A laser blast in California ignites a fleeting, self-sustaining chain reaction.
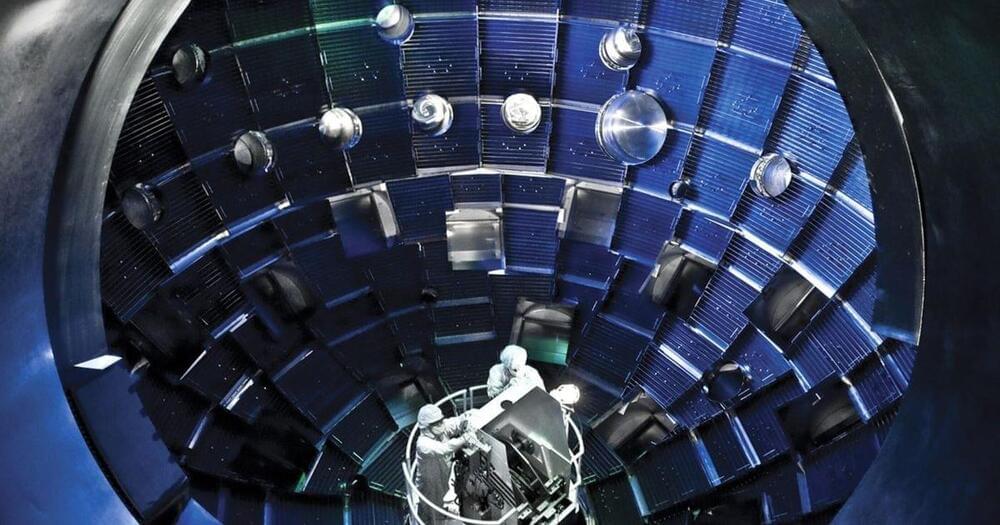



On August 8 2021, an experiment at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s (LLNL’s) National Ignition Facility (NIF) made a significant step toward ignition, achieving a yield of more than 1.3 megajoules (MJ). This advancement puts researchers at the threshold of fusion ignition, an important goal of the NIF, and opens access to a new experimental regime.
The experiment was enabled by focusing laser light from NIF — the size of three football fields — onto a target the size of a BB that produces a hot-spot the diameter of a human hair, generating more than 10 quadrillion watts of fusion power for 100 trillionths of a second.
“These extraordinary results from NIF advance the science that NNSA depends on to modernize our nuclear weapons and production as well as open new avenues of research,” said Jill Hruby, DOE under secretary for Nuclear Security and NNSA administrator.
It’s one of the most profound innovations of our time — and Manhattan-based Australian Kate Crawford wants us to wake up to AI’s inherent risks.

Let the record show that the current COVID-19 vaccines work, and they work well. But what is the next step in vaccine development, especially amid increasing rates of breakthrough infections and emergence of variants of concern?
In a new Northwestern Medicine study in mice, researchers took one of the current vaccines, which is based on the novel coronavirus’s infamous spike protein, and added a different antigen, the nucleocapsid protein, to form a new, potentially improved version of the COVID vaccine. The nucleocapsid protein, which is an internal RNA-binding protein, may help kick the immune system into high gear much more quickly than the spike protein is capable of since it is among the most rapidly and highly expressed proteins in coronaviruses.
“At this point, we’re just trying to figure out ‘What should the 2.0 vaccines be?’” said senior and corresponding study author Pablo Penaloza-MacMaster, an assistant professor of microbiology-immunology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “It seems like adding nucleocapsid to the vaccine renders it more protective, relative to having only the spike.”
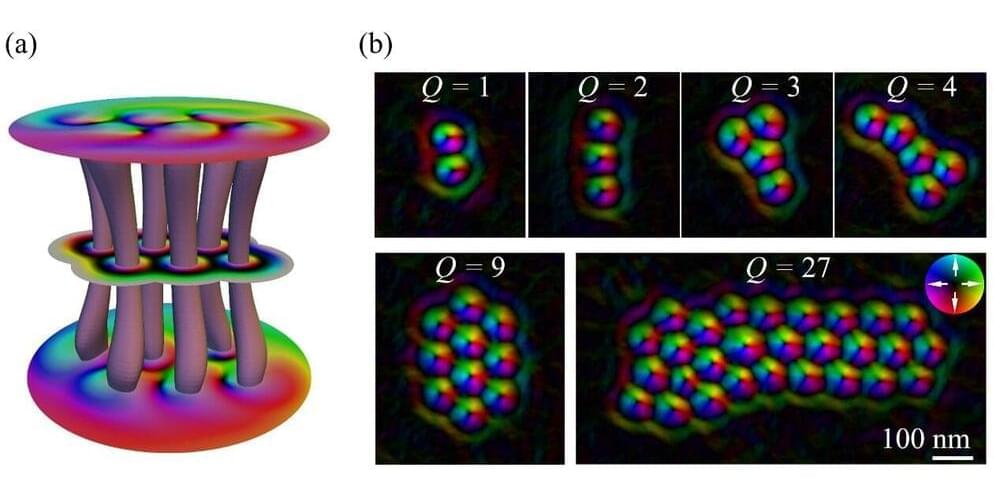
In a study recently published in Nature Nanotechnology, a research group led by Prof. Du Haifeng and Dr. Tang Jin from High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), reported a scientific breakthrough after they found skyrmion bundles, a new family member of topological magnetic structures.
With the help of Lorentz transmission electron microscopy (Lorentz-TEM), the research group clarified, for the first time, a type of magnetic quasiparticles with arbitrary topological charges Q, and then further realized current driven dynamic motion of skyrmion bundles.
Skyrmion, a vortex-like localized chiral topological magnetic structure, has a potential to be the information carrier applied in future high-performance spintronic devices. The topological charge is a fundamental parameter of magnetic domains and determines their topology-related properties. Among the topological structures including skyrmions, merons, vortex, and skyrmion bubbles, the topological charges are both one or smaller than one. Although theory has proposed “skyrmion bags” and “high-order skyrmions” as multi-Q topological magnetic structures, their experimental observations remain elusive.

I think I posted about the work in Texas, but here is more work.
Israeli and American researchers have discovered a nanobody cocktail that could neutralize coronavirus, including the Delta mutation.
Nanobodies are single domain antibodies derived from llamas — or other members of the camel family.
The discovery of the cocktail and their effectiveness in combating coronavirus was published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications.
“If we can produce an innovative drug through the cocktail, it will be a life-saving treatment — if given early in the disease,” according to Hebrew University School of Engineering and Computer Science Dr. Dina Schneidman-Duhovy, who helped lead the study with University of Pittsburgh researcher Dr. Yi Shi.
A team of Israeli and American researchers have found a combination of antibodies derived from llamas that may be effective in treating the coronavirus.
Development of the aircraft isn’t focused solely around military use; Hermeus is intent on bringing innovation to commercial flight, too. “While this partnership with the US Air Force underscores US Department of Defense interest in hypersonic aircraft, when paired with Hermeus’ partnership with NASA announced in February 2,021 it is clear that there are both commercial and defense applications for what we’re building,” said Hermeus CEO and co-founder AJ Piplica.
Hermeus’ Quarterhorse is a hypersonic aircraft that can fly at Mach 5 speeds, or 3,000 mph—fast enough to go from the US to Europe in 90 minutes.

