Sri Lanka has declared a state of emergency as the food crisis worsened after private banks ran out of foreign exchange to finance imports.



Science from industry, federal agencies and independent researchers now links 6:2 FTOH to kidney disease, cancer, neurological damage, developmental problems, mottled teeth and autoimmune disorders, while researchers also found higher mortality rates among young animals and human mothers exposed to the chemicals.
Experts previously considered food and water to be the two main routes by which humans are exposed to PFAS, but the study’s authors note that many humans spend about 90% of their time indoors, and the findings suggest that breathing in the chemicals probably represents a third significant exposure route.
“It’s an underestimated and potentially important source of exposure to PFAS,” said Tom Bruton, a co-author and senior scientist at Green Science.
PFAS, or per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a class of about 9,000 compounds used to make products water-, stain-or heat-resistant. Because they are so effective, the chemicals are used across dozens of industries and are in thousands of everyday consumer products such as stain guards, carpeting and shoes. Textile manufacturers use them to produce waterproof clothing, and they are used in floor waxes, nonstick cookware, food packaging, cosmetics, firefighting foam and much more.
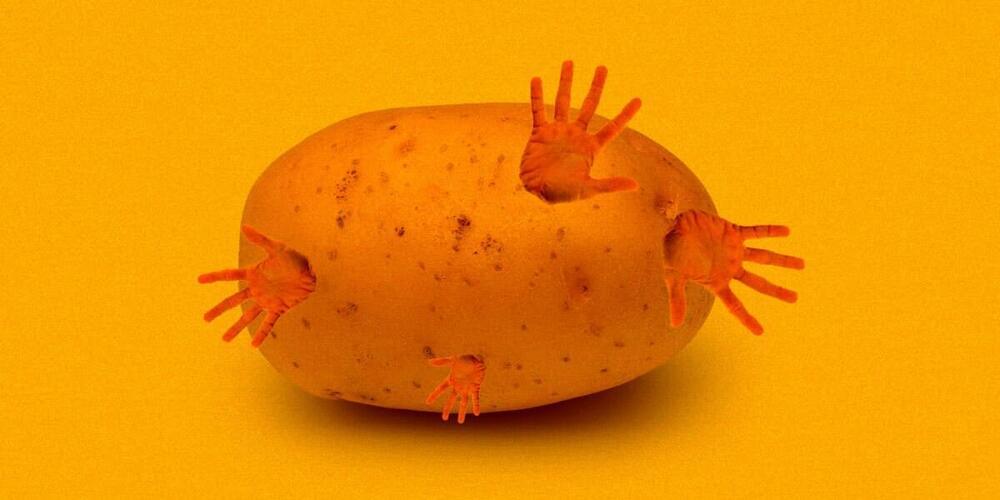
A team of scientists found an unusual trick for growing bigger, heartier crops: inserting a human gene related to obesity and fat mass into plants to supersize their harvest.
Augmenting potatoes with the human gene that encodes a fat-regulating protein called FTO, which essentially alters the genetic code to rapidly mass-produce proteins, made otherwise identical potato plants grow crops that were 50 percent larger, Smithsonian Magazine reports. By growing more food without taking up more space for agriculture, the scientists say their work could help fight global hunger — without adding to its climate impact.
“It [was] really a bold and bizarre idea,” University of Chicago chemist Chuan He, coauthor of a paper published in Nature Biotechnology, told Smithsonian. “To be honest, we were probably expecting some catastrophic effects.”



“I think it’s changed everything, and I think it’s changed everything fundamentally,” James Livingston, a history professor at Rutgers University and the author of No More Work: Why Full Employment Is a Bad Idea, told Vox.
We’ll (probably) always have work, but could the job as the centerpiece of American life be on the way out?
To understand the question, you have to know how the country got to where it is today. The story starts, to some degree, with a failure. Much of American labor law — as well as the social safety net, such as it is — stems from union organizing and progressive action at the federal level in the 1930s, culminating in the New Deal. At that time, many unions were pushing for a national system of pensions not dependent on jobs, as well as national health care, Nelson Lichtenstein, a history professor at the University of California Santa Barbara, told Vox. They did win Social Security, but with many people left out, such as agricultural and domestic workers, it wasn’t a full nationwide retirement system. And when it came to universal health care, they lost entirely.
Using nature against nature.
While no one enjoys seeing carefully nurtured crops destroyed by hordes of hungry insects, the most common way to prevent it – the use of insecticides – is causing massive ecological problems.
Some are wreaking havoc on bee populations globally, killing birds and piling onto the challenges already faced by endangered species. Thankfully, insecticides are generally only in our food at low levels, but they do harm humans who are highly exposed to them too, like the workers growing our crops.
They also destroy predatory insect populations, which just makes the problem of crop pests worse in the long term — with fewer pest enemies around to keep their numbers in check.

