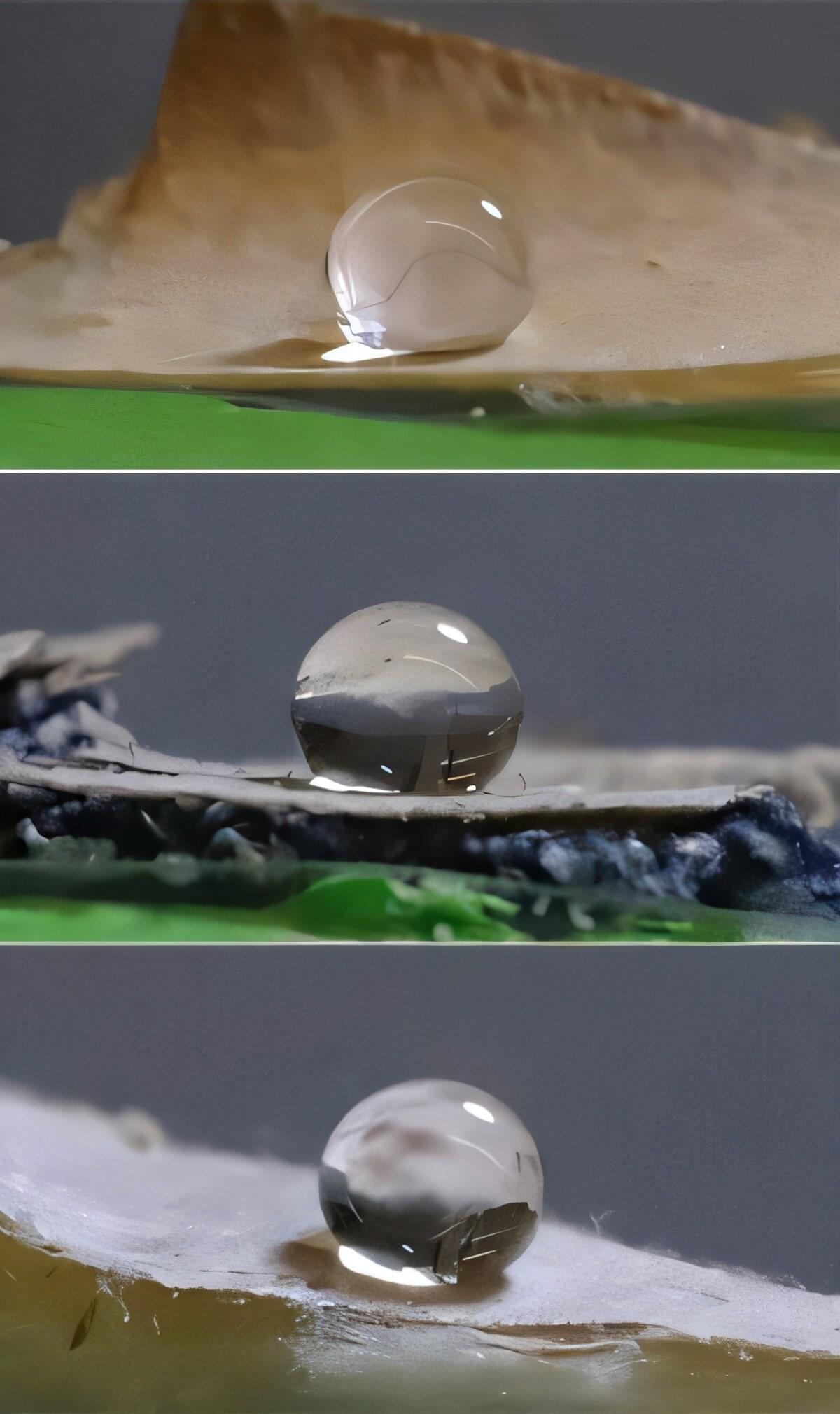
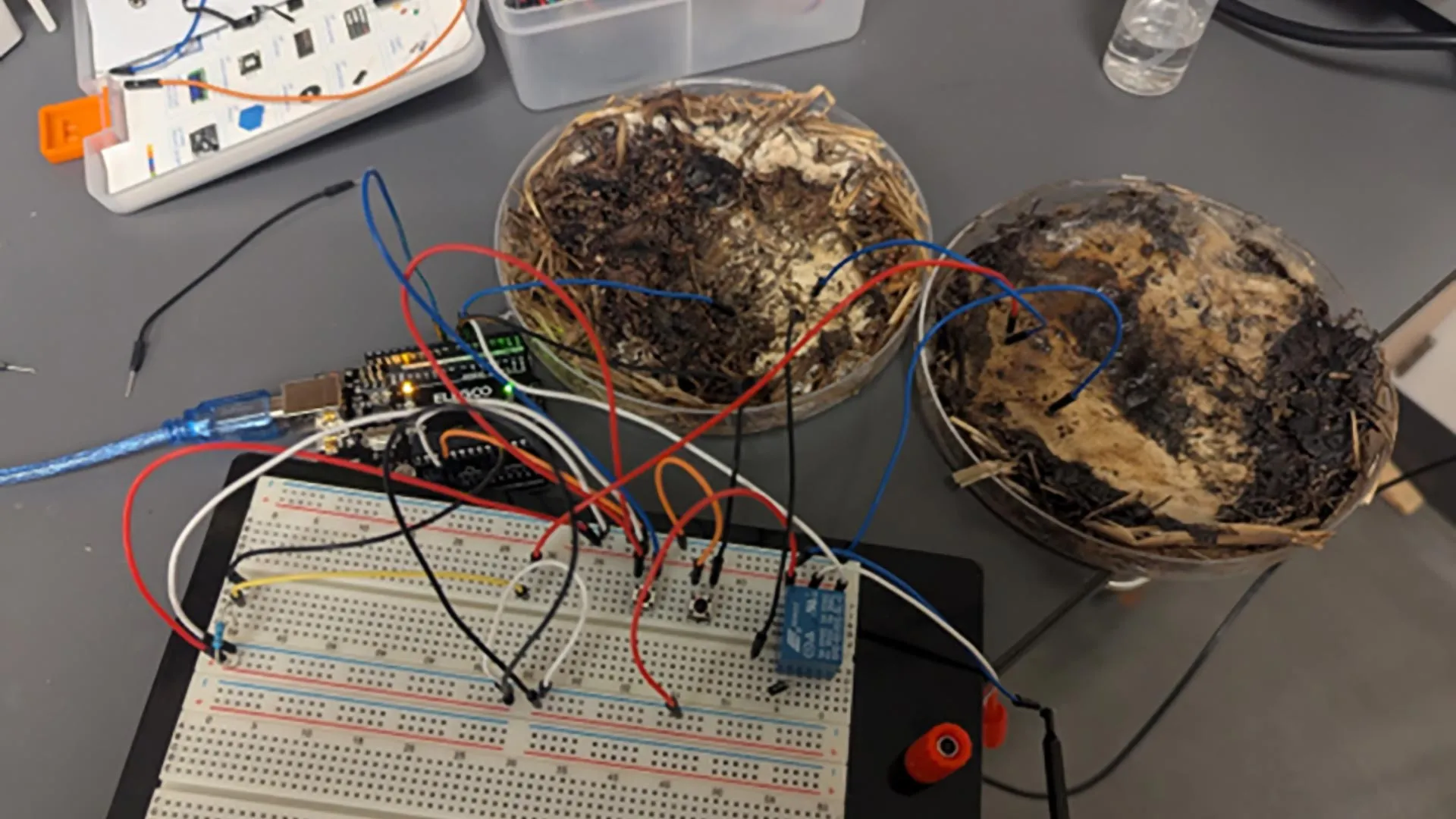
As an alternative to single-use plastic wrap and paper cup coatings, researchers in Langmuir report a way to waterproof materials using edible fungus. Along with fibers made from wood, the fungus produced a layer that blocks water, oil and grease absorption. In a proof-of-concept study, the impervious film grew on common materials such as paper, denim, polyester felt and thin wood, revealing its potential to replace plastic coatings with sustainable, natural materials.
“Our hope is that by providing more ways to potentially reduce our reliance on single-use plastics, we can help lessen the waste that ends up in landfills and the ocean; nature offers elegant, sustainable solutions to help us get there,” says Caitlin Howell, the corresponding author of the study from the University of Maine.
Fungi are more than their mushroom caps; underground they form an extensive, interwoven network of feathery filaments called mycelium. Recently, researchers have been inventing water-resistant materials made from these fibrous networks, including leather-like, electrically conductive gauze and spun yarn, because the surface of mycelium naturally repels water.