To grow the Cryonics movement — switch over to a more accurate one.


There are more than 100,000 people on organ transplant lists in the U.S., some of whom will wait years to receive one—and some may not survive the wait. Even with a good match, there is a chance that a person’s body will reject the organ. To shorten waiting periods and reduce the possibility of rejection, researchers in regenerative medicine are developing methods to use a patient’s own cells to fabricate personalized hearts, kidneys, livers, and other organs on demand.
Ensuring that oxygen and nutrients can reach every part of a newly grown organ is an ongoing challenge. Researchers at Stanford have created new tools to design and 3D print the incredibly complex vascular trees needed to carry blood throughout an organ. Their platform, published June 12 in Science, generates designs that resemble what we actually see in the human body significantly faster than previous attempts and is able to translate those designs into instructions for a 3D printer.
“The ability to scale up bioprinted tissues is currently limited by the ability to generate vasculature for them—you can’t scale up these tissues without providing a blood supply,” said Alison Marsden, the Douglas M. and Nola Leishman Professor of Cardiovascular Diseases, professor of pediatrics and of bioengineering at Stanford in the Schools of Engineering and Medicine and co-senior author on the paper. “We were able to make the algorithm for generating the vasculature run about 200 times faster than prior methods, and we can generate it for complex shapes, like organs.”

Dr. Eric Topol, a 70-year-old cardiologist, challenges conventional aging perceptions by embracing strength training. Abandoning cardio, he discovered that building muscle mass significantly improves health span. His regimen of simple exercises at home led to increased strength, balance, mental focus, and confidence, proving that aging can be a period of renewal, not decline.
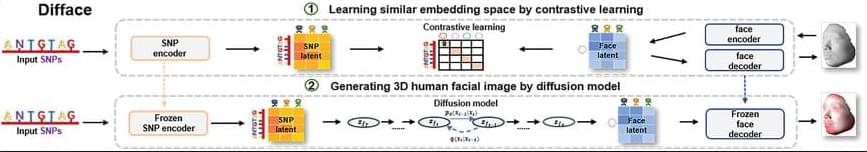
Facial morphology is a distinctive biometric marker, offering invaluable insights into personal identity, especially in forensic science. In the context of high-throughput sequencing, the reconstruction of 3D human facial images from DNA is becoming a revolutionary approach for identifying individuals based on unknown biological specimens. Inspired by artificial intelligence techniques in text-to-image synthesis, it proposes Difface, a multi-modality model designed to reconstruct 3D facial images only from DNA. Specifically, Difface first utilizes a transformer and a spiral convolution network to map high-dimensional Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and 3D facial images to the same low-dimensional features, respectively, while establishing the association between both modalities in the latent features in a contrastive manner; and then incorporates a diffusion model to reconstruct facial structures from the characteristics of SNPs. Applying Difface to the Han Chinese database with 9,674 paired SNP phenotypes and 3D facial images demonstrates excellent performance in DNA-to-3D image alignment and reconstruction and characterizes the individual genomics. Also, including phenotype information in Difface further improves the quality of 3D reconstruction, i.e. Difface can generate 3D facial images of individuals solely from their DNA data, projecting their appearance at various future ages. This work represents pioneer research in de novo generating human facial images from individual genomics information.
(Repost)
This study has introduced Difface, a de novo multi-modality model to reconstruct 3D facial images from DNA with remarkable precision, by a generative diffusion process and a contrastive learning scheme. Through comprehensive analysis and SNP-FACE matching tasks, Difface demonstrated superior performance in generating accurate facial reconstructions from genetic data. In particularly, Difface could generate/predict 3D facial images of individuals solely from their DNA data at various future ages. Notably, the model’s integration of transformer networks with spiral convolution and diffusion networks has set a new benchmark in the fidelity of generated images to their real images, as evidenced by its outstanding accuracy in critical facial landmarks and diverse facial feature reproduction.
Difface’s novel approach, combining advanced neural network architectures, significantly outperforms existing models in genetic-to-phenotypic facial reconstruction. This superiority is attributed to its unique contrastive learning method of aligning high-dimensional SNP data with 3D facial point clouds in a unified low-dimensional feature space, a process further enhanced by adopting diffusion networks for phenotypic characteristic generation. Such advancements contribute to the model’s exceptional precision and ability to capture the subtle genetic variations influencing facial morphology, a feat less pronounced in previous methodologies.
Despite Difface’s demonstrated strengths, there remain directions for improvement. Addressing these limitations will require a focused effort to increase the model’s robustness and adaptability to diverse datasets. Future research should aim to incorporating variables like age and BMI would allow Difface to simulate age-related changes, enabling the generation of facial images at different life stages an application that holds significant potential in both forensic science and medical diagnostics. Similarly, BMI could help the model account for variations in body composition, improving its ability to generate accurate facial reconstructions across a range of body types.

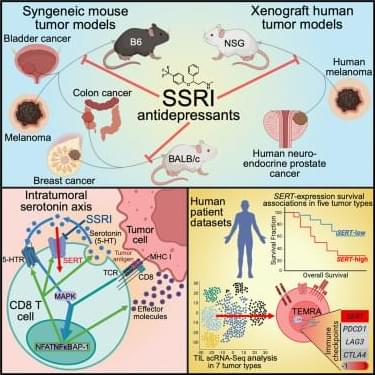
Serotonin signaling and gut-immune crosstalk: the microbiome’s role in antitumor immunity.
“…Serotonin transporter inhibits cytotoxic CD8-positive T lymphocyte antitumor immunity by depleting serotonin within the tumor microenvironment…”
“…Serotonin transporter-blocking selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants enhance cytotoxic CD8-positive T lymphocyte antitumor immunity and act synergistically with programmed cell death protein 1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy…”
To this end, here…
“…Tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic CD8-positive T lymphocytes were identified as the primary producers and mediators of a local, immunomodulatory serotonin signaling pathway independent of the gastrointestinal tract…”
“…Upon recognition of tumor antigens, tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic CD8-positive T lymphocytes upregulate tryptophan hydroxylase 1, which synthesizes serotonin followed by its release into the tumor microenvironment to enhance T lymphocyte activation via serotonin signaling…”
In short…

Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

Researchers publishing in Aging Cell have used single-cell transcriptomics to discover new insights into how neural stem cells (NSCs) change with aging.
Adults do generate neurons
The adult brain does generate new neurons [1], particularly in the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for memory formation [2]. Neurogenesis is limited to very specific niches, however, and does not occur across the entire brain [3]. This is accomplished by NSCs, cells that can differentiate into neural progenitors (NPs), which can themselves differentiate into both neurons and astrocytes and have less ability to proliferate [4]. Astrocytes are helper cells that support neurons’ connections and metabolism [5].