Duangkamon Panyapatiphan/iStock.
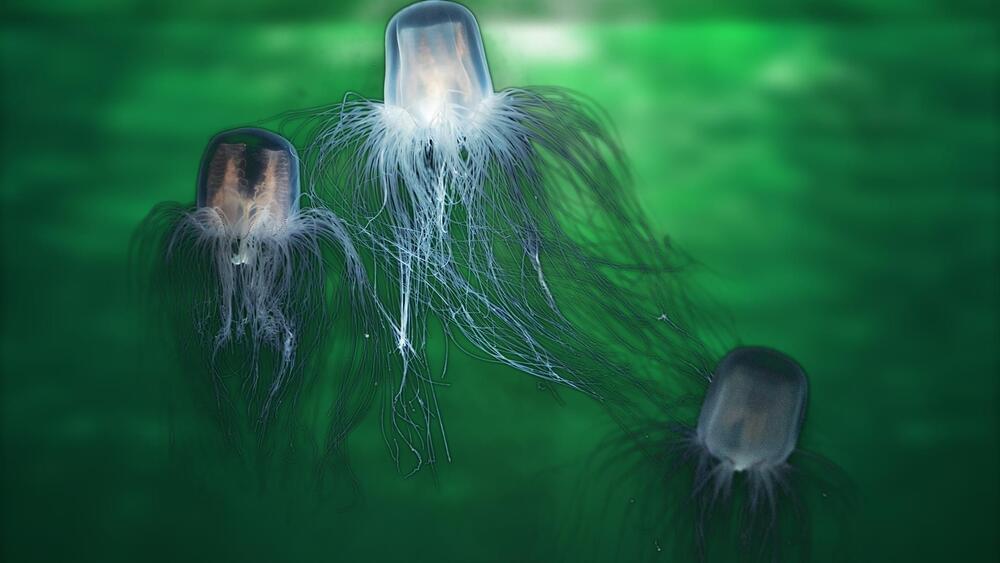
Button was suffering from a rare ailment that made him age backward. Meanwhile, in another similar scenario, a species of jellyfish — called turritopsis dohrnii — seems to have reached immortality.


Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
TruDiagnostic Discount Link (Epigenetic Testing)
CONQUERAGING!
https://bit.ly/3Rken0n.
Bristle Discount Link (Oral microbiome quantification):
ConquerAging15
https://www.bmq30trk.com/4FL3LK/GTSC3/
Cronometer Discount Link (Daily diet tracking):
https://shareasale.com/r.cfm?b=1390137&u=3266601&m=61121&urllink=&afftrack=
Support the channel with Buy Me A Coffee!
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/mlhnrca

Summary: Brief exposure to Rapamycin, a promising anti-aging drug that has positive effects on health and lifespan, has the same effect as long-term exposure to the drug in animal models. The findings pave the way for testing the effects of short-term rapamycin exposure on the lifespan of humans.
Source: Max Planck Institute.
Imagine you could take a medicine that prevents the decline that come with age and keeps you healthy. Scientists are trying to find a drug that has these effects.

Dr. Max More is a philosopher, writer, speaker and expert in Cryonics — the process of cryopreserving a body at the time of legal death in the hopes of reviving them in the future.
Theo talks with Dr. More about what actually happens when we die, the future of mankind, and if Theo would preserve his brain for science.
Dr. More is the Ambassador for Alcor Life Extension, a non-profit in Scottsdale, Arizona practicing cryonics. Max received a Doctorate in Philosophy in 1995 from the University of Southern California after completing a degree in Philosophy, Politics, and Economics from Oxford University.
Dr. Max More: https://www.maxmore.com/
Learn more about Alcor: https://www.alcor.org/
Tour Dates! https://theovon.com/tour.
New Merch: https://www.theovonstore.com.
Podcastville mugs and prints available now at https://theovon.pixels.com.
Support our Sponsors:
Hey it’s Han from WrySci-HX talking about how the anti diabetic drug Empagliflozin, brand name Jardiance, has reversed signs of vascular aging in mice! Is this why we’re seeing its benefits in humans? More below ↓↓↓
Subscribe!
Please consider supporting 🙏
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/wrysci_hx.
Or better yet, consider supporting any of the following!
They boost each other and block side effects? (In mice)
Rapamycin and metformin are viewed by many as the two most promising anti-aging drugs, but now scientists have found that these drugs can work hand in hand and show combined benefits, boosting each other’s effectiveness and blocking side effects — or at least that’s what we’ve seen in mice.
When tested by the Intervention Testing Program metformin failed to significantly increase lifespan in mice. However, in combination with rapamycin, it worked synergistically, leading to a drastic increase in median and maximal lifespan.
In this new study, the researchers put the “combination hypothesis” to the test again, using male mice of a common pre-diabetes model. The mice received either rapamycin, metformin, or a combination from 12 to 30 weeks of age.
Being pre-diabetic, these mice usually gain a lot of weight with age. Metformin treatment did not alleviate this trend, but both the rapamycin and combination treatments allowed the mice to maintain normal weight until the end of the experiment.
Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
TruDiagnostic Discount Link (Epigenetic Testing)
CONQUERAGING!
https://bit.ly/3Rken0n.
Bristle Discount Link (Oral microbiome quantification):
ConquerAging15
https://www.bmq30trk.com/4FL3LK/GTSC3/
Cronometer Discount Link (Daily diet tracking):
https://shareasale.com/r.cfm?b=1390137&u=3266601&m=61121&urllink=&afftrack=
Support the channel with Buy Me A Coffee!
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/mlhnrca.
Papers referenced in the video: