Ahead of the Longevity Leaders World Congress, Cambrian’s James Peyer talks stepping stones and silver bullets in geroscience research.



Seattle-based longevity biotech YouthBio Therapeutics has emerged from stealth mode, revealing it is working on the development of “gene therapies aimed at epigenetic rejuvenation, particularly with the help of partial reprogramming by Yamanaka factors.” The company boasts some top longevity science talent, with Dr João Pedro de Magalhães serving as its chief scientific officer and Dr Alejandro Ocampo as lead research collaborator.
Longevity. Technology: Cellular reprogramming is hot, hot hot! YouthBio joins a growing list of companies, including Altos Labs, Shift Bioscience and Turn Bio, among others, all aiming to change the course of human health through this exciting, yet early stage, science. Like everyone else, we’ll be watching all the players very closely – where will the first major breakthrough come from?
Cellular reprogramming is the process by which aged cells can be returned to a pluripotent (embryonic-like) state. This process, which can be achieved using Yamanaka factors, also improves the cells’ aging hallmarks. Partial reprogramming means that Yamanaka factors are induced only for short periods, which is not enough to fully change cells beyond a point of no return but is enough to induce rejuvenation.

The Interventions Testing Program is the gold standard for testing longevity drugs. What do the results say about which ones extend lifespan in mice? Rapamycin is a big winner!
New podcast w/ Richard Miller on the data on several longevity supplements including Acarbose, NR, Resveratrol, Fisetin, MCT Oil, Curcumin, Fish Oil + more!
Live Longer World is bringing information on longevity science from scientists to everyone. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.

Best known therapeutically as a treatment for bipolar disorder, lithium has long intrigued researchers with its potential age-defying properties.
The element has been shown in lab experiments to extend the lifespan of fruit flies and roundworms, while observational studies have suggested tap water naturally laced with trace amounts of lithium might improve human longevity.
Researchers at The University of Toledo have recently found that low-dose lithium acts as a powerful anti-aging agent in the kidneys.
Musing on living long enough to know.
Do aliens really exist? “It is virtually inconceivable to me that there isn’t intelligence somewhere in the universe,” says psychologist and astrobiologist Dr. Douglas Vakoch. “It’s just numbers.”
What happens if aliens send us a message? Learn more in this video from Life Noggin — https://youtu.be/P7afrpjnNCk.
Dr. Vakoch has spent his career carefully composing and transmitting messages to nearby stars in hopes of finally making contact with intelligent extraterrestrial life. As the president of METI International, an organization dedicated to messaging extraterrestrial intelligence, part of his job is to seek out the corners of the universe that could be home to planets that are within the “Goldilocks zone”: not too hot, not too cold, but just right to support life.
In 2017, astronomers announced that three planets in the planetary system of the star TRAPPIST-1 fit the bill. Now, Dr. Vakoch and his team of scientists are using the Goonhilly Satellite Earth Station to send a transmission to the area. The only problem? By the time a signal sent from TRAPPIST-1 could reach Earth, Dr. Vakoch will be long gone. In order to experience this for himself, he would have to live to 140 years old.

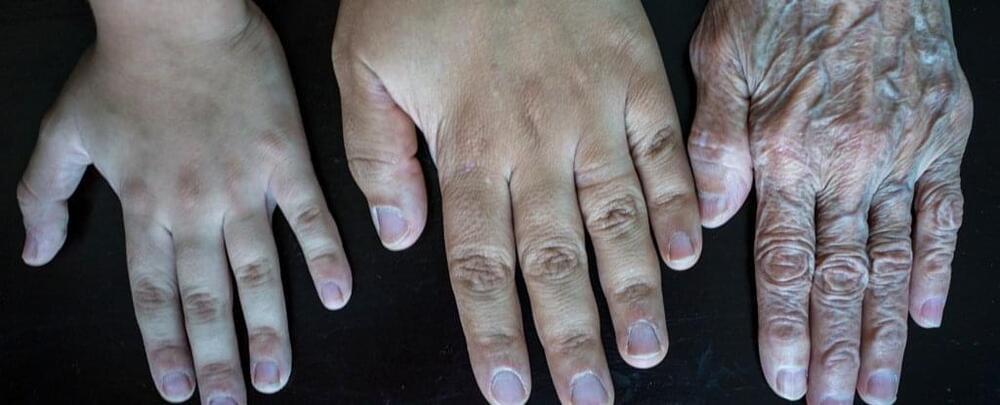
It’s not quite the mythical fountain of youth but it is, perhaps, a start: Scientists have managed to engineer human skin cells to reverse 30 years of aging, resetting them to a much more youthful state in terms of certain molecular measurements.
While it’s very early days for the research – so we shouldn’t get carried away too quickly – the technique could play a major part in efforts to produce rejuvenative medicine that’s able to undo some of the damaging consequences of our bodies getting older.
What makes the research particularly notable is that the skin cells were reprogrammed to be biologically younger while still keeping some of the functionality that made them skin cells in the first place.

A new supplement that stimulates a natural body process also promotes muscle recovery in humans. New research indicates that urolithin A can play an important role in improving muscles and prolonging activity – this is especially important as muscles decline with age, exposing us to the dangers of frailty.
Longevity. Technology sponsored content: As fast as we are unlocking the secrets of urolithin A we are also discovering obstacles. Urolithin A boosts mitochondrial and muscle function for sure, but it’s a metabolite, meaning it is made by the body from raw materials that we get from fruits, especially pomegranates; however, not everyone can make sufficient quantities of this antiaging molecule, and that’s where Mitopure steps in.
It seems to be universally accepted that the older we get, the more easily we get tired and the less energy we have – but perhaps it doesn’t have to be this way. The secret lies in our mitochondria, tiny organelles that pack a mighty punch when it comes to energy production. These minute powerhouses take oxygen and glucose and create a chemical called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and this is the energy our bodies use for movement, growth and repair.