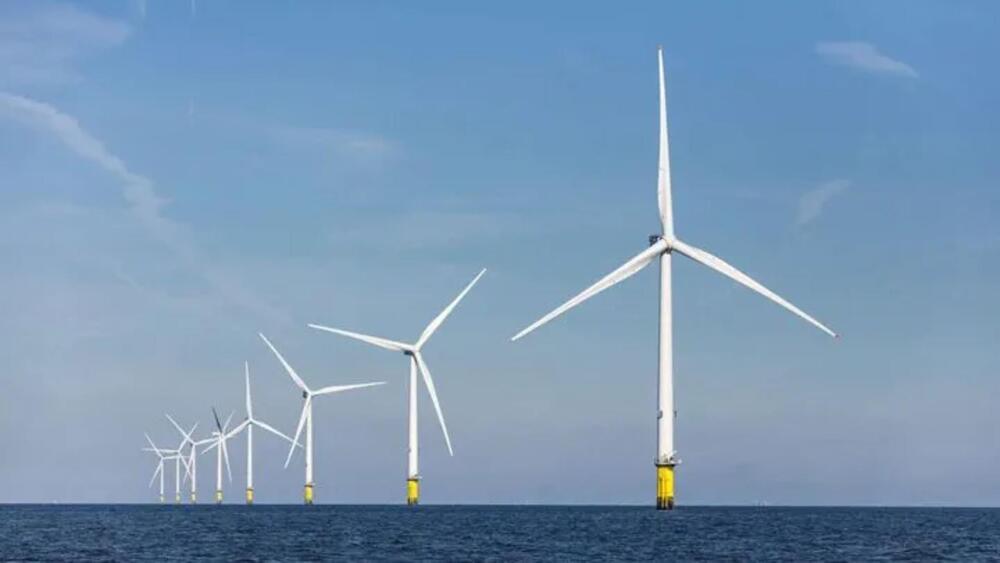
It can generate 1.3 gigawatts of clean energy.
Hornsea 2, the world’s largest offshore wind farm located in the North Sea, has gone fully operational, a press release from its builder, Orsted, said. In its bid to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050, the U.K. is banking heavily on wind-generated power. To this effect, it commissioned the Hornsea One project, which was the largest offshore wind farm in the world at the time of achieving fully operational status in 2020. Two years later, the Hornsea 2 project is fully operational and has claimed the bragging rights for being the largest offshore wind farm in the world.
The Hornsea zone, an area of the North Sea covering more than 2,000 km2, is also set to include Hornsea 3. The 2.8 GW project is planned to follow Hornsea 2 having been awarded a contract for difference from the UK government earlier this year.
Hornsea 2 has played a key role in the ongoing development of a larger and sustainably competitive UK supply chain to support the next phase of the UK’s offshore wind success story. In the past five years alone, Ørsted has placed major contracts with nearly 200 UK suppliers. Ørsted has invested GBP 4.5 billion in the UK supply chain to date and expects to make another GBP 8.6 billion of UK supply chain investments over the next decade.
Ørsted now has 13 operational offshore wind farms in the UK, providing 6.2GW of renewable electricity for the UK – enough to power more than 7 million homes. Hornsea 2 makes a significant contribution to Ørsted’s global ambition of installing 30 GW offshore wind by 2030. Ørsted currently has approx. 8.9 GW offshore wind in operation, approx. 2.2 GW under construction, and another approx. 11 GW of awarded capacity under development including Hornsea 3.