The pointy edges of petals rely on a type of geometric feedback never before seen in nature.



A UNSW Sydney mathematician has discovered a new method to tackle algebra’s oldest challenge—solving higher polynomial equations.
Polynomials are equations involving a variable raised to powers, such as the degree two polynomial: 1 + 4x – 3x2 = 0.
The equations are fundamental to math as well as science, where they have broad applications, like helping describe the movement of planets or writing computer programs.

The quantum black hole with (almost) no equations by Professor Gerard ‘t Hooft.
How to reconcile Einstein’s theory of General Relativity with Quantum Mechanics is a notorious problem. Special relativity, on the other hand, was united completely with quantum mechanics when the Standard Model, including Higgs mechanism, was formulated as a relativistic quantum field theory.
Since Stephen Hawking shed new light on quantum mechanical effects in black holes, it was hoped that black holes may be used to obtain a more complete picture of Nature’s laws in that domain, but he arrived at claims that are difficult to use in this respect. Was he right? What happens with information sent into a black hole?
The discussion is not over; in this lecture it is shown that a mild conical singularity at the black hole horizon may be inevitable, while it doubles the temperature of quantum radiation emitted by a black hole, we illustrate the situation with only few equations.
About the Higgs Lecture.
The Faculty of Natural, Mathematical & Engineering Sciences is delighted to present the Annual Higgs Lecture. The inaugural Annual Higgs Lecture was delivered in December 2012 by its name bearer, Professor Peter Higgs, who returned to King’s after graduating in 1950 with a first-class honours degree in Physics, and who famously predicted the Higgs Boson particle.


Humans are known to make mental associations between various real-world stimuli and concepts, including colors. For example, red and orange are typically associated with words such as “hot” or “warm,” blue with “cool” or “cold,” and white with “clean.”
Interestingly, some past psychology studies have shown that even if some of these associations arise from people’s direct experience of seeing colors in the world around them, many people who were born blind still make similar color-adjective associations. The processes underpinning the formation of associations between colors and specific adjectives have not yet been fully elucidated.
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison recently carried out a study to further investigate how language contributes to how we learn about color, using mathematical and computational tools, including Open AI’s GPT-4 large language model (LLM). Their findings, published in Communications Psychology, suggest that color-adjective associations are rooted in the structure of language itself and are thus not only learned through experience.

