SpaceX plans to launch another 60 of its Starlink internet satellites on Thursday (Sept. 3), and you can watch the action live.


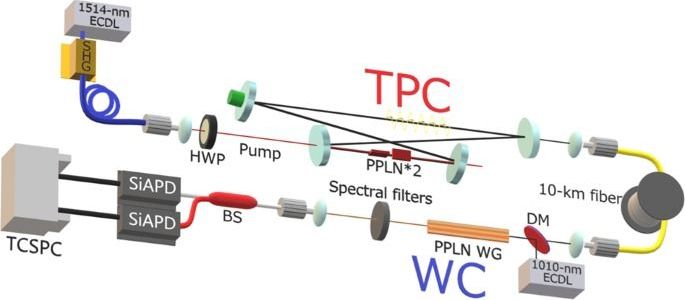
Quantum technologies have seen a remarkable development in recent years and are expected to contribute to quantum internet technologies. The authors present an experimental implementation over commercial telecom fibres of a two-photon comb source for quantum communications with long coherence times and narrow bandwidth, which is used in a 20 km distribution experiment to show the presence of remote two-photon correlations.
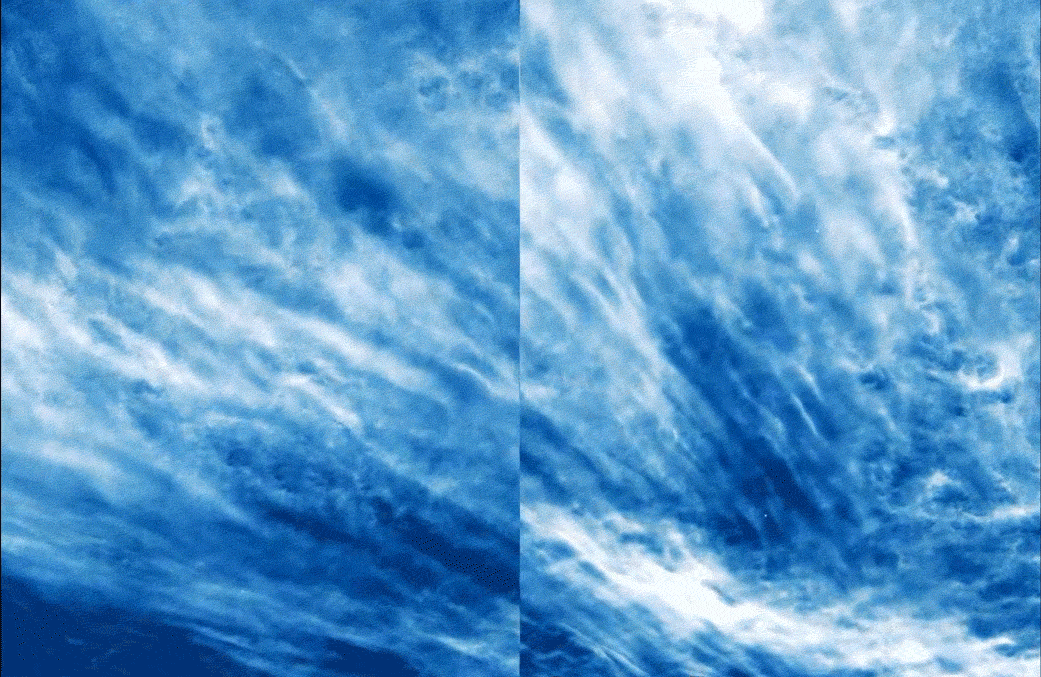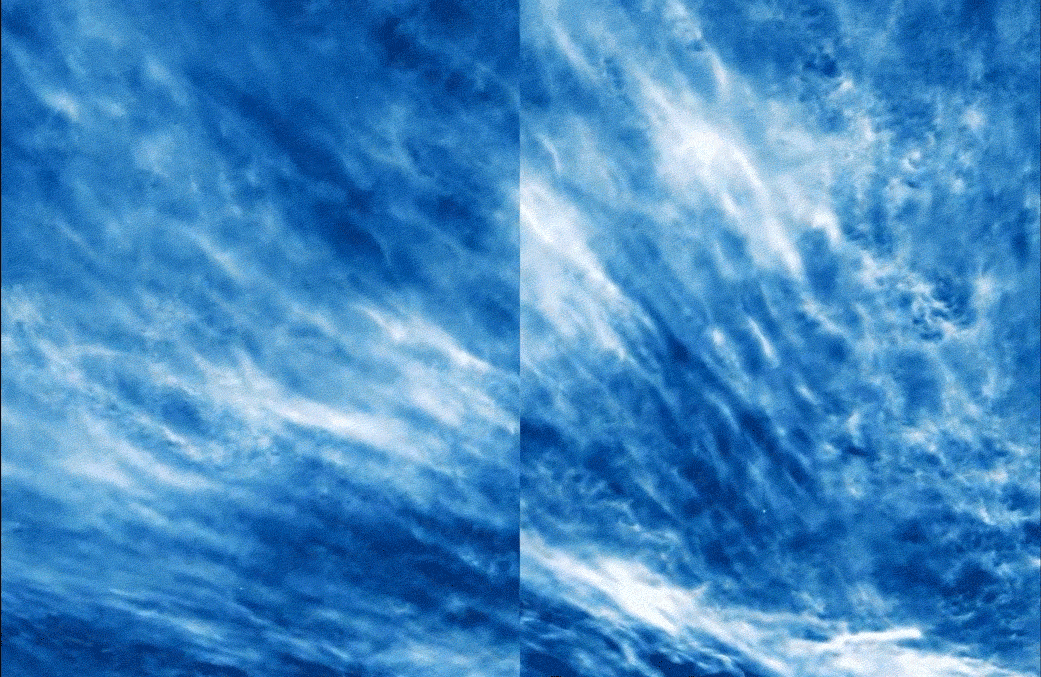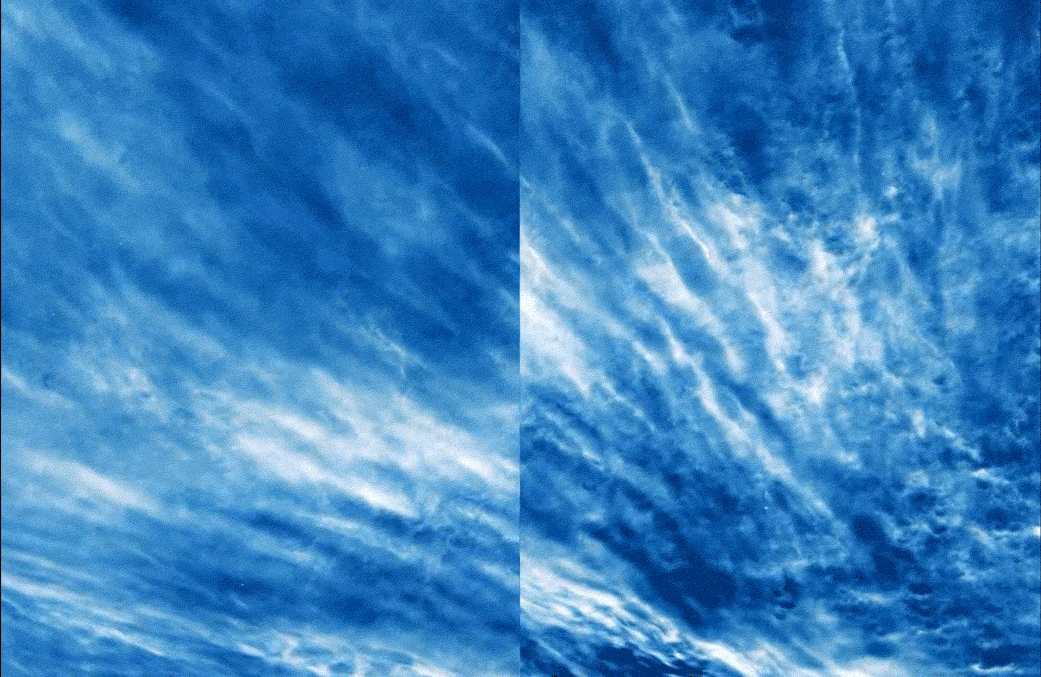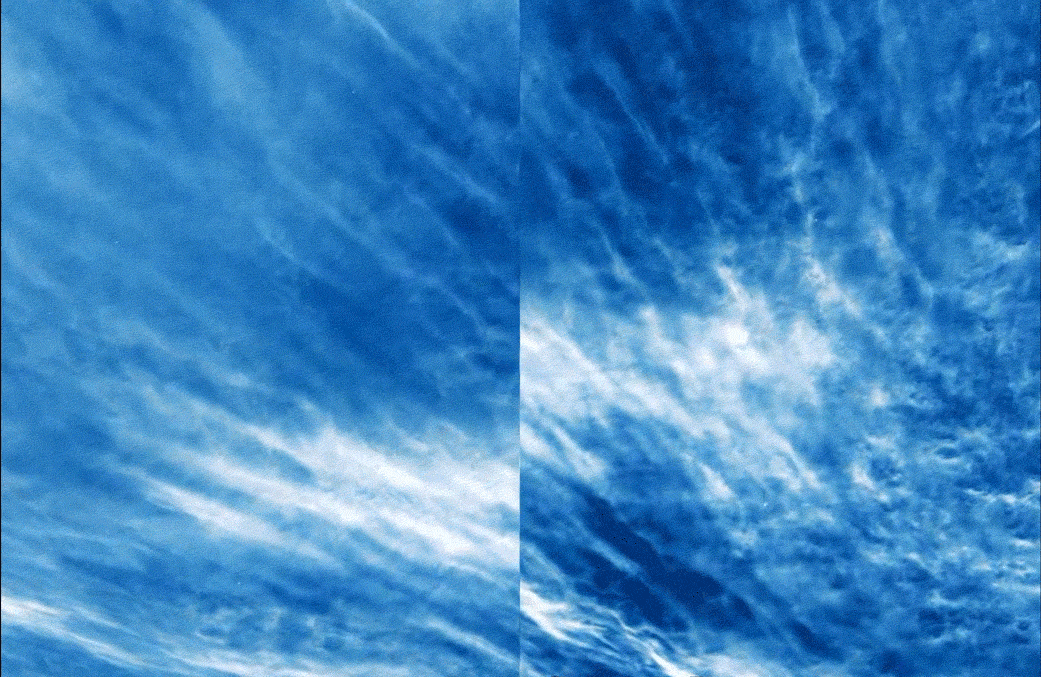
