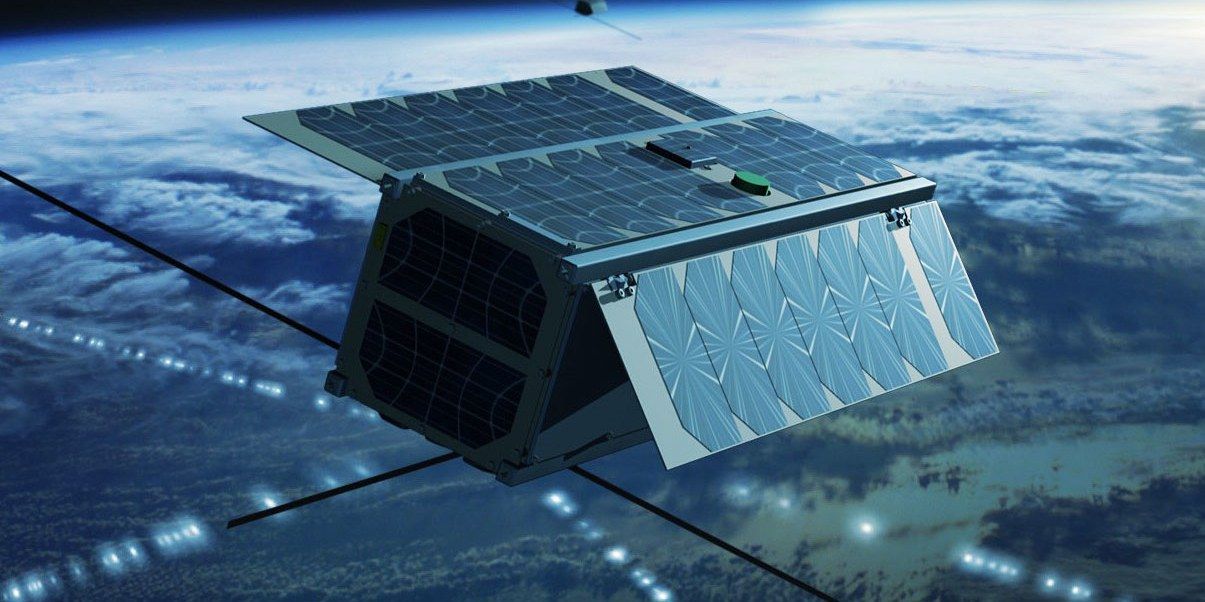
An unusual SpaceX launch will carry several startups’ satellites, some of which will jockey to provide dirt-cheap internet for earthbound IoT sensors.



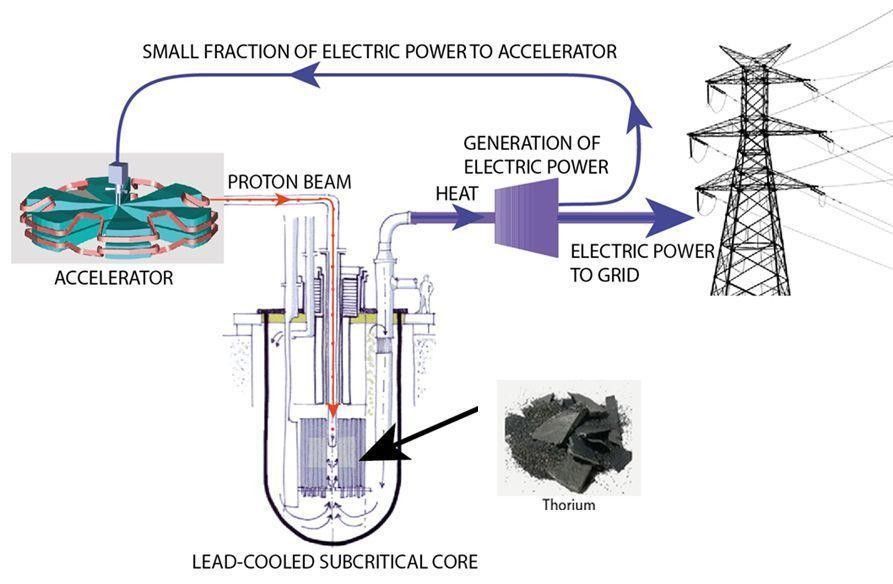
If not for long-term radioactive waste, then nuclear power would be the ultimate “green” energy. The alternative to uranium is thorium, a radioactive ore whose natural decay is responsible for half of our geothermal energy, which we think of as “green energy.” More than 20 years of research at the European Centre for Nuclear Research (CERN), the birthplace of the internet and where Higgs boson was discovered, demonstrate that thorium could become a radically disruptive source of clean energy providing bountiful electricity any place and at any time.
Coal and gas remain by far the largest sources of electricity worldwide, threatening our climate equilibrium. Non-fossil alternatives, such as solar power, use up a forbidding amount of land, even in sunny California, plus the decommissioning will pose a serious recycling challenge within 20 years. Solar is best used on an individual household basis, rather than centralized plants. Wind requires an even larger surface area than solar.
As Michael Shellenberger, a Time magazine “Hero of the Environment”, recently wrote: “Had California and Germany invested $680 billion into nuclear power plants instead of renewables like solar and wind farms, the two would already be generating 100% or more of their electricity from clean energy sources.” Correct, but the disturbing issue of long-term nuclear waste produced by conventional, uranium based, nuclear plants still remains.

