😀
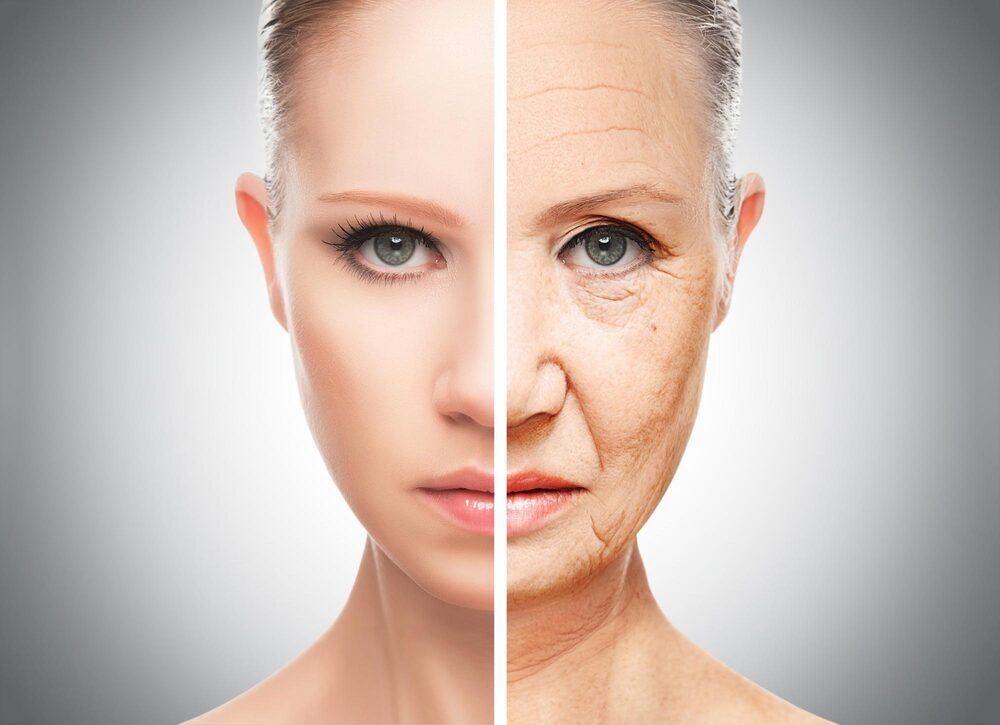
Cellular senescence, a state of permanent growth arrest, has emerged as a hallmark and fundamental driver of organismal aging. It is regulated by both genetic and epigenetic factors. Despite a few previously reported aging-associated genes, the identity and roles of additional genes involved in the regulation of human cellular aging remain to be elucidated. Yet, there is a lack of systematic investigation on the intervention of these genes to treat aging and aging-related diseases.
How many aging-promoting genes are there in the human genome? What are the molecular mechanisms by which these genes regulate aging? Can gene therapy alleviate individual aging? Recently, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have shed new light on the regulation of aging.
Recently, researchers from the Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Peking University, and Beijing Institute of Genomics of CAS have collaborated to identify new human senescence-promoting genes by using a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screening system and provide a new therapeutic approach for treating aging and aging-related pathologies.