To understand why gravity modification is not yet a reality, let’s analyze other fundamental discoveries/inventions that changed our civilization or at least the substantially changed the process of discovery. There are several that come to mind, the atomic bomb, heavier than air manned flight, the light bulb, personal computers, and protein folding. There are many other examples but these are sufficient to illustrate what it takes. Before we start, we have to understand four important and related concepts.
(1) Clusters or business clusters, first proposed by Harvard prof. Michael Porter, “a business cluster is a geographic concentration of interconnected businesses, suppliers, and associated institutions in a particular field. Clusters are considered to increase the productivity with which companies can compete, nationally and globally”. Toyota City which predates Porter’s proposal, comes to mind. China’s 12 new cities come to mind, and yes there are pro and cons.
(2) Hot housing, a place offering ideal conditions for the growth of an idea, activity, etc. (3) Crowdsourcing, is a process that involves outsourcing tasks to a distributed group of people. This process can occur both online and offline. Crowdsourcing is different from an ordinary outsourcing since it is a task or problem that is outsourced to an undefined public rather than a specific body. (4) Groundswell, a strong public feeling or opinion that is detectable even though not openly expressed.
I first read about the fascinating story of the making of the atom bomb from Stephane Groueff’s The Manhattan Project-the Making of the Atomic Bomb, in the 1970s. We get a clear idea why this worked. Under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves, and J. Robert Oppenheimer the US, UK & Canada hot housed scientist, engineers, and staff to invent and produce the atomic bomb physics, engineering and manufacturing capabilities. Today we term this key driver of success ‘hot housing’, the bringing together a group of experts to identify avenues for further research, to brainstorm potential solutions, and to test, falsify and validate research paths, focused on a specific desired outcome. The threat of losing out to the Axis powers helped increase this hot housing effect. This is much like what the Aspen Center for Physics is doing (video here).
In the case of the invention of the light bulb, the airplane, and the personal computer, there was a groundswell of public opinion that these inventions could be possible. This led potential inventors with the necessary basic skills to attempt to solve these problems. In the case of the incandescent light bulb, this process took about 70 years from Humphrey Davy in 1809, to Thomas A. Edison and Joseph Wilson Swan in 1879. The groundswell started with Humphrey and had included many by the time of Edison in 1879.
In the case of the airplane the Wright brothers reviewed other researchers’ findings (the groundswell had begun much earlier), and then invented several new tools & skills, flight control, model testing techniques, test pilot skills, light weight motors and new propeller designs.
The invention of the personal computer had the same groundswell effect (see Homebrew Computer Club & PBS TV transcripts). Ed Roberts, Gordon French, Fred Moore, Bob Harsh, George Morrow, Adam Osborne, Lee Felsenstein, Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, John Draper, Jerry Lawson, Ron Jones and Bill Gates all knew each other before many of them became wealthy and famous. Bill Gates wrote the first personal computer language, while the others invented various versions of the microcomputer, later to be known as the personal computer, and peripherals required. They invented the products and the tools necessary for the PC industry to take off.
With protein folding, Seth Cooper, game designer, developed Fold It, the tool that would make the investigation into protein folding accessible to an undefined public. Today we describe this ‘crowdsourcing’. Notice that here it wasn’t a specialized set of team that was hot housed, but the reverse, the general public, were given the tools to make crowdsourcing a viable means to solving a problem.
Thus four key elements are required to foster innovation, basic skills, groundswell, hothouse or crowdsourcing, and new tools.
So why hasn’t this happened with gravity modification? Some form of the groundswell is there. In his book The Hunt for Zero Point, Nick Cook (an editor of the esteemed Jane’s Defense Weekly) describes a history that goes back to World War II, and Nazi Germany. It is fund reading but Kurt Kleiner of Salon provides a sober review of The Hunt for Zero Point.
There are three primary reasons for this not having happened with gravity modification. First, over the last 50 years or so, there have only been about 50 to 100 people (outside of black projects) who have investigated this in a scientific manner. That is, the groundswell of researchers with the necessary basic skills has not reached a critical mass to take off. For example, protein folding needed at least 40,000 participants, today Fold It has 280,000 registered participants.
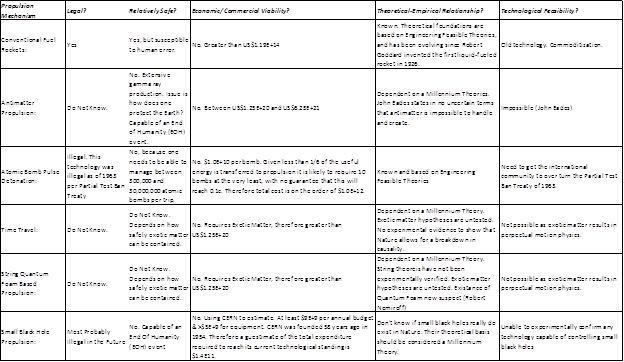
Second, pseudoscience has crept into the field previously known as ‘antigravity’. In respectable scientific circles the term used is gravity modification. Pseudoscience, has clouded the field, confused the public’s perception and chased away the talent – the 3 C’s of pseudoscience. Take for example, plutonium bomb propulsion (written by a non-scientist/non-engineer), basic investigation shows that this is neither feasible nor legal, but it still keeps being written up as a ‘real’ proposition. The correct term for plutonium bomb propulsion is pseudoscience.
Third reason. Per the definition of gravity modification, we cannot use existing theories to propose new tools because all our current status quo theories require mass. Therefore, short of my 12-year study, no new tools are forth coming.
—————————————————————————————————
Benjamin T Solomon is the author & principal investigator of the 12-year study into the theoretical & technological feasibility of gravitation modification, titled An Introduction to Gravity Modification, to achieve interstellar travel in our lifetimes. For more information visit iSETI LLC, Interstellar Space Exploration Technology Initiative.
Solomon is inviting all serious participants to his LinkedIn Group Interstellar Travel & Gravity Modification.