Quantum computing is about to enter an important stage — the era of quantum advantage. The first claims of quantum advantage are emerging, and over the next few years, we expect researchers and developers to continue presenting compelling hypotheses for quantum advantages. In turn, the broader community will either disprove these hypotheses with cutting-edge techniques — or the advantage holds.
Put simply, quantum advantage means that a quantum computer can run a computation more accurately, cheaply, or efficiently than a classical computer. Between now and the end of 2026, we predict that the quantum community will have uncovered the first quantum advantages. But there’s more to it than that.
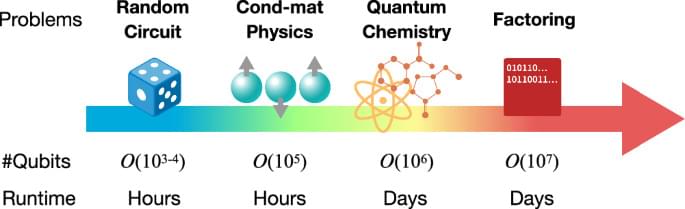
We have arrived already at a place where quantum computing is a useful scientific tool capable of performing computations that even the best exact classical algorithms can’t. We and our partners are already conducting a range of experiments on quantum computers that are competitive with the leading classical approximation methods. At the same time, computing researchers are testing advantage claims with innovative new classical approaches.