
Category: materials – Page 264

In vitro efficacy of artemisinin-based treatments against SARS-CoV-2
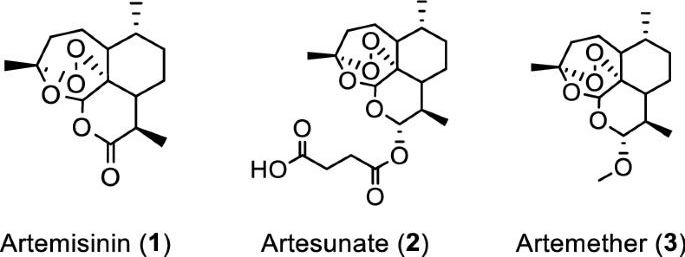
Artemisia annua plants grown from a cultivated seed line in Kentucky, USA, were extracted using either absolute ethanol or distilled water at 50 °C for 200 min and analyzed, as described in “Materials and methods” and Supplementary Information (Figures S1 and S2). Solids were removed by filtration and the solvents were evaporated. The extracted materials were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (ethanol extract) or a DMSO: water mixture (3:1 for aqueous extract) and filtered (see supporting information for details). Artemisinin (Fig. 1, (1)) was synthesized and purified following a published procedure or purchased17, while artesunate (Fig. 1, (2)) and artemether (Fig. 1, (3)) were only obtained from commercial sources.
Initial experiments were carried out at FU Berlin, Germany. To initially screen whether extracts and pure artemisinin were active against SARS-CoV-2, their antiviral activity was tested by pretreating VeroE6 cells at different time points during 120 min with selected concentrations of the extracts or compounds prior to infection with the first European SARS-CoV-2 isolated in München (SARS-CoV-2/human/Germany/BavPat 1/2020). The virus-drug mixture was then removed and cells were overlaid with medium containing 1.3% carboxymethylcellulose to prevent virus release into the medium. DMSO was used as a negative control. Plaque numbers were determined either by indirect immunofluorescence using a mixture of antibodies to SARS-CoV N protein18 or by staining with crystal violet19. The addition of either ethanolic or aqueous A. annua extracts prior to virus addition resulted in reduced plaque formation in a concentration dependent manner, while artemisinin exhibited little antiviral activity (Supplemental Tables S1 – S8).
Concentration–response experiments were carried out at Copenhagen University Hospital-Hvidovre. In these experiments the Danish SARS-CoV-2 isolate SARS-CoV-2/human/Denmark/DK-AHH1/2020 was used employing a 96-well plate based concentration–response antiviral treatment assay, allowing for multiple replicates per concentration, as described in “Materials and methods” and Supplementary Information (Figures S3 and S4)20,21. Seven replicates were measured at each concentration and a range of concentrations was evaluated to increase data accuracy when compared to the plaque-reduction assay, which was carried out in duplicates. Extracts or compounds were added to VeroE6 cells either 1.5 h prior to (pretreatment (pt)) or 1 h post infection (treatment (t)), respectively, followed by a 2-day incubation of virus with extracts or compounds. Both protocols yielded similar results, with slightly lower median effective concentration (EC50) values observed for treatment assays.

