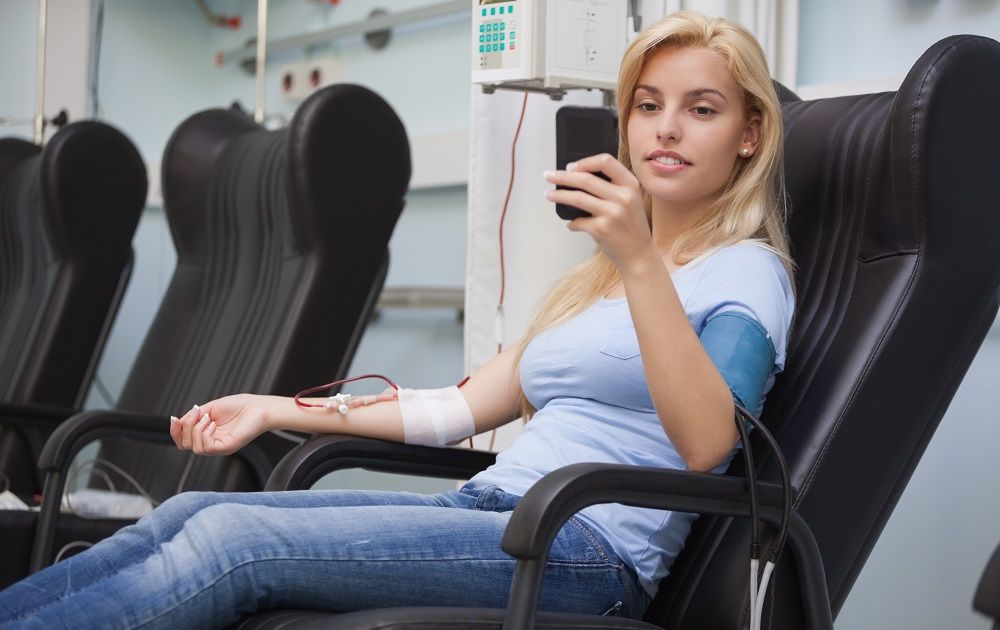
Summary: A recently announced parabiosis trial in humans – the practice of transfusing young blood to old – may have profound implications for treating the chronic diseases of old age, including metabolic changes, frailty, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other forms of dementia. However, some geroscientists say that variations of the procedure could cause severe side effects. [This article first appeared on the website LongevityFacts.com. Author: Brady Hartman. ]
The idea that youthful blood might rejuvenate our aging bodies has lingered in the popular imagination for centuries, fueled by recent experiments in which these transfusions revitalized aging mice.
Last week, Bill Faloon of the Life Extension Foundation (LEF) in partnership with the Young Blood Institute (YBI), announced a bold new human trial of the rejuvenating effects of the young blood / old blood swap, saying.