An unusually hopeful story about a very long life without death


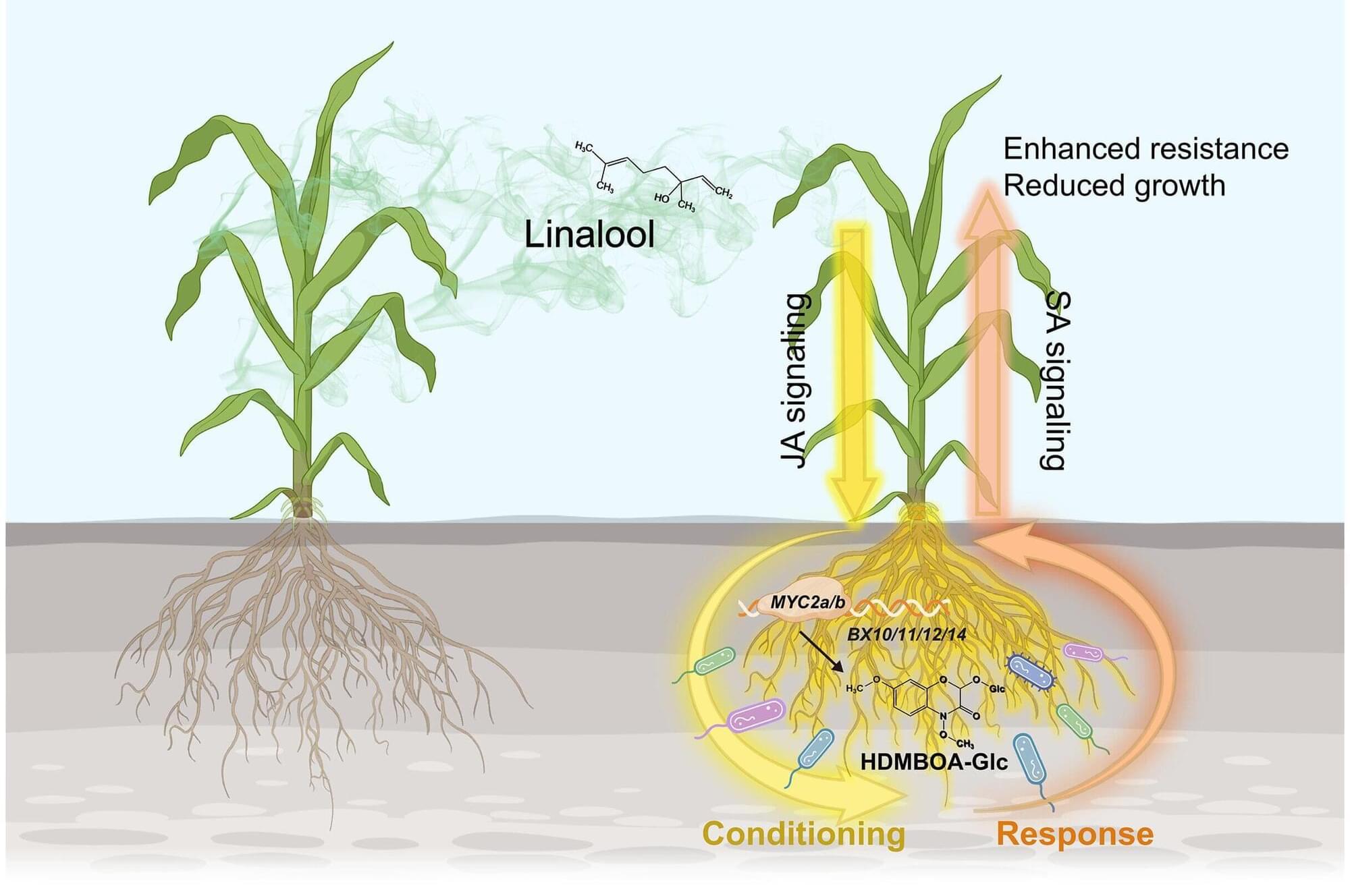
When maize fields become too crowded, the plants signal each other to boost their defenses. A research team led by Dongsheng Guo of Zhejiang University found that in crowded conditions, maize plants release a volatile gas called linalool into the air. When it reaches neighboring plants, the gas triggers a defensive response in their roots.
