npj Computational Materials volume 6, Article number: 73 (2020) Cite this article.

npj Computational Materials volume 6, Article number: 73 (2020) Cite this article.
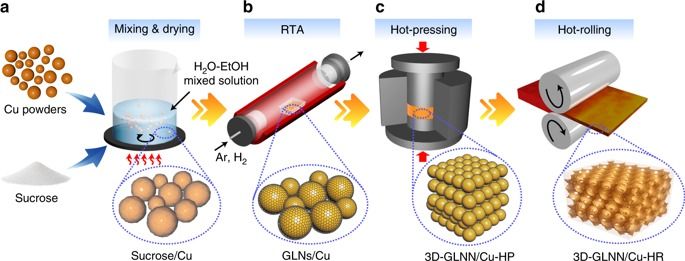
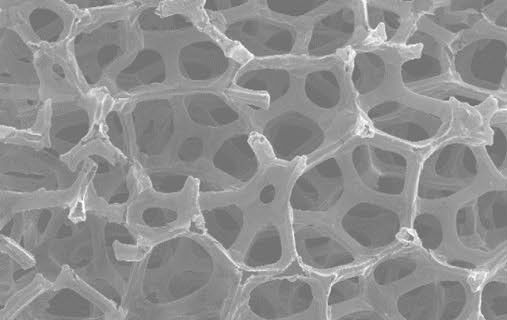
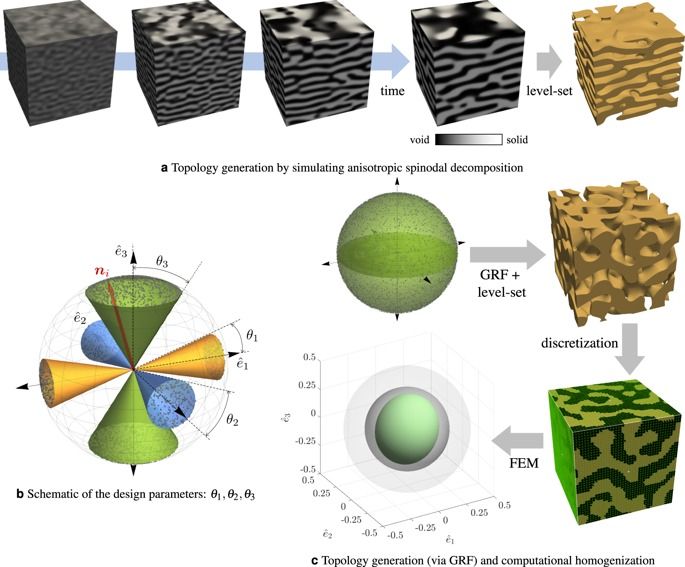
Three-dimensional graphene network is a promising structure for improving both the mechanical properties and functional capabilities of reinforced polymer and ceramic matrix composites. However, direct application in a metal matrix remains difficult due to the reason that wetting is usually unfavorable in the carbon/metal system. Here we report a powder-metallurgy based strategy to construct a three-dimensional continuous graphene network architecture in a copper matrix through thermal-stress-induced welding between graphene-like nanosheets grown on the surface of copper powders. The interpenetrating structural feature of the as-obtained composites not only promotes the interfacial shear stress to a high level and thus results in significantly enhanced load transfer strengthening and crack-bridging toughening simultaneously, but also constructs additional three-dimensional hyperchannels for electrical and thermal conductivity. Our approach offers a general way for manufacturing metal matrix composites with high overall performance.

Polarization, the direction in which light vibrates, is invisible to the human eye. Yet, so much of our optical world relies on the control and manipulation of this hidden quality of light.
Materials that can manipulate the polarization of light —known as birefringent materials—are used in everything from digital alarm clocks to medical diagnostics, communications and astronomy.
Just as light’s polarization can vibrate along a straight line or an ellipse, materials can also be linearly or elliptically birefringent. Today, most birefringent materials are intrinsically linear, meaning they can only manipulate the polarization of light in a limited way. If you want to achieve broad polarization manipulation, you need to stack multiple birefringent materials on top of one another, making these devices bulky and inefficient.
