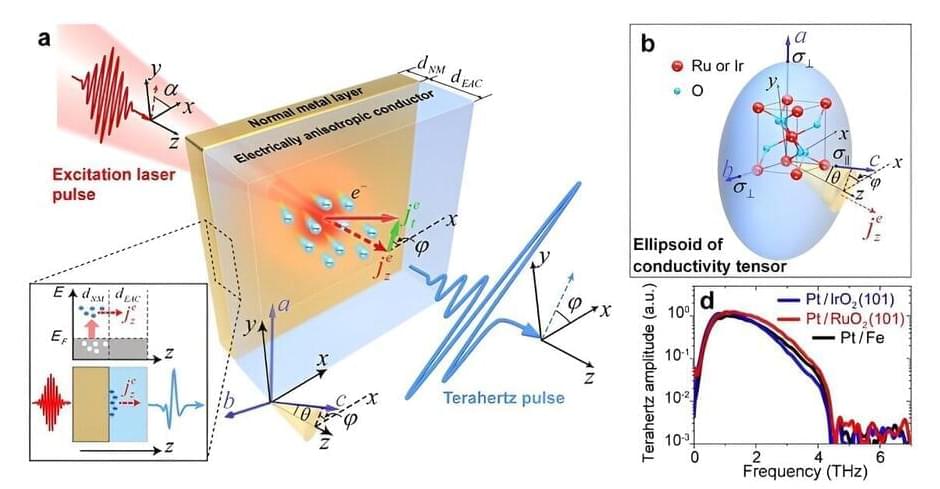
Scientists and engineers keep developing ever faster and more powerful technological devices. But there is a need for even faster and more efficient electronics. A promising route is to take advantage of terahertz waves, a less-explored part of the electromagnetic spectrum nestled between the infrared and microwave regions. Terahertz waves are uniquely sensitive to charge carriers in conducting systems, proving a powerful probe to understand the magnetic properties of new materials.
The quest for ultrafast electronics and coherent terahertz sources can be significantly aided by the precise and ultrafast control of light-induced charge currents at nanoscale interfaces.
Existing methods, including inverse spin-Hall effect (ISHE), inverse Rashba–Edelstein effect, and inverse spin-orbit-torque effect, convert longitudinally injected spin-polarized currents from magnetic materials to transverse charge currents, thus generating terahertz waves. However, these relativistic mechanisms rely on external magnetic fields and suffer from low spin-polarization rates and relativistic spin-to-charge conversion efficiencies characterized by spin-Hall angle.