling and particle physics.”

Google Deepmind says that a new artificial intelligence system has made a major breakthrough in one of the most difficult tests for AI.
The company says that it has created a new AI system that can solve geometry problems at the level of the very top high-school students.
Geometry is one of the oldest branches of mathematics, but has proven particularly difficult for AI systems to work with. It has been difficult to train them because of a lack of data, and succeeding requires building a system that can take on difficult logical challenges.
In 1,827, botanist Robert Brown studied pollen particles’ motion as they were suspended in water. These little grains seemed to jitter around randomly. Brown performed as variety of tests on them and realized that all small particles, not just pollen, exhibited the same motion when suspended in water. Something other than the presence of life was causing these little particles to move around. Mathematicians took note and quickly developed a theory describing this process and named it Brownian Motion in his honor.
This theory has expanded well beyond its original context and become a beautiful subfield of mathematics called Stochastic Processes. Nowhere was this influence illustrated better than in 1905 when Albert Einstein used the theory of Brownian Motion to verify the existence of atoms. The makeup of our universe’s tiniest particles was highly debated at the time, and Einstein’s work helped solidify atomic theory.
Wow, that’s quite the leap! In order to understand how we got from pollen grains to confirming atomic theory, we’re going to have to learn some background about Brownian Motion. In this article, I’ll spend some time talking about the basics. This includes some cool videos that demonstrate the patterns of Brownian Motion and the statistics going on behind the scenes. We’ll then dive into Einstein’s version which came as one of his extremely influential series of papers in 1905. There’s a lot of ground to cover, so let’s get started!

The possibility of direct interfacing between biological and technological information devices could result in a merger of mind and machine — Ultimate Computing. This book, a thorough consideration of this idea, involves a number of disciplines, including biochemistry, cognitive science, computer science, engineering, mathematics, microbiology, molecular biology, pharmacology, philosophy, physics, physiology, and psychology.