Giant balloons launched into the stratosphere to beam internet service to Earth have helped scientists measure tiny ripples in our upper atmosphere, uncovering patterns that could improve weather forecasts and climate models.
The ripples, known as gravity waves or buoyancy waves, emerge when blobs of air are forced upward and then pulled down by gravity. Imagine a parcel of air that rushes over mountains, plunges toward cool valleys, shuttles across land and sea and ricochets off growing storms, bobbing up and down between layers of stable atmosphere in a great tug of war between buoyancy and gravity. A single wave can travel for thousands of miles, carrying momentum and heat along the way.
Although lesser known than gravitational waves —undulations in the fabric of space-time— atmospheric gravity waves are ubiquitous and powerful, said Stanford University atmospheric scientist Aditi Sheshadri, senior author of a new study detailing changes in high-frequency gravity waves across seasons and latitudes. They cause some of the turbulence felt on airplanes flying in clear skies and have a strong influence on how storms play out at ground level.
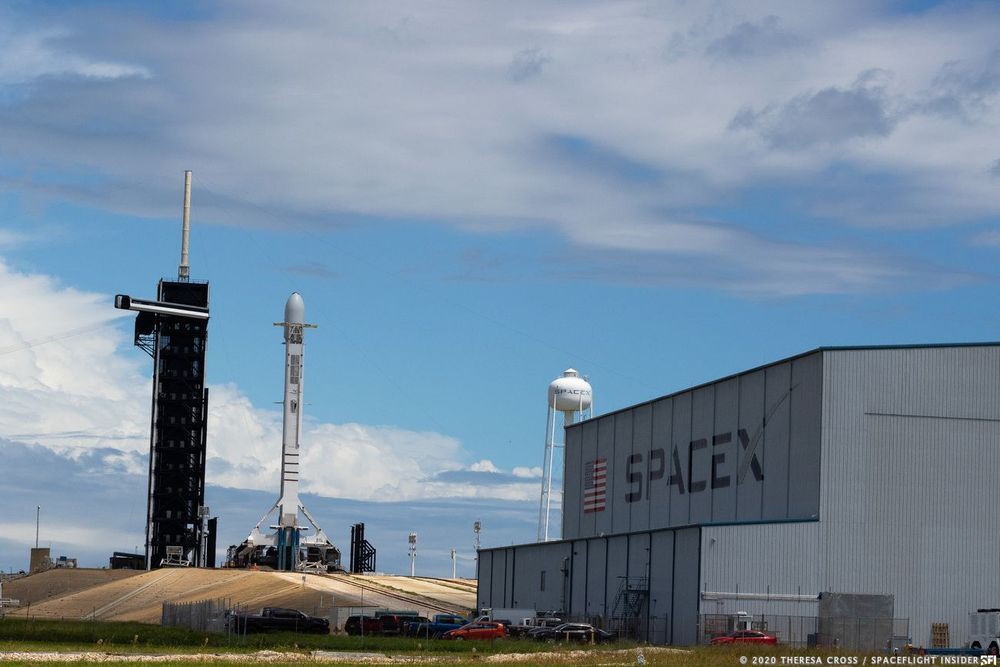

SpaceX has officially shifted Tuesday’s planned launch of 60 Starlink internet satellites from pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from SpaceX wrote on Twitter, “Now targeting Thursday, September 3 at 8:46 a.m. EDT for launch of Starlink from Launch Complex 39A, pending Range acceptance — team is using additional time for data review.” Prior to the flight schedule change being made and published on Monday, members of the media had been out at the remote camera setup event at LC 39A. It is unclear whether there will be any need for additional.
