One of the vast untapped potentials of medicine is the access to imaging equipment. A billion people have difficulty getting access to an x-ray, and that says nothing about access to MRIs or CAT scans. Over the past few years, [Jean Rintoul] has been working on a low-cost way to image the inside of a human body using nothing more than a few electrodes. It can be done cheaply and easily, and it’s one of the most innovative ways of bringing medical imaging to the masses. Now, this is a crowdfunding project, aiming to provide safe, accessible medical imaging to everyone.
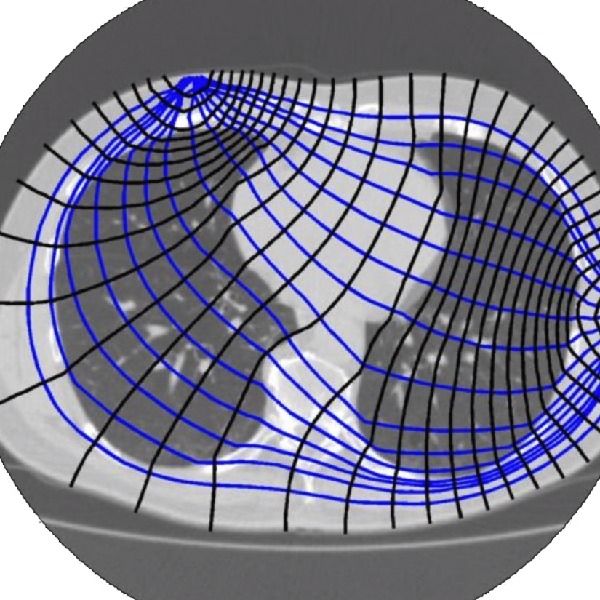
It’s called Spectra, and uses electrical impedance tomography to image the inside of a chest cavity, the dielectric spectrum of a bone, or the interior of a strawberry. Spectra does this by wrapping an electrode around a part of the body and sending out small AC currents. These small currents are reconstructed using tomographic techniques, imaging a cross-section of a body.
[Jean] gave a talk about Spectra at last year’s Hackaday Superconference, and if you want to look at the forefront of affordable medical technology, you needn’t look any further. Simply by sending an AC wave of around 10kHz through a body, software can reconstruct the internals. Everything from lung volume to muscle and fat mass to cancers can be detected with this equipment. You still need a tech or MD to interpret the data, but this is a great way to bring medical imaging technology to the people who need it.