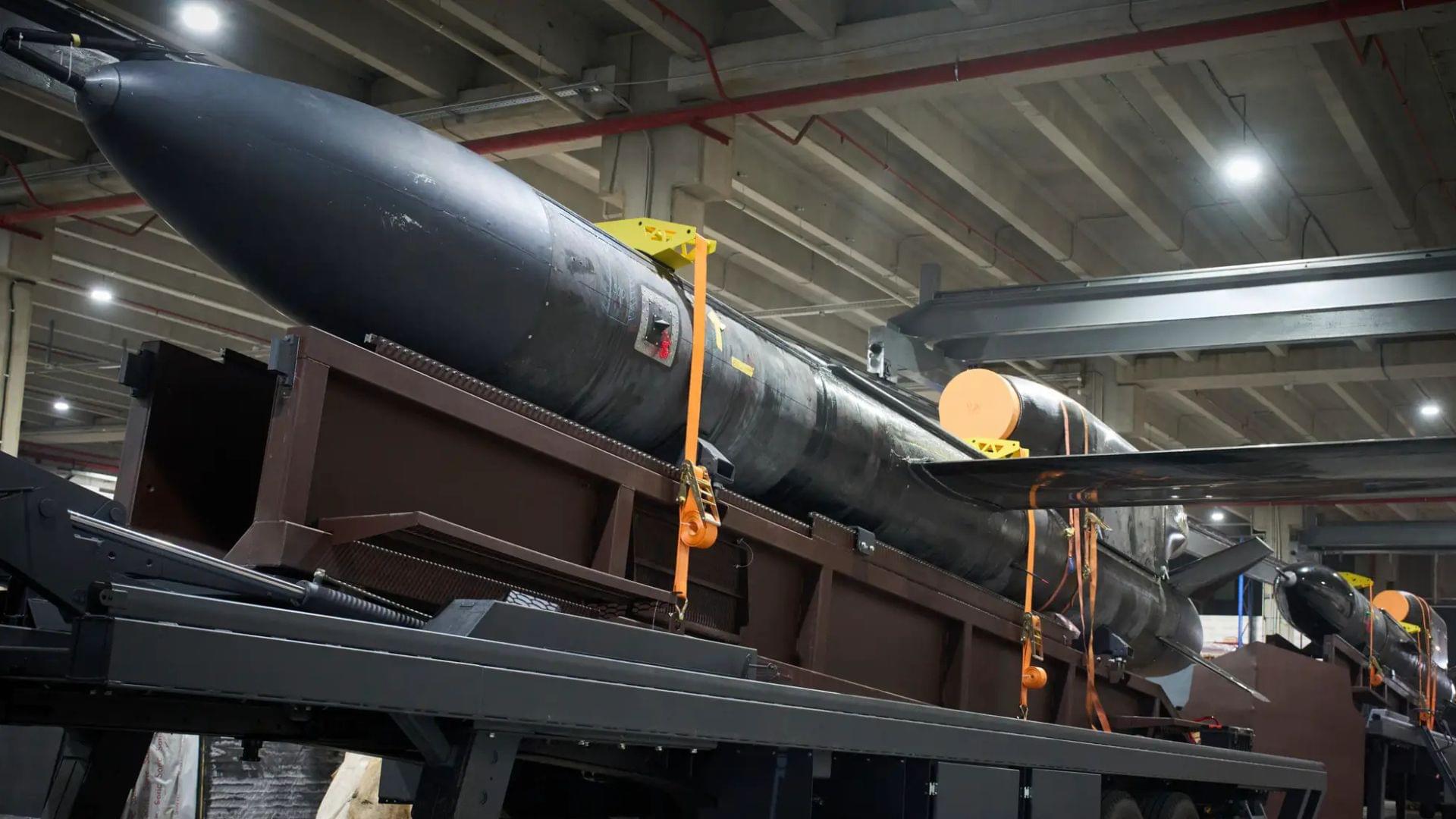

Ukraine’s biggest-ever cruise missile carries 2,205-pound warhead, 1,860-mile range.
A Ukrainian defense manufacturer has unveiled the country’s newest long-range cruise missile, the “Flamingo,” which is reportedly entering serial production, according to photographs shared on social media by an Associated Press photographer, Efrem Lukatsky, on August 18.
The images, taken inside a facility operated by the defense company Fire Point, show the missile during assembly.
According to Lukatsky, the missile is intended to strike targets more than 3,000 kilometers (1,864 miles) away, extending Ukraine’s ability to hit strategic targets deep inside Russian-controlled territory.