This is the second scrub for this mission in as many days; Sunday’s planned launch, the first in what was planned to be a back-to-back double launch day, pushed to Tuesday September 1 due to inclement weather during pre-flight operations.
Beyond this mission, Starlink 12 and Starlink 13 are currently scheduled for September 12 and 13 respectively, launch times TBD.

FP Trending Sep 02, 2020 12:48:13 IST
SpaceX postponed the launch date of its next batch of Starlink satellites to 3 September. The space firm was going to loft the 60 satellites aboard the Falcon 9 rocket yesterday morning.
The official handle of Elon Musk’s company tweeted about the delay, saying the team will be utilising the extra time to review data. Now the launch from Launch Complex 39A has been set at 6.16 pm IST (8.46 am EDT) on 3 September.

Adapting the Intelligence Community
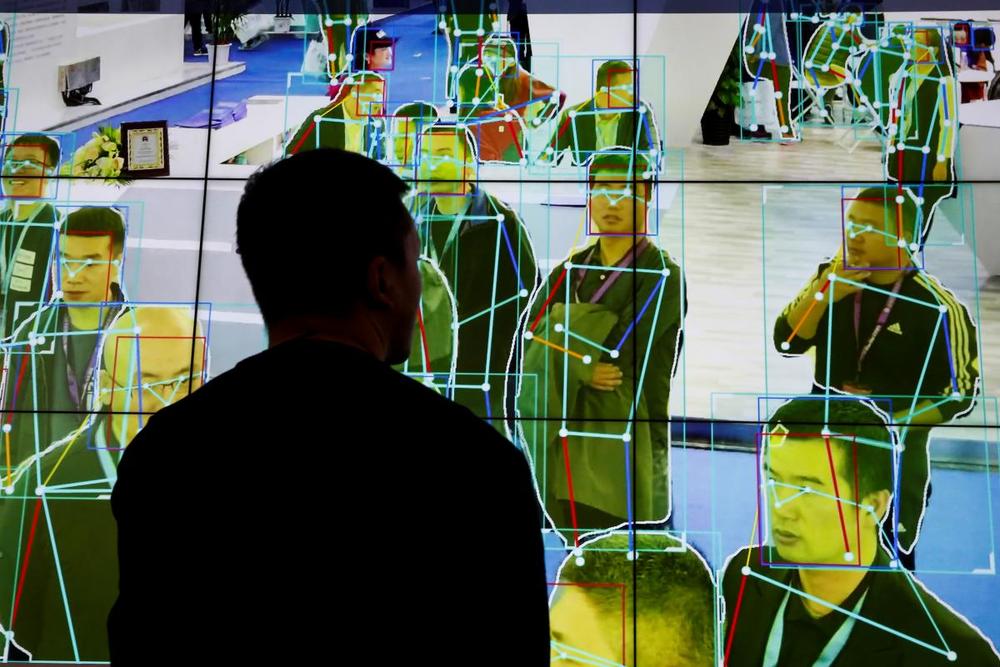
As machines become the primary collectors, analysts, consumers, and targets of intelligence, the entire U.S. intelligence community will need to evolve. This evolution must start with enormous investments in AI and autonomization technology as well as changes to concepts of operations that enable agencies to both process huge volumes of data and channel the resulting intelligence directly to autonomous machines. As practically everything becomes connected via networks that produce some form of electromagnetic signature or data, signals intelligence in particular will need to be a locus of AI evolution. So will geospatial intelligence. As satellites and other sensors proliferate, everything on earth will soon be visible at all times from above, a state that the federal research and development center Aerospace has called the “GEOINT Singularity.” To keep up with all this data, geospatial intelligence, like signals intelligence, will need to radically enhance its AI capabilities.
