Understanding the biological processes of getting older could help us lead longer lives, and stay healthier later in life – and a new study links the speed at which our brain ages with the nutrients in our diets.
Researchers from the University of Illinois and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln mapped brain scans against nutritional intake for 100 volunteers aged between 65 and 75, looking for connections between certain diets and slower brain aging.
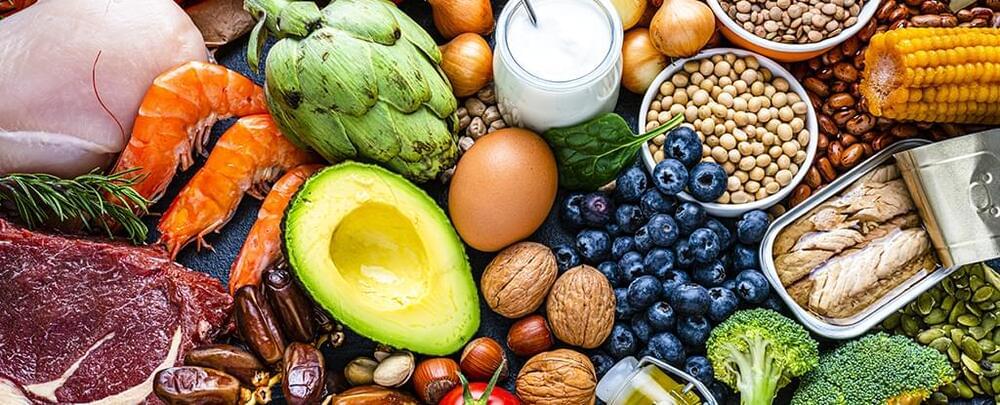
They identified two distinct types of brain aging – and the slower paced aging was associated with nutrient intake similar to what you would get from the Mediterranean diet, shown in previous studies to be one of the best for our bodies.