FutureAzA
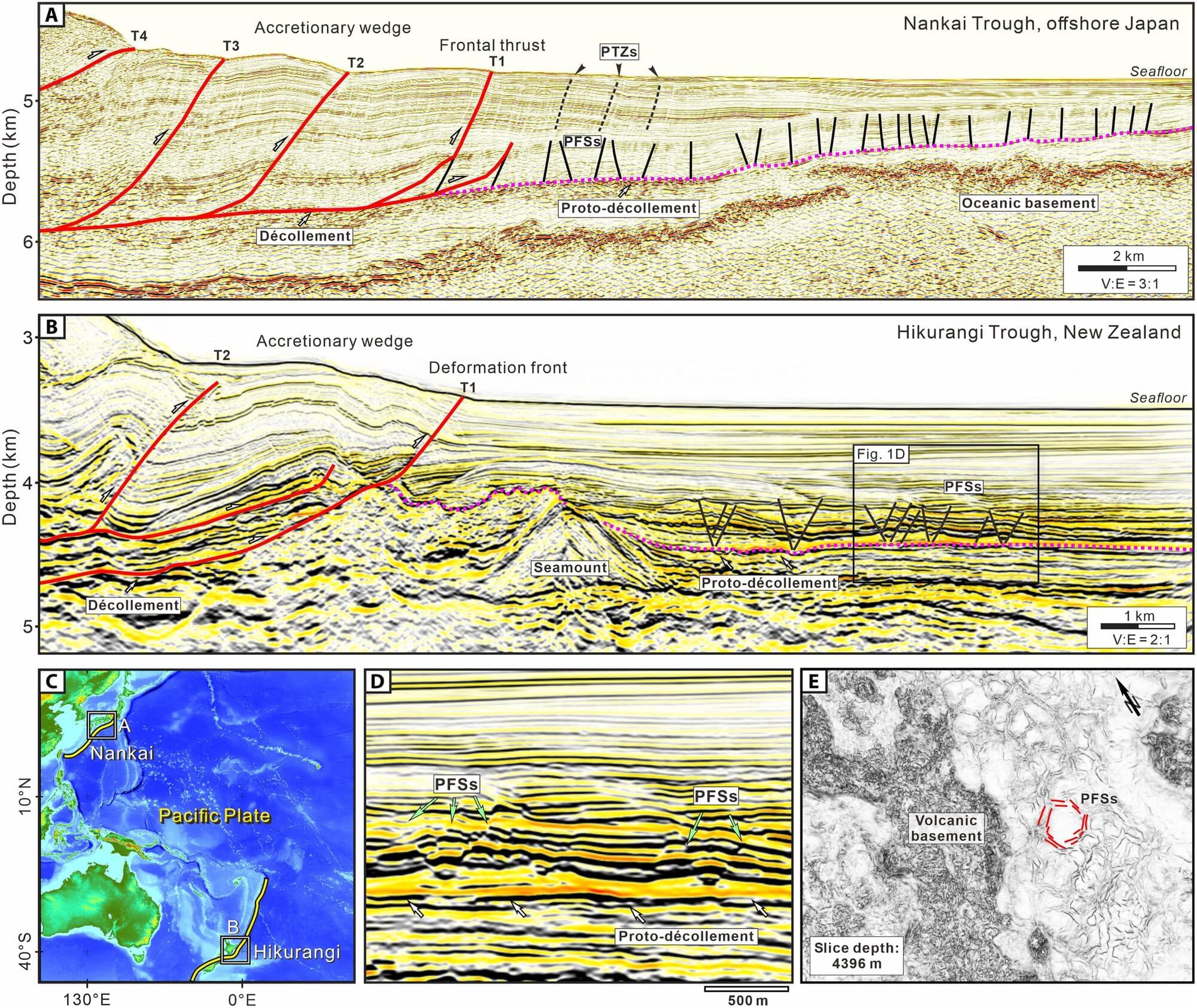
Scientists have uncovered a key piece of the puzzle behind the unusual “slow earthquakes” occurring off the east coast of New Zealand’s North Island.
A new international study, published in Science Advances, identifies hidden fault structures called polygonal fault systems (PFSs) as a major influence on the behavior of the northern Hikurangi subduction zone.
These shallow geological features, found in sediments entering the subduction zone, appear to play a critical role in where and how slow slip earthquakes occur.
