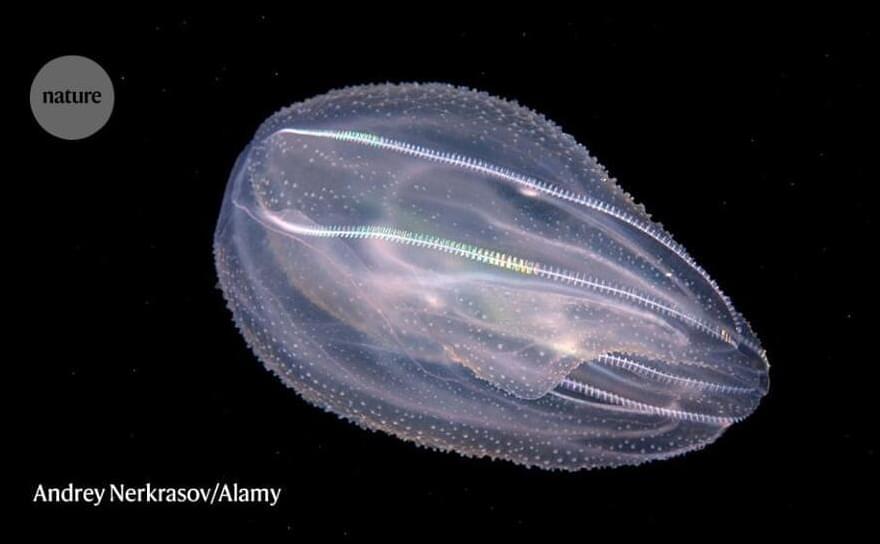
Fused neurons suggest ctenophores’ nervous system evolved independently of that in other animals.


In this episode, my guest is Oded Rechavi, Ph.D., professor of neurobiology at Tel Aviv University and expert in how genes are inherited, how experiences shape genes and remarkably, how some memories of experiences can be passed via genes to offspring. We discuss his research challenging long-held tenets of genetic inheritance and the relevance of those findings to understanding key biological and psychological processes including metabolism, stress and trauma. He describes the history of the scientific exploration of the “heritability of acquired traits” and how epigenetics and RNA biology can account for some of the passage of certain experience-based memories. He discusses the importance of model organisms in scientific research and describes his work on how stressors and memories can be passed through small RNA molecules to multiple generations of offspring in ways that meaningfully affect their behavior. Nature vs. nurture is a commonly debated theme; Dr. Rechavi’s work represents a fundamental shift in our understanding of that debate, as well as genetic inheritance, brain function and evolution.
Thank you to our sponsors.
AG1 (Athletic Greens): https://athleticgreens.com/huberman.
ROKA: https://roka.com/huberman.
HVMN: https://hvmn.com/huberman.
Eight Sleep: https://eightsleep.com/huberman.
InsideTracker: https://www.insidetracker.com/huberman.
Supplements from Momentous.
https://www.livemomentous.com/huberman.
Huberman Lab Social & Website.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/hubermanlab.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/hubermanlab.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/hubermanlab.
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@hubermanlab.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/andrew-huberman.
Website: https://hubermanlab.com.
Newsletter: https://hubermanlab.com/neural-network.
Dr. Rechavi.
Academic Profile: https://en-lifesci.tau.ac.il/profile/odedrech_66
Lab Website: https://www.odedrechavilab.com.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/OdedRechavi.
TEDx Talk: https://www.ted.com/talks/oded_rechavi_transgenerational_biology?language=en.
Articles.
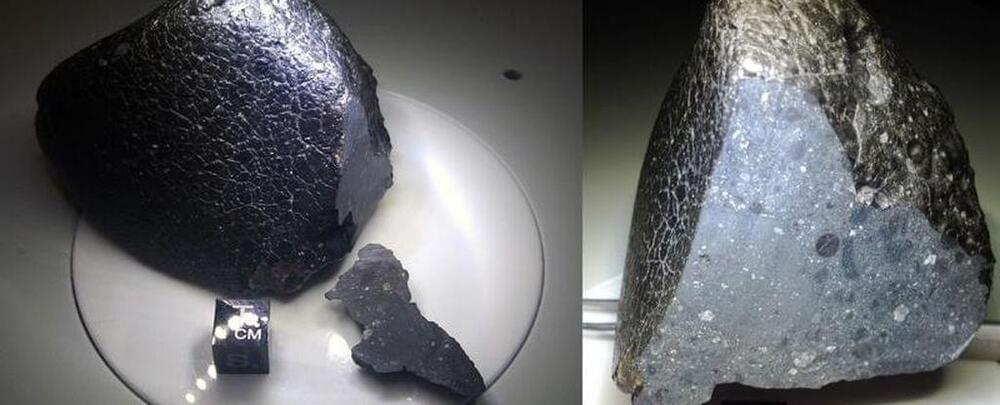