It’s imperative that Humanity understands the reality of warfare in these times when advanced and secret technologies are used against us on a daily basis.
From WiFi and cell phone frequencies to televisions and microwave ovens on up to the most exotic sonic weapons—it’s all disruptive and even lethal to the Human body and mind.
Because these weapons are silent and invisible, the war-loving aspects of society have been able to experiment with these methods for decades but the time for secrecy and these covert attacks on the life on our planet has come to an end.
What harm does it do? We can see the carnage if we will just look. Whales and dolphins washing up by the hundreds on beaches, bleeding from their ears, flocks of birds falling from the sky with no outward trauma, multiple forms of cancer rampant… it’s endless.

Multinational engineering and electronics giant Bosch recently highlighted a new device connectivity method which will work with the Iota marketplace, among other things, for real-time IoT (Internet of Things) data collection and sales.
Data Collection for the IOTA Marketplace
In a recent blog post the firm opened with a quote from 1999 from Nobel Prize winner Milton Friedman extolling the virtues of anonymously transferring funds on the internet, way before cryptocurrencies were even conceived. It continued to elaborate on the Iota ecosystem, its advantages over Bitcoin, and why it has been chosen as a partner.
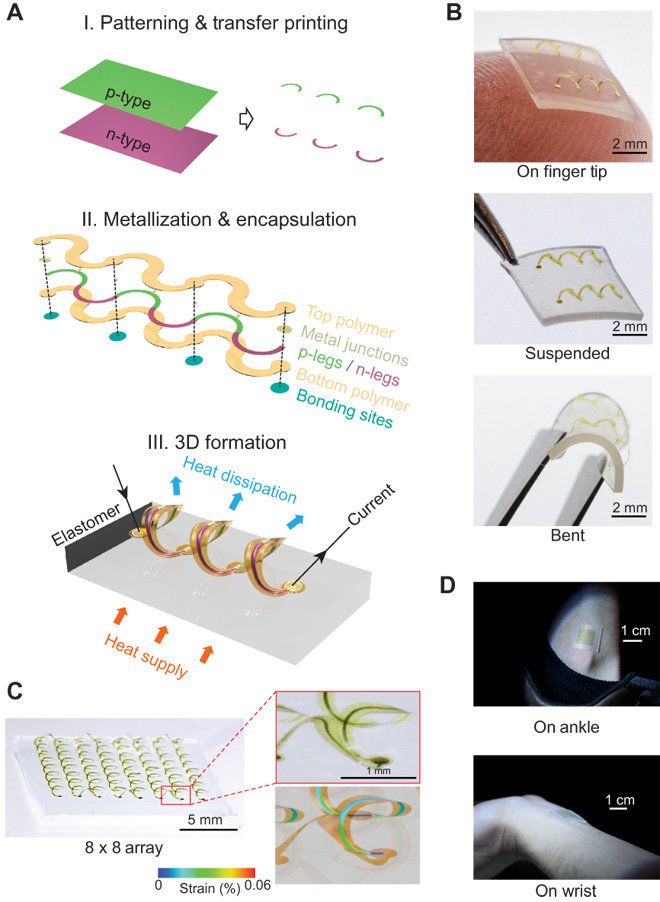
Miniaturized semiconductor devices with energy harvesting features have paved the way to wearable technologies and sensors. Although thermoelectric systems have attractive features in this context, the ability to maintain large temperature differences across device terminals remains increasingly difficult to achieve with accelerated trends in device miniaturization. As a result, a group of scientists in applied sciences and engineering has developed and demonstrated a proposal on an architectural solution to the problem in which engineered thin-film active materials are integrated into flexible three-dimensional (3D) forms.
The approach enabled efficient thermal impedance matching, and multiplied heat flow through the harvester to increase efficient power conversion. In the study conducted by Kewang Nan and colleagues, interconnected arrays of 3D thermoelectric coils were built with microscale ribbons of the active material monocrystalline silicon to demonstrate the proposed concepts. Quantitative measurements and simulations were conducted thereafter to establish the basic operating principles and key design features of the strategy. The results, now published on Science Advances, suggested a scalable strategy to deploy hard thermoelectric thin-films within energy harvesters that can efficiently integrate with soft material systems including human tissue to develop wearable sensors in the future.