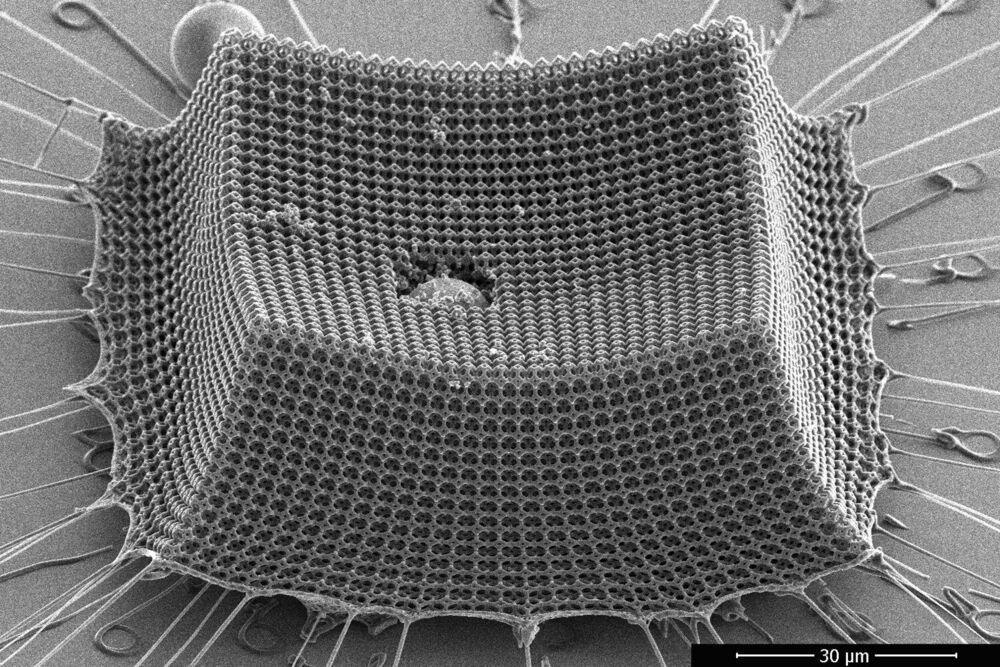
Ultralight material withstands supersonic microparticle impacts
A new study by engineers at MIT, Caltech, and ETH Zürich shows that “nanoarchitected” materials—materials designed from precisely patterned nanoscale structures—may be a promising route to lightweight armor, protective coatings, blast shields, and other impact-resistant materials.
The researchers have fabricated an ultralight material made from nanometer-scale carbon struts that give the material toughness and mechanical robustness. The team tested the material’s resilience by shooting it with microparticles at supersonic speeds, and found that the material, which is thinner than the width of a human hair, prevented the miniature projectiles from tearing through it.
The researchers calculate that compared with steel, Kevlar, aluminum, and other impact-resistant materials of comparable weight, the new material is more efficient at absorbing impacts.

NASA is Testing out new Composite Materials for Building Lightweight Solar Sail Supports
Space exploration is driven by technology – sometimes literally in the case of propulsion technologies. Solar sails are one of those propulsion technologies that has been getting a lot of attention lately. They have some obvious advantages, such as not requiring fuel, and their ability to last almost indefinitely. But they have some disadvantages too, not the least of which is how difficult they are to deploy in space. Now, a team from NASA’s Langley Research Center has developed a novel time of composite boom that they believe can help solve that weakness of solar sails, and they have a technology demonstration mission coming up next year to prove it.
The mission, known as the “Advanced Composite Solar Sail System” (ACS3) mission is designed around a 12U CubeSat, which measures in at a tiny 23cm x 23 cm x 34 cm (9 in x 9 in x 13 in). The solar sail it hopes to deploy will come in at almost 200 square meters (527 sq ft), and both it and its composite booms will fit inside the CubeSat enclosure, which is not much larger than a toaster oven.
The booms themselves are made out of a novel composite that is 75% lighter than previous deployable booms, while also suffering from only 1% of the thermal distortion that previous metallic booms were subjected to. They also conveniently roll into a 18 cm diameter spool that can be easily stored and easily deployed once the CubeSat is in space.
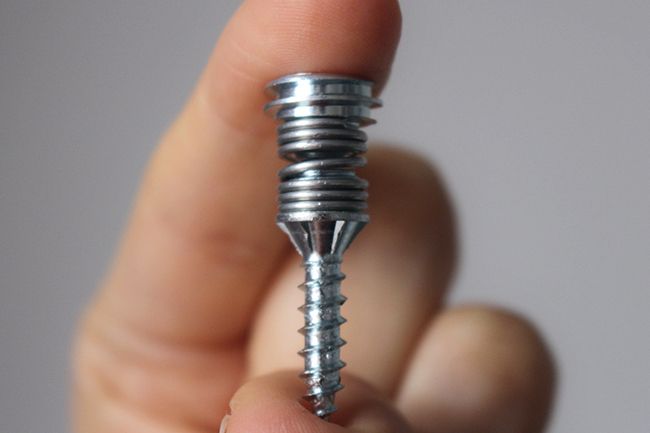

