Using ultrafast x-ray pulses, researchers have probed the chirality of spin spirals in synthetic antiferromagnets.
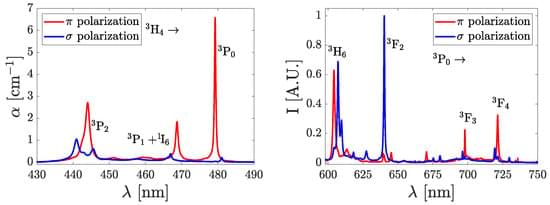
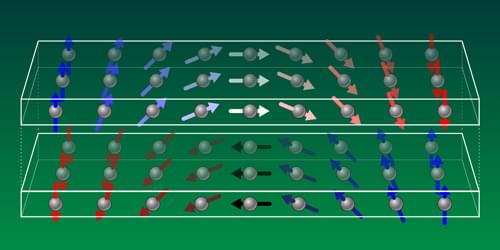
Magnetism is a constant companion in our daily lives. Data storage, sensors, electric motors—none of these devices would function without it. Yet most technologies exploit only the simplest form of magnetic order: ferromagnetism, in which all magnetic moments within a domain align in the same direction. But magnetic order can be far more intricate. In conventional antiferromagnets (AFMs), the magnetic moments align in opposite directions to produce zero net magnetization, a type of order which has several advantages over ferromagnetism in many next-generation technological applications. In more exotic materials, the magnetic moments can twist into spirals, vortices, and other spin structures that might one day be used to store information. Occurring in both ferromagnets and AFMs, these spin structures are defined by their chirality, the direction in which the spins rotate relative to a fixed axis.
The chirality is a key fingerprint of the competing interactions at play in complex magnetic systems. However, observing the dynamics of chirality and magnetization in AFMs has been experimentally challenging, as both can evolve over nanometer length scales and on femtosecond timescales. In a new study, Zongxia Guo from the French National Centre for Scientific Research and colleagues have taken a major step forward by probing both quantities with ultrashort and ultrabright pulses from a free-electron laser (FEL) [1]. The researchers look specifically at spin spirals in an AFM, and they find that—under laser excitation—the chirality and magnetization evolve together in near unison and on significantly faster time scales than is observed for ferromagnets. Such fast spin dynamics in chiral spin structures offers a promising new route for how we will store, transfer, and compute information in the future.