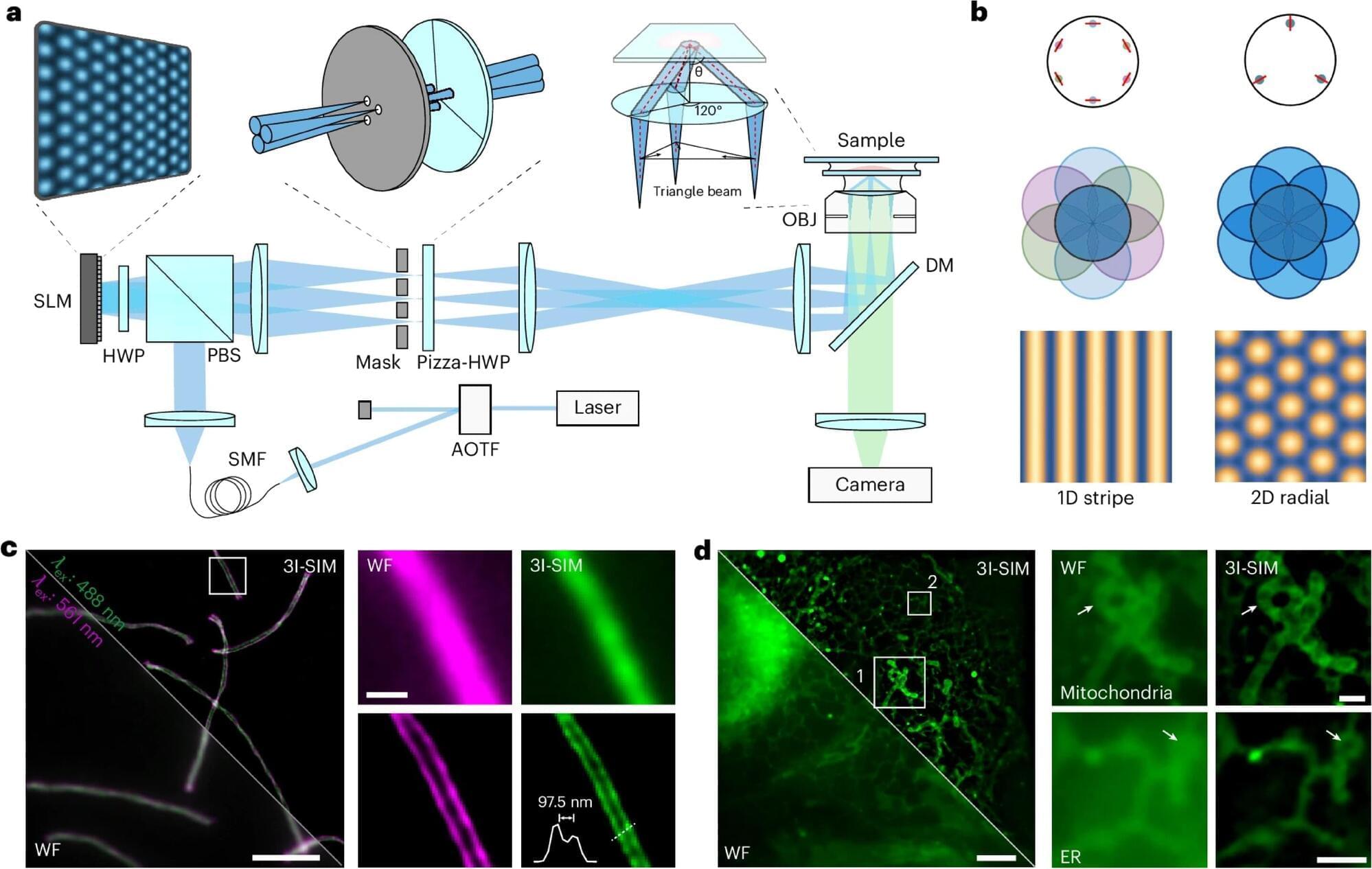
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is the most preferable system for live-cell super-resolution imaging. It enables the observation of intricate subcellular dynamics. However, conventional SIM has long relied on the complex rotation of one-dimensional stripe illumination at three angles, requiring nine exposures to reconstruct a uniform super-resolution image. This greatly hinders imaging speed and causes unnecessary photobleaching, limiting the available information flux in live-cell imaging.
Professor Xi Peng’s team from the College of Future Technology at Peking University has developed a triangle-beam interference SIM (3I-SIM) that enables gentler, sustained super-resolution live-cell imaging. This novel method upgrades the super-resolution imaging to an unprecedented kilo-Hz speed and half-day-long duration, enabling the study of complex and rapid biological processes with higher data throughput.
The work is published in Nature Photonics.
