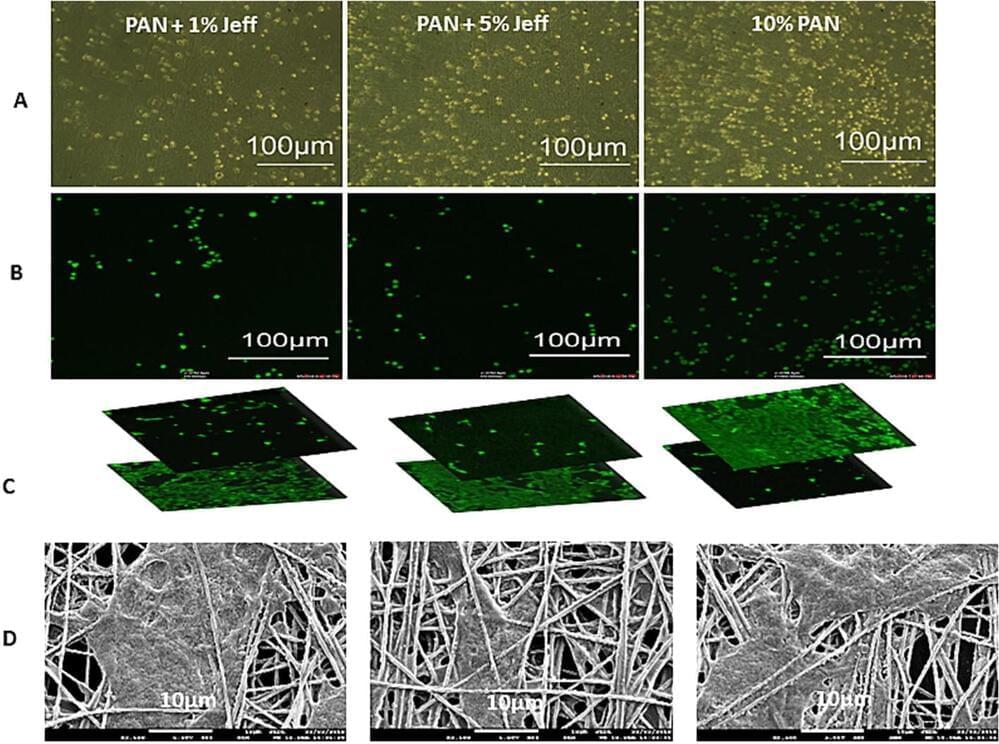
When the scaffold is treated with a steroid called fluocinolone acetonide, which protects against inflammation, the resilience of the cells appears to increase, promoting growth of eye cells. These findings are important in the future development of ocular tissue for transplantation into the patient’s eye.
Scientists have found a way to use nanotechnology to create a 3D ‘scaffold’ to grow cells from the retina-paving the way for potential new ways of treating a common cause of blindness.
Researchers, led by Professor Barbara Pierscionek from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), have been working on a way to successfully grow retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells that stay healthy and viable for up to 150 days. RPE cells sit just outside the neural part of the retina and, when damaged, can cause vision to deteriorate.
It is the first time this technology, called ‘electrospinning’, has been used to create a scaffold on which the RPE cells could grow, and could revolutionise treatment for one of age-related macular degeneration, one of the world’s most common vision complaints.