The truth about graphene. Ever since it was first discovered in 2004, graphene has been hailed as one of the most important breakthroughs in materials since the plastics revolution more than a century ago. The early predictions were that graphene would almost immediately enable the kinds of products and technologies that we’re used to seeing in sci-fi movies. Cut to more than a decade and a half later and that still hasn’t happened. Not even close. With opinions split between people overhyping graphene or calling it a massive disappointment, it’s time we got to the truth of what is really happening with this so-called ‘wonder material’.
▻ Watch the truth about solid state batteries — how close are they?: https://youtu.be/x8FEyaZxqAU
▻ Full script and citations: https://undecidedmf.com/episodes/2020/5/20/the-truth-about-g…he-hold-up
——————-
▶ ▶ ▶ ADDITIONAL INFO ◀ ◀ ◀
▻ Support us on Patreon!
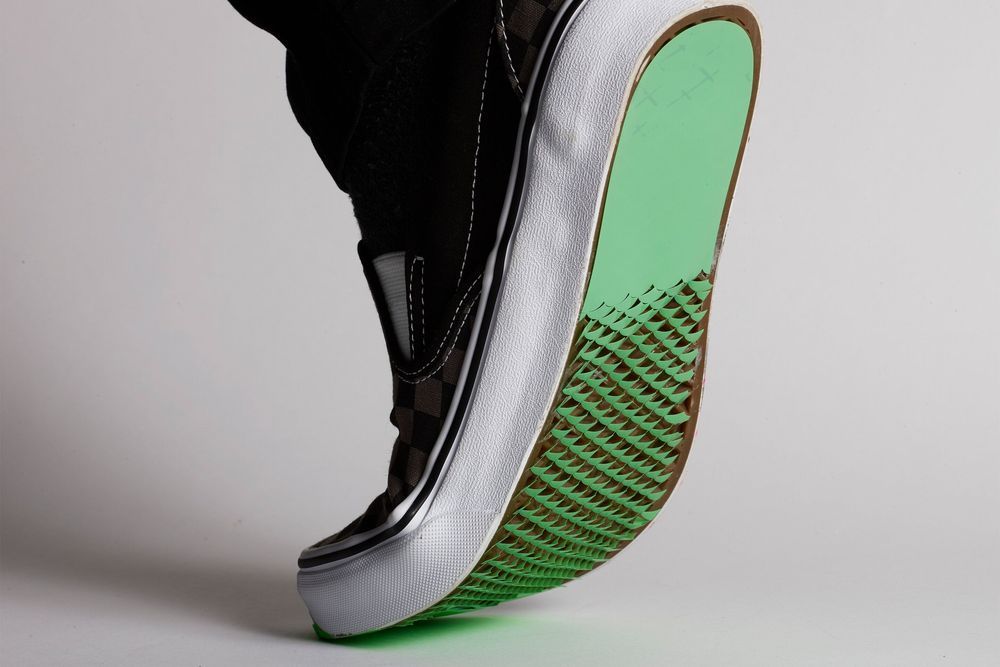

Inspired by the Japanese art of paper cutting, MIT engineers have designed a friction-boosting material that could be used to coat the bottom of your shoes, giving them a stronger grip on ice and other slippery surfaces.
The researchers drew on kirigami, a variation of origami that involves cutting paper as well as folding it, to create the new coating. Laboratory tests showed that when people wearing kirigami-coated shoes walked on an icy surface, they generated more friction than the uncoated shoes.
Incorporating this coating into shoes could help prevent dangerous falls on ice and other hazardous surfaces, especially among the elderly, the researchers say.

In the periodic table of elements there is one golden rule for carbon, oxygen and other light elements: Under high pressures, they have similar structures to heavier elements in the same group of elements. But nitrogen always seemed unwilling to toe the line. However, high-pressure chemistry researchers of the University of Bayreuth have disproved this special status. Out of nitrogen, they created a crystalline structure which, under normal conditions, occurs in black phosphorus and arsenic. The structure contains two-dimensional atomic layers, and is therefore of great interest for high-tech electronics. The scientists have presented this “black nitrogen” in Physical Review Letters.