Spring-loaded screw could be a cheaper form of soundproofing
These spring-loaded screws turn your entire drywall into a sound deadening structure that can reduce perceived noise levels by nearly half. They’re pricey for screws, says the Swedish scientist behind them, but very cheap for sound insulation. Known as the Revolutionary Sound Absorbing Screw (or the Sound Screw for short), the device was created by a team at Malmö University, led by senior lecturer Håkan Wernersson. It consists of a threaded section at the bottom, a coil spring in the middle, and a section with a flat head at the top.
Nobody likes hearing their neighbors’ music, TV shows or loud conversations. Soundproof wall materials, however, can be quite thick and expensive. Swedish scientists have developed a thinner, less costly alternative, in the form of a spring-loaded sound-damping screw.
Known as the Revolutionary Sound Absorbing Screw (or the Sound Screw for short), the device was created by a team at Malmö University, led by senior lecturer Håkan Wernersson. It consists of a threaded section at the bottom, a coil spring in the middle, and a section with a flat head at the top.
The screw is inserted into a hole drilled through a drywall panel and into the underlying wooden joist. It is then turned until its threaded section is all the way into the wood, and its head is sitting flush against the outside surface of the drywall. The spring forms of a gap of a few millimeters between the joist and the drywall’s underside.
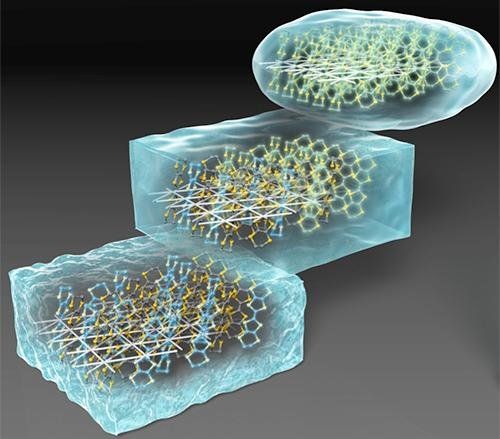
Understanding how electrons turn to glass
Circa 2017
Researchers at Tohoku University have gained new insight into the electronic processes that guide the transformation of liquids into a solid crystalline or glassy state.
The ability of some liquids to transition into glass has been exploited since ancient times. But many fundamental aspects of this transition phase are far from understood. Better understanding could spur the development of new products such as DVDs or Blu-Ray discs that store data by altering their state of matter from one to another, and of new glass materials.
A multi-institutional Japanese team led by Kenichiro Hashimoto of Tohoku University’s Institute for Materials Research compared the molecular dynamics of glass formation in conventional liquids, such as glucose, to an organic metal material containing ‘frustrated’ electrons. These electrons, responsible for conducting electrical currents, are unable to reach their lowest energy state due to their geometric arrangement on the material’s crystal lattice.
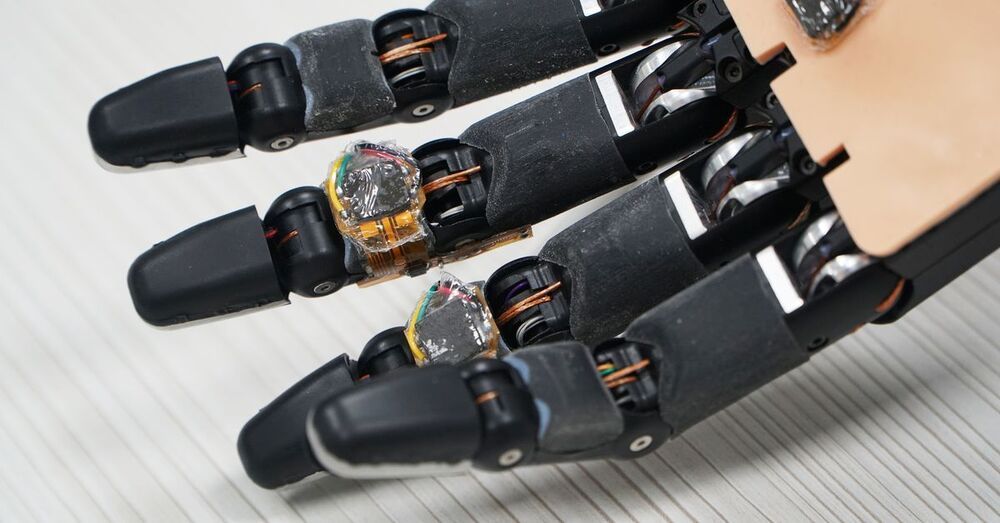

Smart foam material gives robotic hand the ability to self-repair
Tee said AiFoam is the first of its kind to combine both self-healing properties and proximity and pressure sensing. After spending over two years developing it, he and his team hope the material can be put to practical use within five years.
SINGAPORE, July 6 (Reuters) — Singapore researchers have developed a smart foam material that allows robots to sense nearby objects, and repairs itself when damaged, just like human skin.
Artificially innervated foam, or AiFoam, is a highly elastic polymer created by mixing fluoropolymer with a compound that lowers surface tension.
This allows the spongy material to fuse easily into one piece when cut, according to the researchers at the National University of Singapore.
