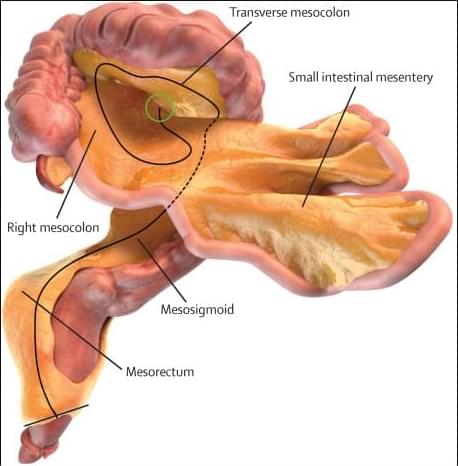
Deterioration of the hippocampus precedes and leads to memory impairment in late adulthood (1, 2). Strategies to fight hippocampal loss and protect against the development of memory impairment has become an important topic in recent years from both scientific and public health perspectives. Physical activity, such as aerobic exercise, has emerged as a promising low-cost treatment to improve neurocognitive function that is accessible to most adults and is not plagued by intolerable side effects often found with pharmaceutical treatments (3). Exercise enhances learning and improves retention, which is accompanied by increased cell proliferation and survival in the hippocampus of rodents (4– 6); effects that are mediated, in part, by increased production and secretion of BDNF and its receptor tyrosine kinase trkB (7, 8).
Aerobic exercise training increases gray and white matter volume in the prefrontal cortex (9) of older adults and increases the functioning of key nodes in the executive control network (10, 11). Greater amounts of physical activity are associated with sparing of prefrontal and temporal brain regions over a 9-y period, which reduces the risk for cognitive impairment (12). Further, hippocampal and medial temporal lobe volumes are larger in higher-fit older adults (13, 14), and larger hippocampal volumes mediate improvements in spatial memory (13). Exercise training increases cerebral blood volume (15) and perfusion of the hippocampus (16), but the extent to which exercise can modify the size of the hippocampus in late adulthood remains unknown.
To evaluate whether exercise training increases the size of the hippocampus and improves spatial memory, we designed a single-blind, randomized controlled trial in which adults were randomly assigned to receive either moderate-intensity aerobic exercise 3D/wk or stretching and toning exercises that served as a control. We predicted that 1 y of moderate-intensity exercise would increase the size of the hippocampus and that change in hippocampal volume would be associated with increased serum BDNF and improved memory function.