The U.S. intelligence community is currently split up into different functions that collect and analyze discrete types of intelligence, such as signals or geospatial intelligence. The RIA may force the intelligence community to reassess whether these divisions still make sense. Electromagnetic information is electromagnetic information, whether it comes from a satellite or an Internet of Things device. The distinction in origin matters little if no human ever looks at the raw data, and an AI system can recognize patterns in all of the data at once. The division between civilian and military intelligence will be similarly eroded, since civilian infrastructure, such as telecommunications systems, will be just as valuable to military objectives as military communications systems. Given these realities, separating intelligence functions may impede rather than aid intelligence operations.

Min-Liang Tan, chief executive of gaming company Razer, said that the Covid-19 pandemic is driving the internet to the next stage of its evolution – something called the ‘Metaverse’ where cyberspace becomes more of an interactive 3D space with commerce and networking alongside content, much like the worlds in popular games such as Fortnite and Roblox.
The metaverse concept was brought to life by the 2018 sci-fi movie Ready Player One, directed by Steven Spielberg.
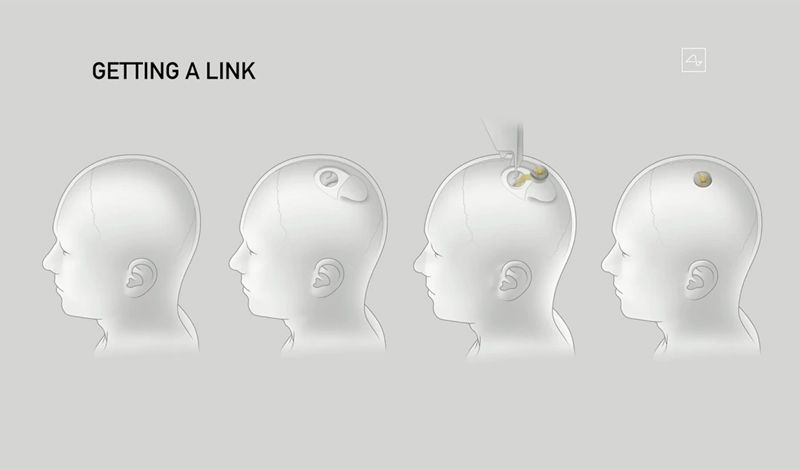
In this video, Elon Musk demonstrates a prototype brain–computer interface chip – implanted in a pig – that his company, Neuralink, has been working on. The device could one day be used by humans to augment their abilities.
Founded in 2016, the Neuralink Corporation remained highly secretive about its work until July 2019, when Musk presented his concept at the California Academy of Sciences. It emerged that he planned to create brain–machine interfaces (BMIs) not only for diseased or injured patients, but also healthy individuals who might wish to enhance themselves.
Yesterday, in a livestream event on YouTube, Musk unveiled a pig called Gertrude with a coin-sized chip in her brain. Simpler and smaller than the original revealed last year, the read/write link device can nevertheless pack 1,024 channels with megabit wireless data rate and all-day battery life. This latest prototype – version 0.9 – has now been approved as an FDA breakthrough device, allowing it to be used in limited human trials under the US federal guidelines for testing medical devices. The chip is removable, Musk explained, as he showed another pig called Dorothy, who no longer had the implant and was healthy, happy and indistinguishable from a normal pig.
This is a working proof of concept of the NeuralLace. It can detect limb motion and smell sensation via neural implants in the brain. So far it’s only been tested in pigs, but an early usecase might be a digital replacement for spinal cord injuries. But the real future goal about is getting to implant an internet enabled AI into your brain.
Elon Musk showed off Neuralink’s new implantable brain chip and demonstrated it working in real time on a pig.
CNET playlists: https://www.youtube.com/user/CNETTV/playlists
Download the new CNET app: https://cnet.app.link/GWuXq8ExzG
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cnet
Follow us on Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/cnet
Follow us on Instagram: http://bit.ly/2icCYYm
DARPA announces a new type of cryptography to protect the Big Tech firm profits from the dawn of quantum computers and allow backdoor access into 3 trillion internet-connected devices.
by Raul Diego
The U.S. Military-Industrial complex is sprinting on a chariot to shore up the encryption space before the next era of computation upends the entire digital edifice built on semiconductors and transistors. But, the core of the effort is protecting markets for Big Tech and all of its tentacles, which stand to lose years or even decades of profits should the new tech be rolled out too quickly.