A popular and easy method for validating whether or not a chunk of rock is a meteorite, and what kind of meteorite it is, has been inadvertently erasing invaluable information locked inside.
The use of rare-earth magnets such as neodymium erases and overwrites the magnetic record locked inside ferromagnetic minerals in meteorites, scientists from MIT in the US and Paris Cité University in France found. Since many meteorites that fall to Earth have a significant iron content, this means we’re losing important data on the way magnetic fields in space have altered these meteorites over billions of years.
Meteorites provide invaluable records of planetary formation and evolution. Studies of their paleomagnetism have constrained accretion in the protoplanetary disk, the thermal evolution and differentiation of planetesimals, and the history of planetary dynamos.
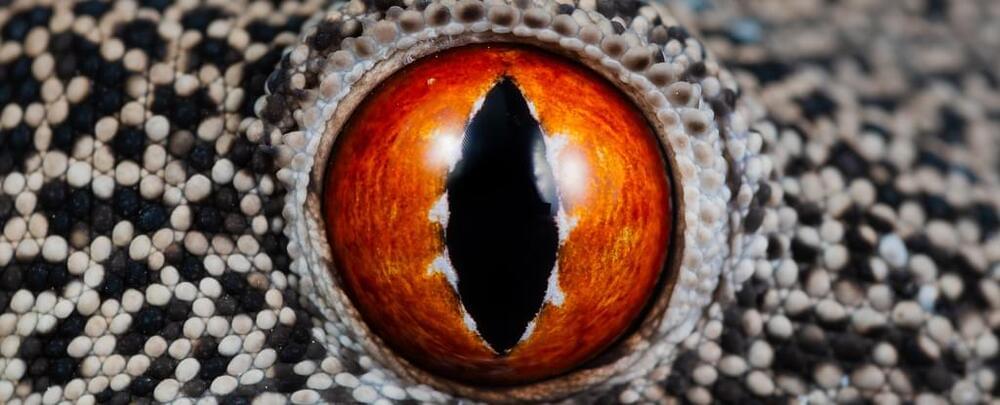

The evolution of the human eye has long been considered one of biology’s more challenging mysteries, drawing debate over the sequence of steps required to turn rudimentary sensitivity to light into a complex photographic system.
New research suggests some components of vertebrate vision may not have been shaped incrementally as their genes passed down family lines, but were ‘stolen’ from entirely different branches of life.
“At least one innovation that led to the current structure of vertebrate eyes did not occur from stepwise “tinkering” with genes that exist in other animals, but came from introduction of novel DNA from bacteria by horizontal gene transfer,” explains molecular biologist Matt Daugherty from the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) on Twitter.



The GPT phenomenon and the future of humanity in the face of advances in Artificial Intelligence.
The Age of Artificial Intelligence is an increasingly present reality in our daily lives. With the rise of technologies such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), the possibility of creating machines capable of performing tasks that were previously exclusive to humans has emerged.
One of these technologies is the Generative Pre-trained Transformer, better known as GPT. It’s the Large Language Model (LLM) developed by OpenAI.
OpenAI was founded in San Francisco, California in 2015 by Sam Altman, Reid Hoffman, Jessica Livingston, Elon Musk, Ilya Sutskever, Peter Thiel, among others, who collectively pledged $1 billion. Musk resigned from the board in 2018, but continued to be a donor to the project.
The Tibetan Plateau, the highest and largest plateau above sea level, is one of the harshest environments settled by humans. It has a cold and arid environment and its elevation often surpasses 4,000 meters above sea level (masl). The plateau covers a wide expanse of Asia—approximately 2.5 million square kilometers—and is home to over 7 million people, primarily belonging to the Tibetan and Sherpa ethnic groups.
However, our understanding of their origins and history on the plateau is patchy. Despite a rich archaeological context spanning the plateau, sampling of DNA from ancient humans has been limited to a thin slice of the southwestern plateau in the Himalayas.
Now, a study published in Science Advances led by Prof. Fu Qiaomei from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has filled this gap by sequencing the genomes of 89 ancient humans dating back to 5,100 BP from 29 archaeological sites spanning the Tibetan Plateau.