The world of lab-grown meats is fast filling with all kinds of tasty bites, from burgers, to chicken breasts, to a series of increasingly complex cuts of steak. Expanding the scope of cultured beef are scientists from Japan’s Osaka University, who have leveraged cutting-edge bioprinting techniques to produce the first lab-grown “beef” that resembles the marbled texture of the country’s famed Wagyu cows.
From humble beginnings that resembled soggy pork back in 2,009 to the classic steaks and rib-eyes we’ve seen pop up in the last few years, lab-grown meat has come along in leaps and bounds. The most sophisticated examples use bioprinting to “print” living cells, which are nurtured to grow and differentiate into different cell types, ultimately building up into the tissues of the desired animal.
The Osaka University team used two types of stem cells harvested from Wagyu cows as their starting point, bovine satellite cells and adipose-derived stem cells. These cells were incubated and coaxed into becoming the different cell types needed to form individual fibers for muscle, fat and blood vessels. These were then arranged into a 3D stack to resemble the high intramuscular fat content of Wagyu, better known as marbling, or sashi in Japan.
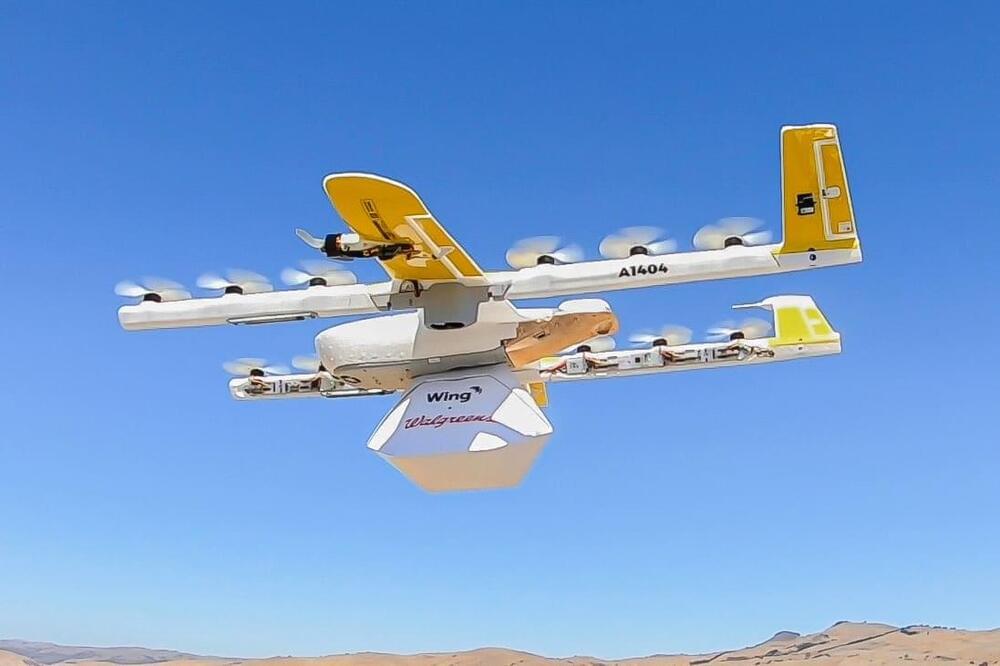

Alphabet’s Wing drone company allows users to order items such as food through a mobile app and is fast approaching 100,000 deliveries since its launch.
Alphabet’s drone company Wing delivered 10,000 cups of coffee, 1,700 snack packs and 1,200 roast chickens to customers in Logan, Australia, over the last year, the company said Wednesday in a blog post outlining its progress.
Wing was initially launched in 2019 in Australia, following a series of drone tests that began in 2014. The service, which was initially part of Alphabet’s experimental research division, allows users to order items such as food through a mobile app and is fast approaching 100,000 deliveries since its launch.
Wing hopes to one day deliver products to people all over the world without having to rely on drivers or delivery trucks like other companies. It’s the reason UPS, Uber and Amazon are also working on drone delivery.

Research indicates that flavonoids may protect against: high blood pressureTrusted Source heart attack and stroke type 2 diabetesTrusted Source certain types of cancer-medicalnewstoday.com
New research finds that people who consume foods high in flavonoids, such as berries, apples, and pears, have lower blood pressure than those who do not.