Scientists have found an elusive third form of magnetism that could help solve a longstanding puzzle about superconductors.
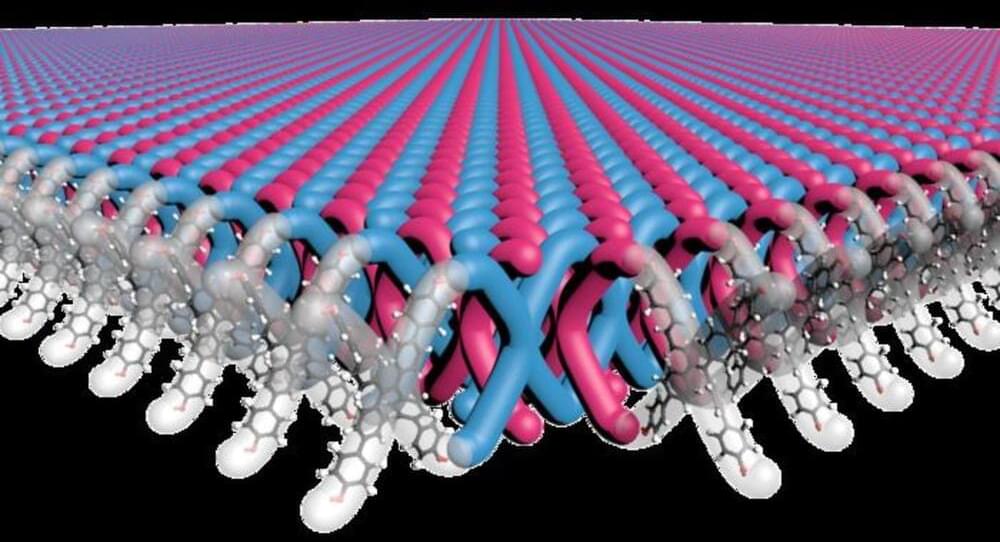
A research team led by scientists at Northwestern University has developed the first-ever two-dimensional mechanically interlocked material with high flexibility and strength. In the future, this could be used to develop lightweight yet high-performance body armor and other such tough materials, a press release said.
It was in the 1980s that Fraser Stoddart, then a chemist at Northwestern University, first introduced the concept of mechanical bonds. Stoddart then expanded the role of these bonds into molecular machines by enabling functions like switching, rotating, contracting, and expanding in multiple ways and using them to develop interlocked structures, which also won him the Nobel Prize in 2016.
A look at the enduring relevance.of Invasion of the Body Snatchers.
https://buymeacoffee.com/cinemollusk.
Review/analysis references the following material:
Invasion of the Body Snatchers (Philip Kaufman, 1978)
Invasion of the Body Snatchers (Don Siegel, 1956)
The Invasion (Oliver Hirschbiegel / James McTeigue, 2007)
Body Snatchers (Abel Ferrara, 1993)
Little Joe (Jessica Hausner, 2019)
The Trap (Adam Curtis, 2007)
Paracelsus (G.W. Pabst, 1943)
Day of Wrath (Carl Dreyer, 1943)
The Devils (Ken Russell, 1971)
Triumph of the Will (Leni Riefenstahl, 1935)
A Clockwork Orange (Stanley Kubrick, 1971)
The Day the Earth Stood Still (Robert Wise, 1951)
Childhood’s End (Arthur C. Clarke, 1953)
For entertainment and educational purposes only.
