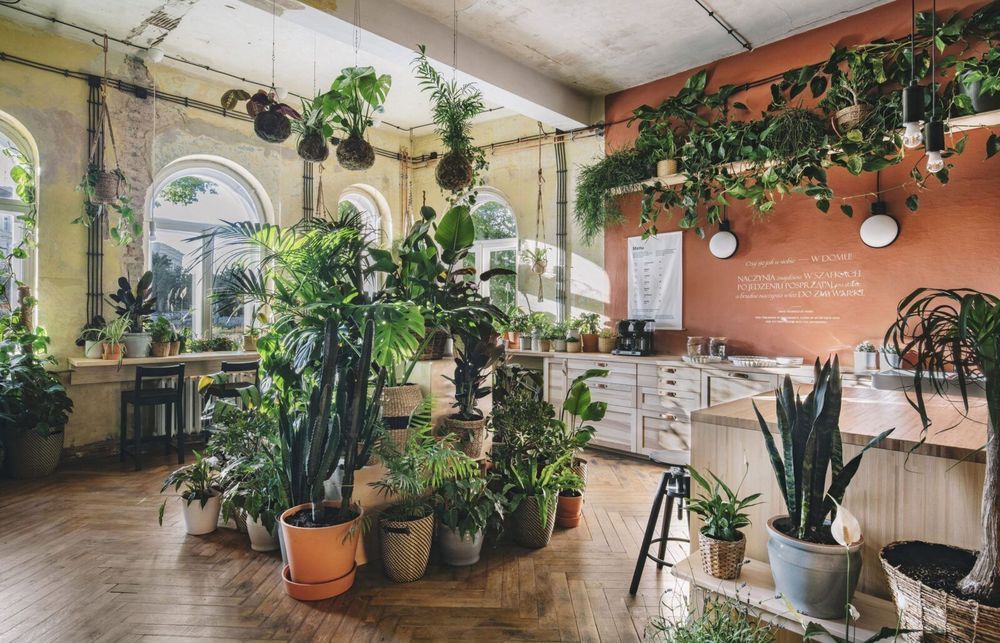
In a recent study of the upper atmosphere of Venus, finding the chemical fingerprint of phosphine has led to speculation that it may be tied to airborne life high in the clouds of our sister planet [1]. We harbour similar suspicion of microbial life on Mars [2], Saturn’s moon Enceledus [3], and Europa, the icy Galilean of the Jovian system [4]. The dwarf planet Ceres of the asteroid belt could be added to that list also, with recent evidence of oceanic water [5], while more exotic variations of life may exist on Titan, which is known to be teeming with organic materials [6]. Should we be more wary of our Solar System as an environment to explore, and the potential of pathogens we may encounter?
If one rewinds 500 years, to when exploration of new worlds involved sailing the oceans, the discovery of the Americas introduced viruses which decimated the native population at that time [7]. That in itself was far from a unique event in history, of course. There have been many occurrences throughout history where travel between distant lands has resulted in the introduction of devastating plagues to one population or the other — not least the Black Death, which arrived in Europe from commercial travel with Asia in the 1300s [8]. Meanwhile, 2020 has reminded us how a novel virus can prove virtually unstoppable from spreading worldwide in a matter of months and reaching pandemic level, once introduced to our now interconnected world [9].
Indeed when the first astronauts returned from the Moon in the 60s, they had to undergo weeks of quarantine as a precaution against introducing a lunar pathogen to Earth [10]. We now know the Moon to be a sterile world, but this should not give us a false sense of security when visiting and returning from other worlds, which are far more likely to harbour microbial life. It is quite plausible to consider that any microbes which have evolved to survive in the harsh environments on other worlds could multiply out of control if introduced to a more fertile environment on Earth. The likelihood of any such foreign microbes being capable of becoming infectious pathogens to our species is difficult to measure, but one could still cause problems regardless, by undermining Earth’s ecosystem in competing with native microbial life as a runaway invasive species.
Fortunately, due to the vast distances involved in inter-planetary travel, returning astronauts would likely show symptoms of infection from any dangerous pathogen long before reaching home, as such a journey would be expected to take many months, even with more advanced propulsion technology than we use in space travel today. That is not to say they could not inadvertently return with microbial life on board — or even on the exterior of craft: Earth’s tardigrades, for example, have proven quite durable in journeys into outer space [11].