Nitrogen—an exception in the periodic system?
When you arrange the chemical elements in ascending order according to their number of protons and look at their properties, it soon becomes obvious that certain properties recur at large intervals (periods). The periodic table of elements brings these repetitions into focus. Elements with similar properties are placed one below the other in the same column, and thus form a group of elements. At the top of a column is the element that has the fewest protons and the lowest weight compared to the other group members. Nitrogen heads element group 15, but was previously considered the “black sheep” of the group. The reason: In earlier high-pressure experiments, nitrogen showed no structures similar to those exhibited under normal conditions by the heavier elements of this group—specifically, phosphorus, arsenic and antimony. Instead, such similarities are observed at high pressures in the neighboring groups headed by carbon and oxygen.
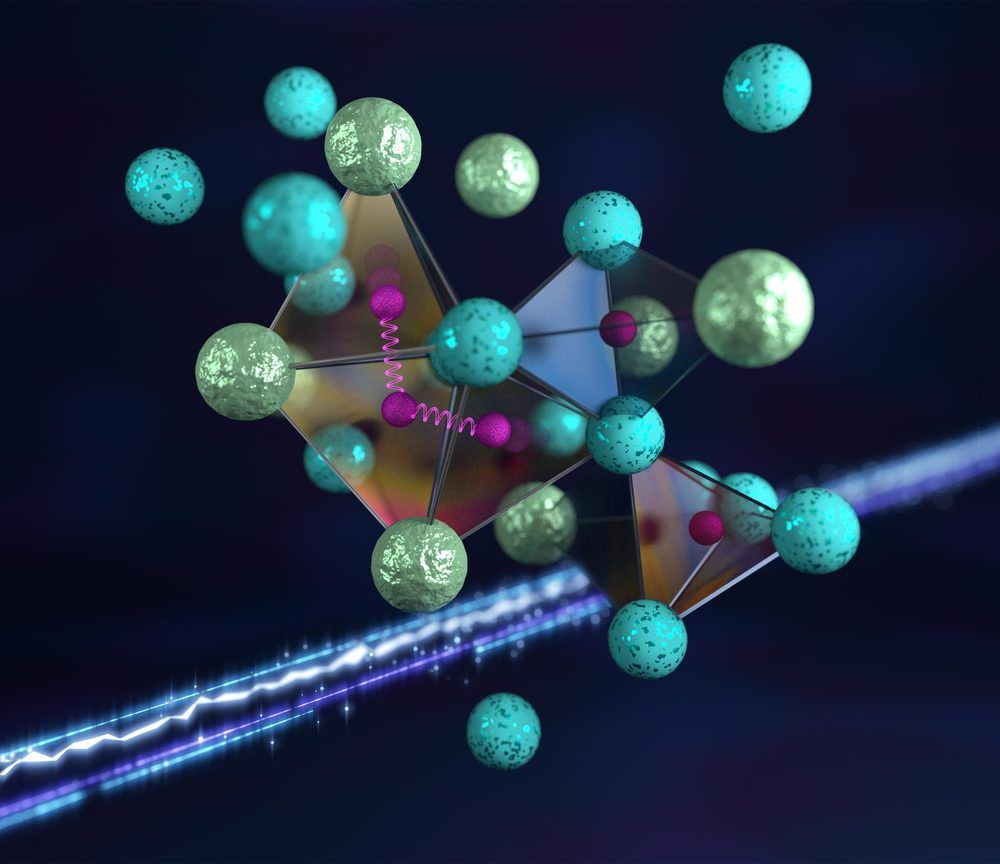
An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.
Such a superconducting material, carrying electricity without any energy loss due to resistance, would revolutionize energy efficiency in a broad range of consumer and industrial applications.
The scientists conducted neutron scattering experiments at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory on samples of zirconium vanadium hydride at atmospheric pressure and at temperatures from −450 degrees Fahrenheit (5 K) to as high as −10 degrees Fahrenheit (250 K) — much higher than the temperatures where superconductivity is expected to occur in these conditions.