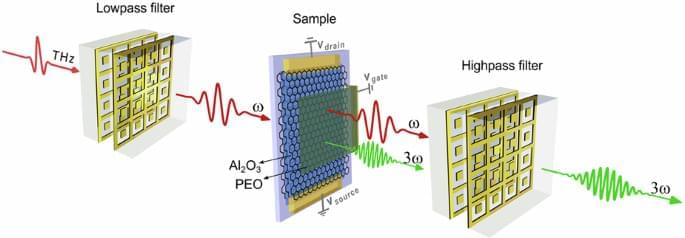
The experimental configuration is shown schematically in Fig. 1. Sensitive detection of the THG signal requires the use of a lowpass filter (LPF), reducing the spectral width of the pump pulse and eliminating any residual pump at the third harmonic frequency. After the generation of the THG inside the graphene-based sample, a highpass filter (HPF) is used to limit the incident pump reaching the detection scheme. Although the HPF used in our experiment does not completely eliminate the pump, it still reduces the pump-induced noise at the third harmonic frequency to a value close to the noise floor. This technique relying on a HPF significantly increases the sensitivity of time-resolved detection to monitor the creation of new spectral components24,29. The general design of these filters are described in previous work31 and their spectral transmission properties are shown in Section 2 of the Supplementary Information. In brief, the LPF transmits multicycle THz pump pulse centered at the frequency, ω = 0.8 THz, and strongly attenuates (∼ 50 dB) spectral components beyond 1.5 THz. The HPF attenuates the pump pulse by 30 dB while transmitting the third harmonic at 3ω
We investigate six nonlinear samples consisting of stacked graphene sheets, from 1 to 15 layers, allowing us to vary the nonlinear interaction length. Figure 2a shows the spectrum of the THz pulse (blue line) transmitted through the LPF and used as the pump at the fundamental frequency ω. This graph only contains spectral measurements collected with the 1-, 3-, and 6-layer graphene samples (purple, green and red lines, respectively) for enhanced clarity of the display. A distinct THG spectral peak at 3ω = 2.4 THz can be observed with an intensity increasing roughly quadratically with the number of graphene layers (see Sections 1 and 3 in the Supplementary Information). The HPF, which role is to decrease the residual pump, allows the noise level at frequencies beyond 1.5 THz to settle close to the noise floor (grey shaded area), enabling sensitive monitoring of the nonlinear effects. Figure 2b shows the time-resolved multicycle pump pulse (blue line) with a peak amplitude of 32 kV/cm.
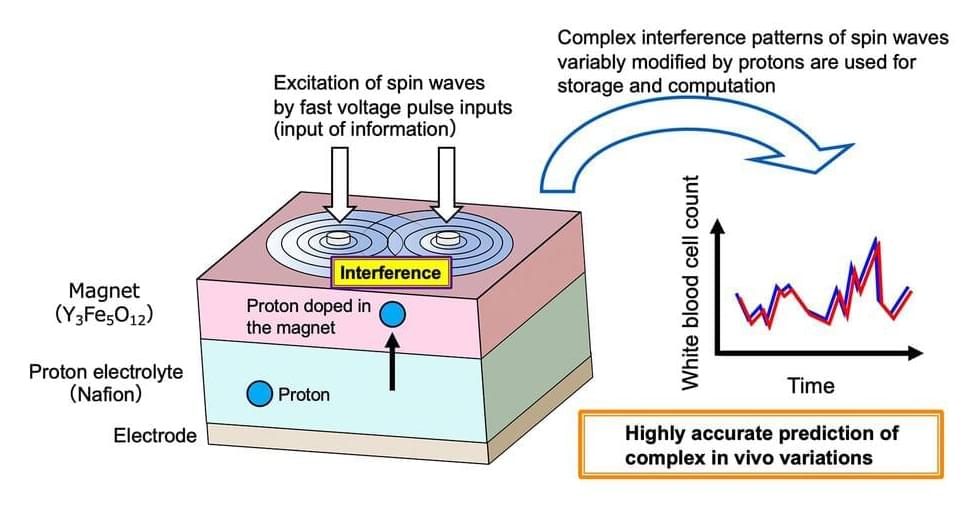
A research team from NIMS and the Japan Fine Ceramics Center (JFCC) has developed a next-generation AI device—a hardware component for AI systems—that incorporates an iono-magnonic reservoir. This reservoir controls spin waves (collective excitations of electron spins in magnetic materials), ion dynamics and their interactions.
