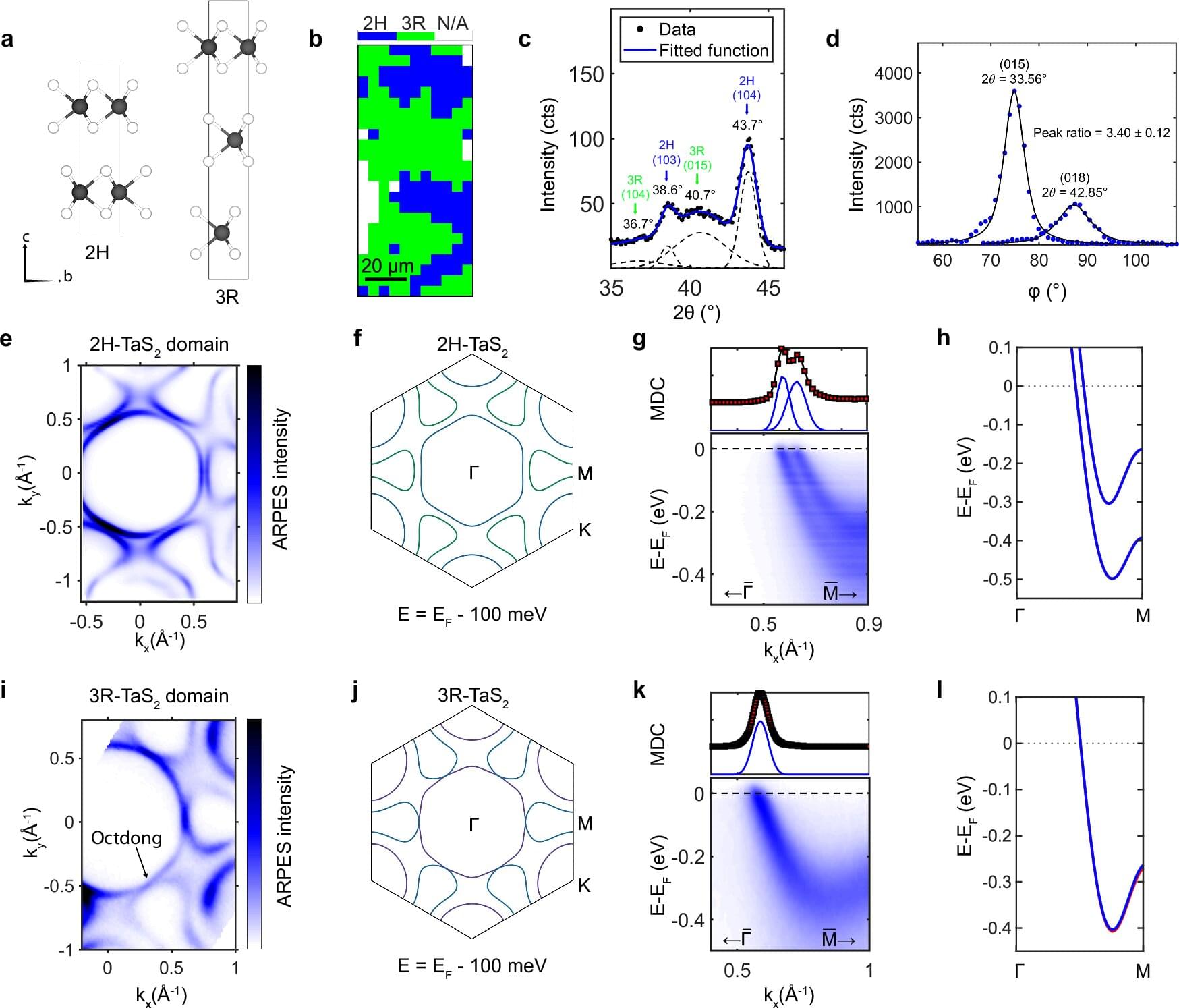
One of the biggest problems facing modern microelectronics is that computer chips can no longer be made arbitrarily smaller and more efficient. Materials used to date, such as copper, are reaching their limits because their resistivity increases dramatically when they become too small. Chiral materials could provide a solution here. These materials behave like left and right hands: they look almost identical and are mirror images of each other, but cannot be made to match.
“It is assumed that the resistivity in some chiral materials remains constant or even decreases as the chiral material becomes smaller. That is why we are working on using electronic chirality to develop materials for a new generation of microchips that are faster, more energy-efficient and more robust than today’s technologies,” says Professor Niels Schröter from the Institute of Physics at MLU. Until now, however, it has been difficult to produce thin layers of these materials without the left-and right-handed areas canceling each other out in their effects.
This is precisely where the new study, in which the Max Planck Institute for Microstructure Physics in Halle was also involved, comes in. “For the first time, we have found materials that are not yet chiral themselves. However, they have the potential to be converted into electronically chiral materials with only a single-handedness through targeted distortion. These achiral materials can serve as so-called parent materials for engineering chiral conductors with reduced resistivity,” explains Schröter.