A new study finds rapalink-1 extends yeast lifespan and uncovers a metabolic loop linking diet, gut microbes and aging.




Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qp0rCU49lMs.
Thank you for listening ❤ Check out our sponsors: https://lexfridman.com/sponsors/cv9485-sb.
See below for guest bio, links, and to give feedback, submit questions, contact Lex, etc.
*GUEST BIO:*
Michael Levin is a biologist at Tufts University working on novel ways to understand and control complex pattern formation in biological systems.
*CONTACT LEX:*
*Feedback* — give feedback to Lex: https://lexfridman.com/survey.
*AMA* — submit questions, videos or call-in: https://lexfridman.com/ama.
*Hiring* — join our team: https://lexfridman.com/hiring.
*Other* — other ways to get in touch: https://lexfridman.com/contact.
*EPISODE LINKS:*
Michael Levin’s X: https://twitter.com/drmichaellevin.
Michael Levin’s Website: https://drmichaellevin.org.
Michael Levin’s Papers: https://drmichaellevin.org/publications/
- Biological Robots: https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.00880
- Classical Sorting Algorithms: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.05375
- Aging as a Morphostasis Defect: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38636560/
- TAME: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.10346
- Synthetic Living Machines: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.abf1571
*SPONSORS:*
To support this podcast, check out our sponsors & get discounts:
*Shopify:* Sell stuff online.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/shopify-cv9485-sb.
*CodeRabbit:* AI-powered code reviews.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/coderabbit-cv9485-sb.
*LMNT:* Zero-sugar electrolyte drink mix.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/lmnt-cv9485-sb.
*UPLIFT Desk:* Standing desks and office ergonomics.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/uplift_desk-cv9485-sb.
*Miro:* Online collaborative whiteboard platform.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/miro-cv9485-sb.
*MasterClass:* Online classes from world-class experts.
Go to https://lexfridman.com/s/masterclass-cv9485-sb.
*PODCAST LINKS:*


The study unexpectedly identified a significant role for a group of enzymes known as agmatinases, which convert the metabolite agmatine into polyamines. These enzymes appear to participate in a previously unrecognized “metabolic feedback loop” that helps maintain balanced TOR activity. When agmatinase activity was disrupted, yeast cells grew more quickly but showed signs of premature aging, revealing a trade-off between rapid growth and long-term cell survival.
The team also found that adding agmatine or putrescine (a related compound) supported longevity in yeast and improved growth under specific conditions.
“By showing that agmatinases are essential for healthy aging, we’ve uncovered a new layer of metabolic control over TOR — one that may be conserved in humans,” said Dr. Rallis. “Because agmatine is produced by diet and gut microbes, this work may help explain how nutrition and the microbiome influence aging.”
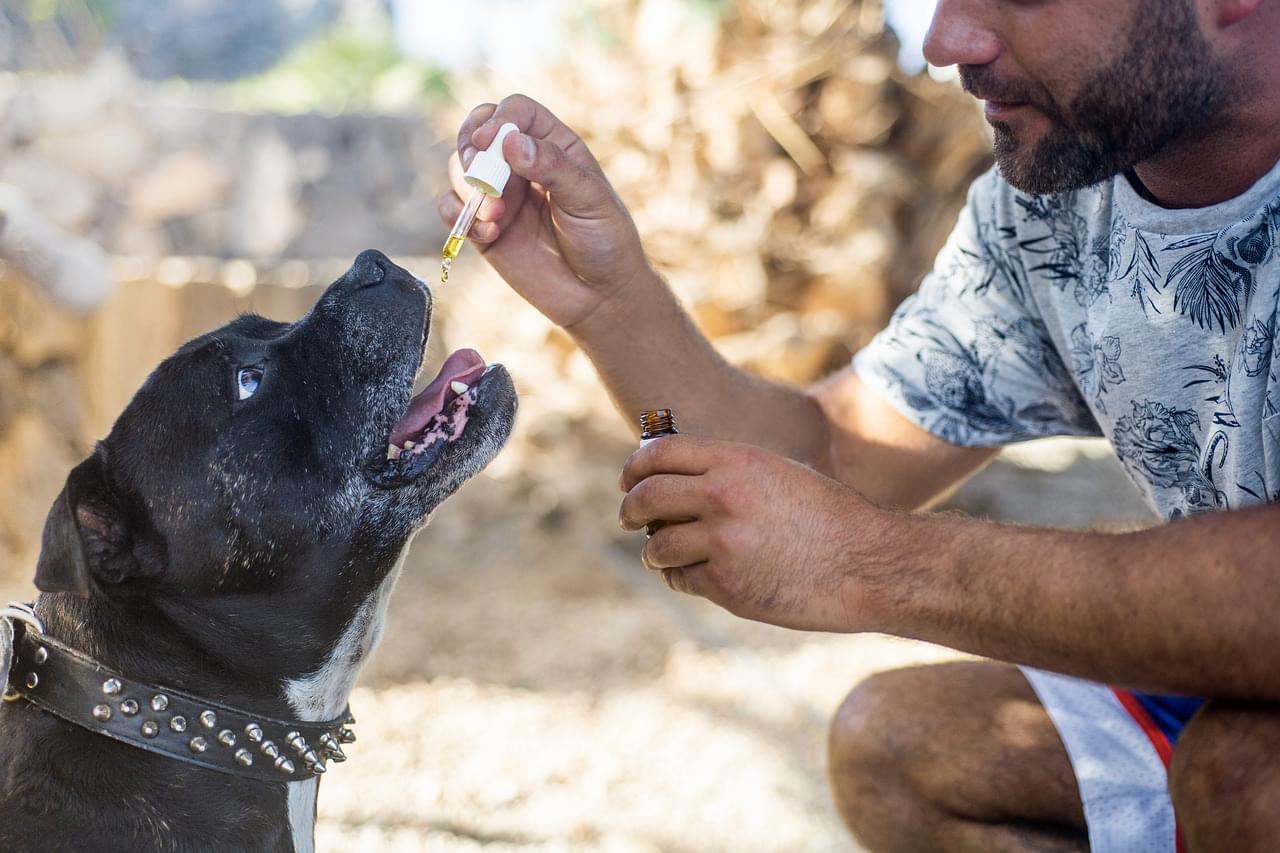

“The long-term use of CBD is associated with less intense aggressive behaviors in dogs.”
Can cannabidiol (CBD) help dogs in the same way it helps humans? This is what a recent study published in Frontiers in Veterinary Science hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated the benefits of incorporating CBD products into dog products. This study has the potential to help scientists, legislators, and the public better understand the health benefits of CBD for both humans and animals.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data obtained from the Dog Aging Project (DAP), which is an organization designed to gain insight into dog aging, lifestyle, diet, and environmental factors. Surveys were conducted from 47,444 dog owners between December 2019 and December 2023, with the first surveys being s baseline regarding a dog’s overall health status, while the second survey was used to ascertain the amount of CBD or hemp the owners fed their dogs while also assessing changes in behavior and/or health.
In the end, the researchers found that healthy dogs were less likely to use CBD, whereas dogs with limiting health conditions like dementia, epilepsy, or cancer were more likely to use CBD. Additionally, CBD-use dogs were found to exhibit less aggressive behavior compared to non-use dogs. Finally, the team found that states where CBD was legal had higher rates of dogs using CBD.