The work is published in the journal Advanced Science.
The technology demonstrated significantly higher information processing performance than conventional physical reservoir computing devices, underscoring its potential to transform AI technologies.

Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have discovered a new superconducting material. They combined iron, nickel, and zirconium, to create a new transition metal zirconide with different ratios of iron to nickel. The findings are published in the Journal of Alloys and Compounds.
While both iron zirconide and nickel zirconide are not superconducting, the newly prepared mixtures are exhibiting a “dome-shaped” phase diagram typical of so-called “unconventional superconductors,” a promising avenue for developing high temperature superconducting materials which can be more widely deployed in society.
Superconductors already play an active role in cutting-edge technologies, from superconducting magnets in medical devices and maglev systems to superconducting cables for power transmission. However, they generally rely on cooling to temperatures of around four Kelvin, a key roadblock in wider deployment of the technology.
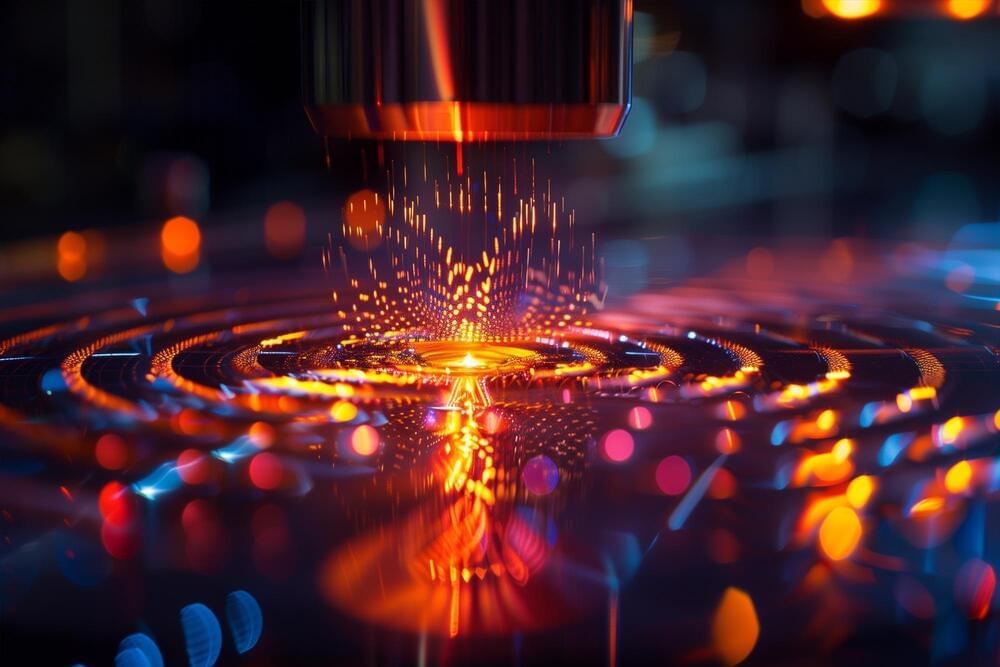

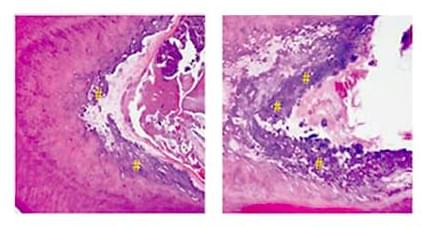
A small dose of low-power laser light activated dental stem cells in rat molars to generate dentin, one of the major components of teeth. The finding may lead to new approaches to develop low-cost, non-invasive therapies for treating dental disease and tooth damage.
Dentists currently use inert materials to repair damaged teeth. Tissue regeneration would be an attractive alternative, because inert materials can fail with time and don’t provide the full function of the tissue. Stimulating regeneration of teeth, however, is a major challenge. Teeth are composed of several parts, including the pulp at the core, dentin in the middle, and enamel on the surface.
Stem cells, found throughout the body, can give rise to specialized cells. Researchers have been able to coax stem cells to transform (differentiate) into many types of cells in the laboratory before infusing them into the body. But these techniques are time consuming and can bring unwanted side effects.
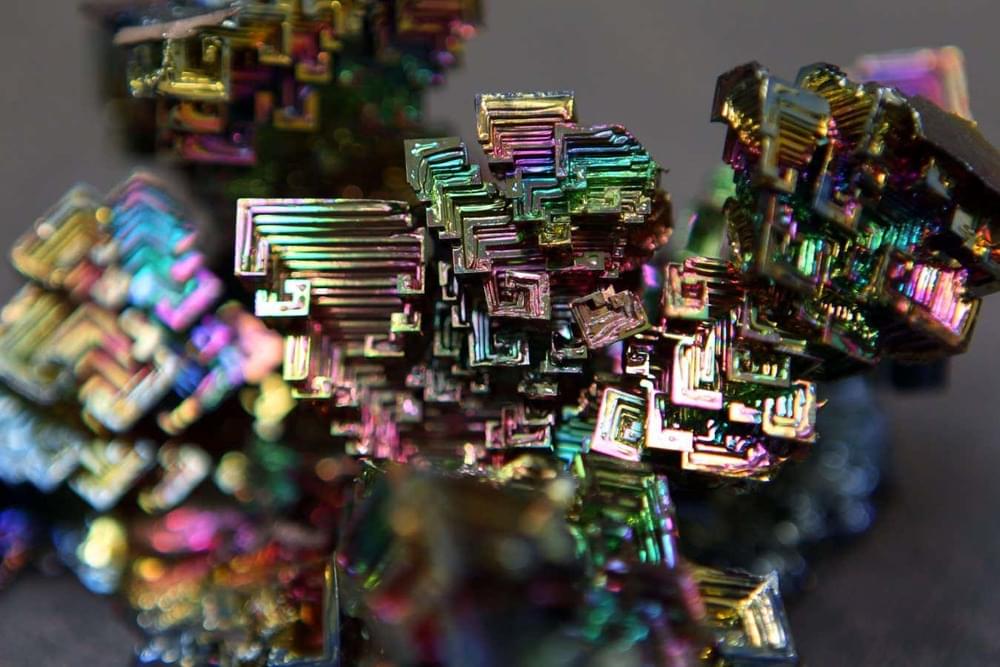

The soft metal bismuth may be a wonder material for electronics – particularly because of one surprising behaviour it displays when exposed to magnetic fields.
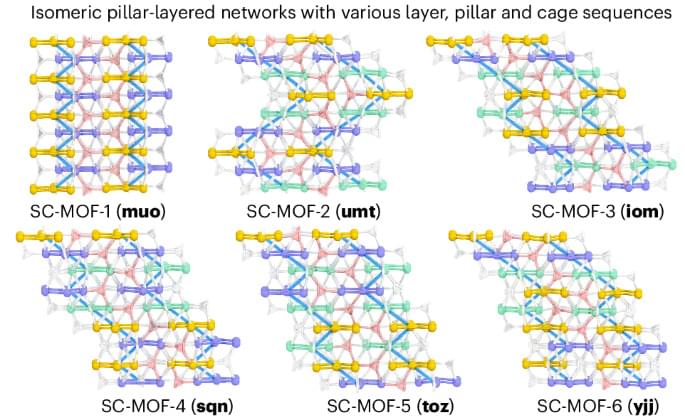
The tailoring of reticular materials is key for enhancing the complexity and diversity of their structure and function. Now, a series of isomeric pillar-layered metal–organic frameworks with tunable topologies have been prepared through altering the layer stacking, which enables variability on the backbone structure, pillar spatial arrangements and pore structure.