A breakthrough regarding dendrites made by MIT researchers may finally open the way to the building of a new type of rechargeable lithium battery that is safer, lighter, and more compact than existing models, a concept that has been pursued by labs all over the world for years.
The replacement of the liquid electrolyte between the positive and negative electrodes with a considerably thinner, lighter layer of solid ceramic material and the replacement of one electrode with solid lithium metal are the two essential components of this prospective advancement in battery technology. By making these changes, the battery’s overall size and weight would be significantly reduced, and the flammable liquid electrolytes that provide a safety risk would be eliminated. Dendrites, however, have proven to be a significant obstacle in that pursuit.
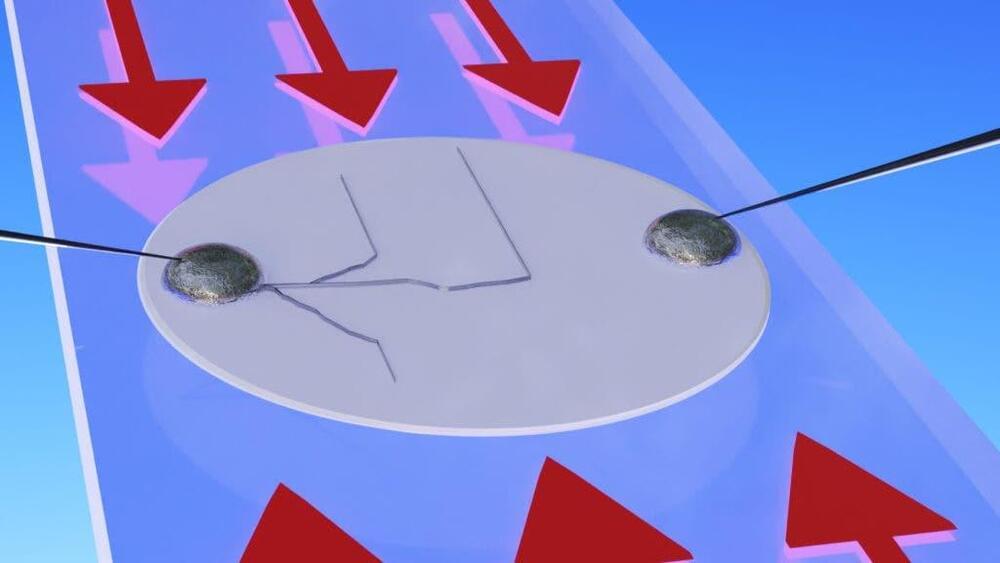
Dendrites are metal growths that can accumulate on the lithium surface, pierce through the solid electrolyte, and finally cross from one electrode to the other, shorting out the battery cell. Their name is from the Latin word for branches. There hasn’t been much advancement in the understanding of what causes these metal filaments or how to stop them from occurring, making lightweight solid-state batteries a problematic alternative.