But now, a bold new idea is challenging this tidy system. Scientists at Rice University in Texas believe there may be a third kind of particle—one that doesn’t follow the rules of fermions or bosons. They’ve developed a mathematical model showing how these unusual entities, called paraparticles, could exist in real materials without breaking the laws of physics.
“We determined that new types of particles we never knew of before are possible,” says Kaden Hazzard, one of the researchers behind the study. Along with co-author Zhiyuan Wang, Hazzard used advanced math to explore this idea.
Their work, published in Nature, suggests that paraparticles might arise in special systems and act differently than anything scientists have seen before.
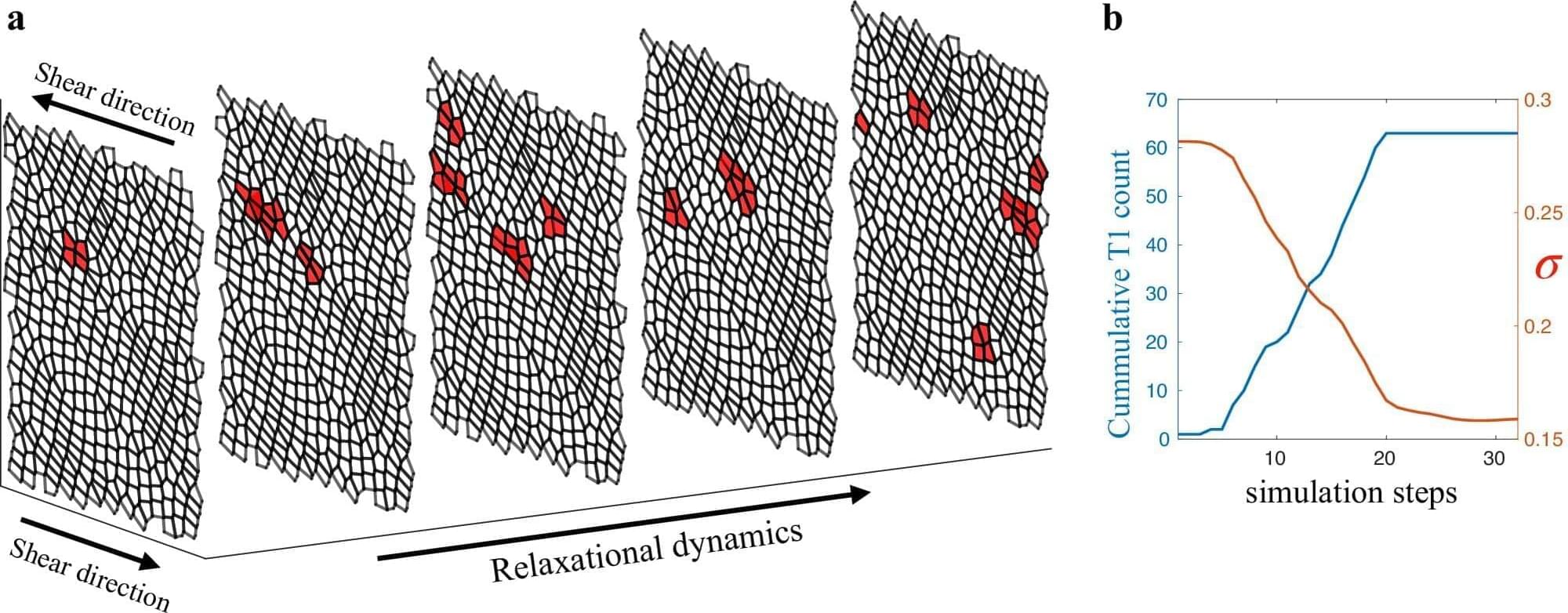
An avalanche is caused by a chain reaction of events. A vibration or a change in terrain can have a cascading and devastating impact.
A similar process may happen when living tissues are subject to being pushed or pulled, according to new research published in Nature Communications, by Northeastern University doctoral student Anh Nguyen and supervised by Northeastern physics professor Max Bi.
As theoretical physicists, Bi and Nguyen use computational modeling and mathematics to understand the mechanical processes that organisms undergo on a cellular level. With this more recent work, they have observed that when subjected to sufficient stress, tissues can “suddenly and dramatically rearrange themselves,” similar to how avalanches are formed in the wild.
Curt Jaimungal and Graham Priest sit down to discuss various philosophical themes including the nature of truth, logic and paradoxes, the philosophy of mathematics, concepts of nothingness and existence, and the influence of Eastern philosophy on Western logical traditions.
Consider signing up for TOEmail at https://www.curtjaimungal.org.
Support TOE:
- Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal (early access to ad-free audio episodes!)
- Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE
- PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE
- TOE Merch: https://tinyurl.com/TOEmerch.
Follow TOE:
- NEW Get my ‘Top 10 TOEs’ PDF + Weekly Personal Updates: https://www.curtjaimungal.org.
- Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/theoriesofeverythingpod.
- TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@theoriesofeverything_
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/TOEwithCurt.
- Discord Invite: https://discord.com/invite/kBcnfNVwqs.
- iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/ca/podcast/better-left-unsaid-wit…1521758802
- Pandora: https://pdora.co/33b9lfP
- Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b92xAErofYQA7bU4e.
- Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: https://reddit.com/r/theoriesofeverything.
Join this channel to get access to perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCdWIQh9DGG6uhJk8eyIFl1w/join.
Timestamps: