Humans’ relationships with plants is largely utilitarian, serving our needs. We generally either eat them or make things out of them.
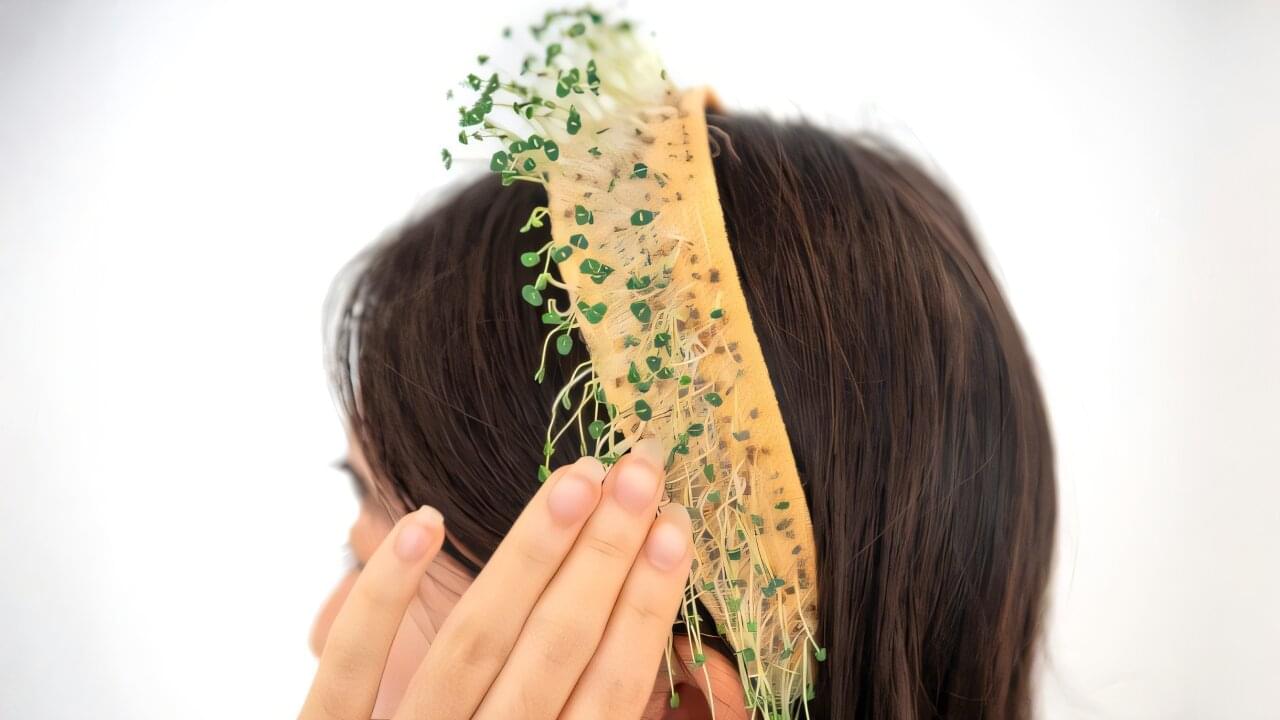
Researchers in the College of Human Ecology (CHE) have developed a design and fabrication approach that treats these living things as companions to humans, with seeds woven into hydrogel material for hairbands, wristbands, hats and sandals, among other applications. The seeds grow into sprouts if taken care of properly.
“For most of human history, we have lived alongside plants, and they’ve been leveraged by humans to be used as food or spun into yarns for fabric,” said Cindy Hsin-Liu Kao, associate professor of human centered design (CHE).