Although the German scientist Hanns Kaiser published a number of articles in the 1970s relating inflammation to diseases in the elderly (Kaiser, 1971), the last 20 years have seen a burst in the study of the aging immune system, inflammation and the associated diseases. One of the most iconic studies in aging and immunity was the OCTO and NONA longitudinal study of healthy 80–90 year old people that took place in Jonkoping Sweden in the 1990s (Wikby AJ and Ferguson, 2003). These studies were unique for several reasons. First, they were longitudinal studies of elderly individuals. Second, the 80-and 90-year-olds were very healthy. As people age, they naturally acquire more disease and it becomes increasingly difficult to distinguish the effects of disease vs. aging on the immune parameters being measured. To overcome these confounders, the OCTO and NONA immune longitudinal study was a community population-based study that continually and carefully evaluated individual health parameters. Study participants had normal cognition, were not on drugs that would influence their immune responses, and were non-institutionalized (Wikby AJ and Ferguson, 2003). Several important findings resulted from these studies; 1) the establishment of an Immune Risk Profile (IRP) based on altered CD4/CD8 T cell ratios (decreasing CD4+ T cell numbers and often increasing CD8+ T cell numbers) (Wikby et al., 1998) and 2) germane to this review, the discovery of a link between elevated plasma IL-6 levels, mortality and IRP in the very old (Wikby et al., 2006).
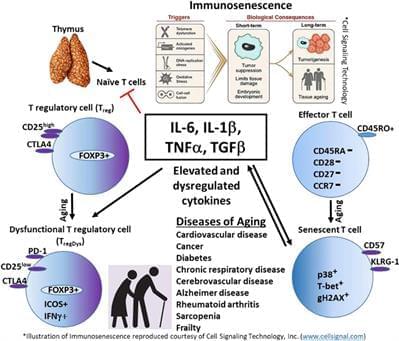
An optimal immune response requires the appropriate interaction between the innate and the adaptive arms of the immune system as well as a proper balance of activation and regulation. After decades of life, the aging immune system is continuously exposed to immune stressors and inflammatory assaults that lead to immune senescence (Salama et al., 2014; Aiello et al., 2019; Di Micco et al., 2021). In this review, we will discuss inflammaging in the elderly, specifically concentrating on IL-6 and IL-1β in the context of T lymphocytes, and how inflammation is related to mortality and morbidities, specifically cardiovascular disease and cancer. Although a number of studies suggests that the anti-inflammatory cytokine TGF-β is elevated in the elderly, heightened inflammation persists. Thus, the regulation of the immune response and the ability to return the immune system to homeostasis is also important. Therefore, we will discuss cellular alterations in aging, concentrating on senescent T cells and CD4+ CD25 + FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) in aging.
Inflammaging is a phenomenon of inflammatory pathogenesis characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation, and is a significant risk factor for morbidity and mortality in elderly people. Claudio Franceschi first coined the term “inflammaging” in the manuscript “Inflamm-aging.