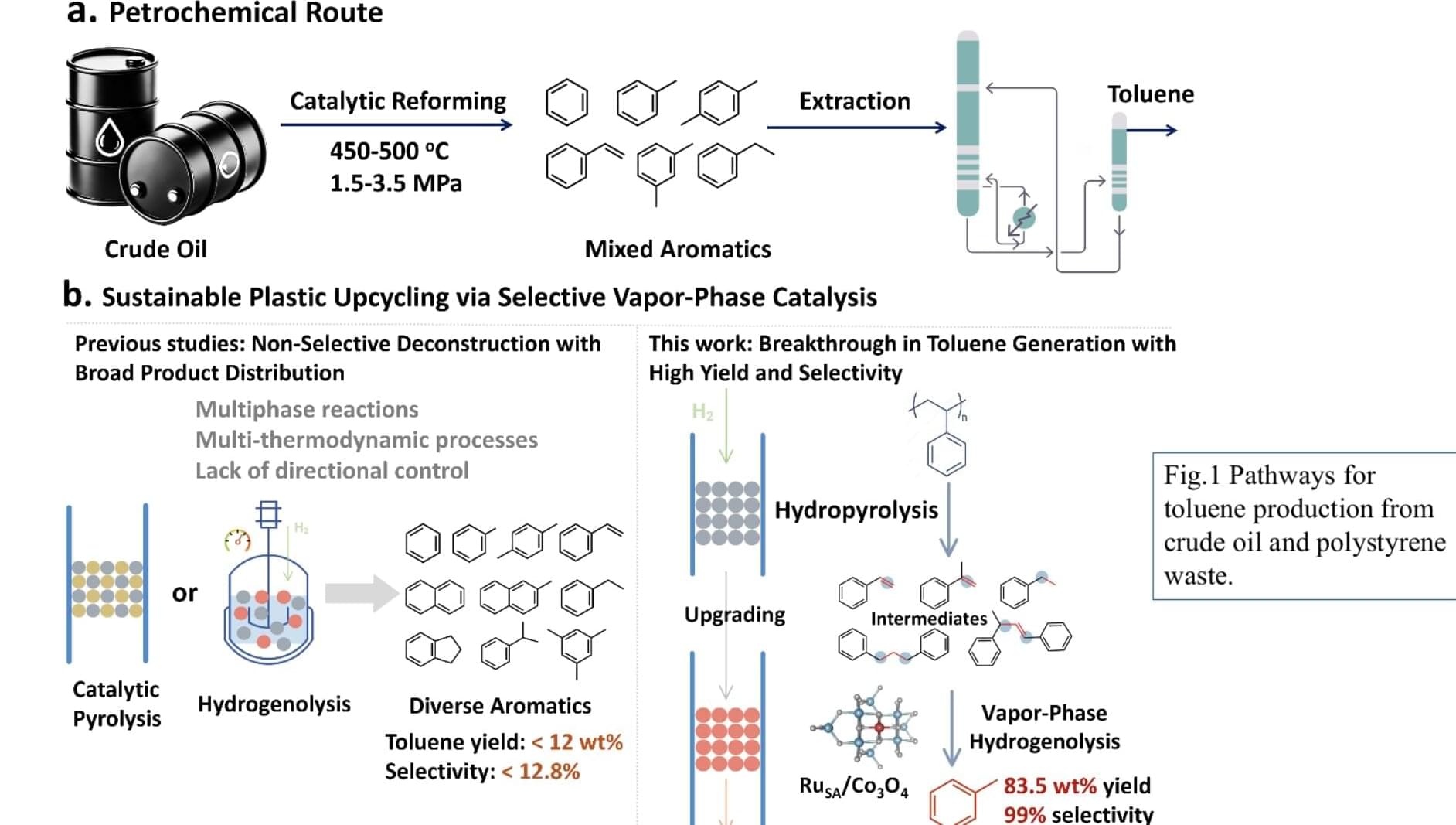
The rapid accumulation of plastic waste is currently posing significant risks for both human health and the environment on Earth. A possible solution to this problem would be to recycle plastic waste, breaking it into smaller molecules that can be used to produce valuable chemicals.
Researchers at Nanjing Forestry University and Tsinghua University recently introduced a new approach to convert polystyrene (PS), a plastic widely used to pack some foods and other products, into toluene, a hydrocarbon that is of value in industrial and manufacturing settings. Their proposed strategy, outlined in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, entails heating polystyrene waste in hydrogen and breaking it down into smaller vapor molecules, a process known as hydro-pyrolysis.
Life-cycle and techno-economic analyses performed by the team showed that the newly introduced process could reduce the carbon footprint of toluene production by 53%, producing toluene at an estimated cost of $0.61/kg, which is below the current industry benchmark.