Thermoelectric devices provide a platform to incorporate ubiquitous thermal gradients that generate electrical power. To operate wearable sensors or the “Internet of Things” devices, the temperature gradient between the surrounding environment and the human body/inanimate objects should provide small-scale power supplies. Continued advances in the field focus on aggressive downscaling of power requirements for miniaturized systems to enhance their potential in thermoelectric and energy harvesting applications. Integrated processors and radio transmitters for example can operate with power in the range of subnanowatts, some recent examples are driven via ambient light-based energy harvesting and endocochlear potential. Such platforms can be paired with sensors with similar power to enable distributed, continuous and remote environmental/biochemical monitoring.
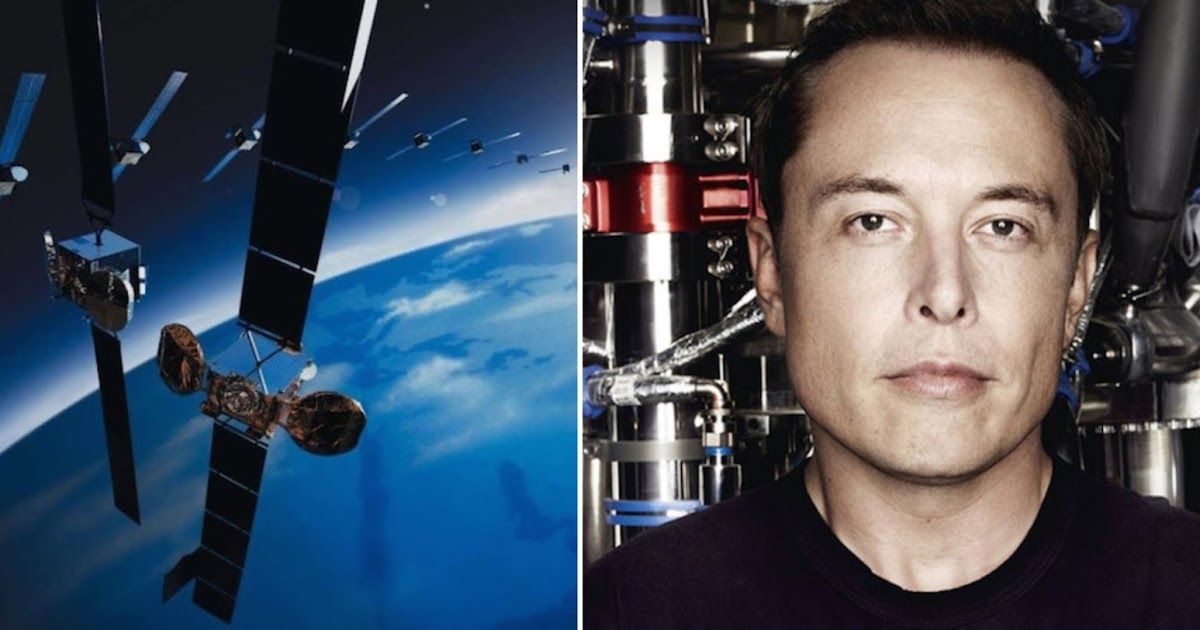

The very same guy, who invented PayPal, created the Tesla Cars, plans to create “SolarCities” and developed cars that will make money for you when you don’t use them, has ANOTHER brilliant idea. Elon Musk plans to launch 4,000 low-orbit satellites in order to give free internet access worldwide, two of them has already been launched a month ago.
The billionaire’s company, SpaceX, revealed the initial framework of the plan in January, with the official request being submitted to the Federal Communications Commission.

Scientists are planning to create a network in the Chicago area tapping the principles of quantum physics. The idea is to prove that quantum physics could provide the basis for an unhackable internet.
This, they say, could have wide-ranging impact on communications, computing and national security.
The quantum network development, supported by the US Department of Energy (DOE), will stretch between the DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory and Fermi National Acceleratory Laboratory, a connection that is said will be the longest in the world to send secure information using quantum physics.

China’s state-run press agency Xinhua has unveiled what it claims are the world’s first AI-generated news anchors.
Xinhua revealed the anchors at the World Internet Conference on Thursday. Modeled on two real presenters, the agency showcased two AI-generated anchors, one who speaks Chinese and another who speaks English.