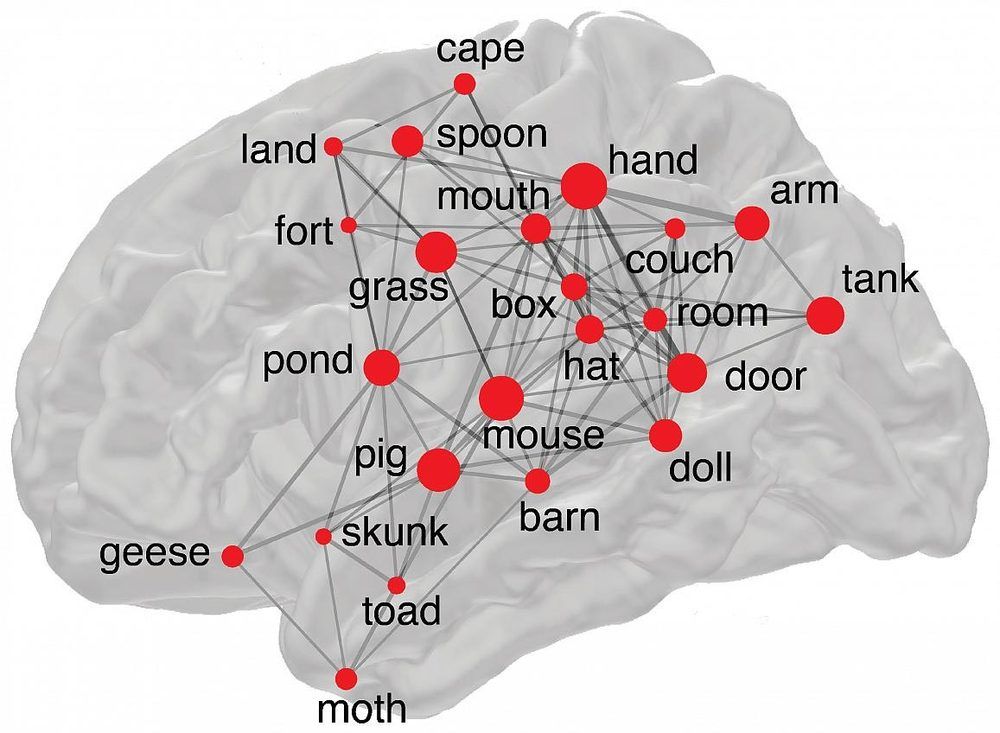
Thousands of words, big and small, are crammed inside our memory banks just waiting to be swiftly withdrawn and strung into sentences. In a recent study of epilepsy patients and healthy volunteers, National Institutes of Health researchers found that our brains may withdraw some common words, like “pig,” “tank,” and “door,” much more often than others, including “cat,” “street,” and “stair.” By combining memory tests, brain wave recordings, and surveys of billions of words published in books, news articles and internet encyclopedia pages, the researchers not only showed how our brains may recall words but also memories of our past experiences.
“We found that some words are much more memorable than others. Our results support the idea that our memories are wired into neural networks and that our brains search for these memories, just the way search engines track down information on the internet,” said Weizhen (Zane) Xie, Ph.D., a cognitive psychologist and post-doctoral fellow at the NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), who led the study published in Nature Human Behaviour. “We hope that these results can be used as a roadmap to evaluate the health of a person’s memory and brain.”
Dr. Xie and his colleagues first spotted these words when they re-analyzed the results of memory tests taken by 30 epilepsy patients who were part of a clinical trial led by Kareem Zaghloul, M.D., Ph.D., a neurosurgeon and senior investigator at NINDS. Dr. Zaghloul’s team tries to help patients whose seizures cannot be controlled by drugs, otherwise known as intractable epilepsy. During the observation period, patients spend several days at the NIH’s Clinical Center with surgically implanted electrodes designed to detect changes in brain activity.