What if it could solve all of our energy problems?


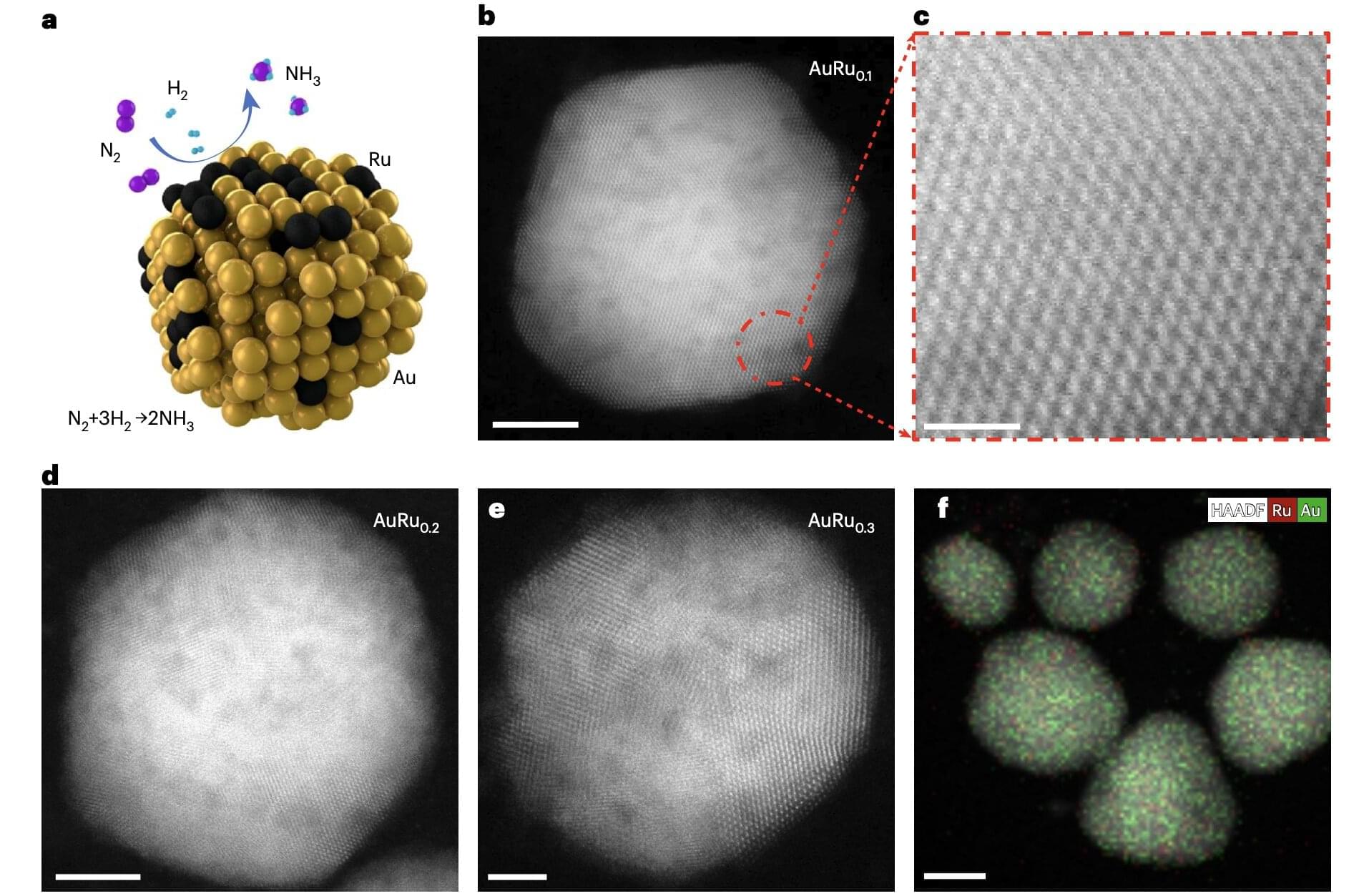
Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless chemical compound comprised of nitrogen and hydrogen that is widely used in agriculture and in industrial settings. Among other things, it is used to produce fertilizers, as well as cleaning products and explosives.
Currently, ammonia is primarily produced via the so-called Haber-Bosch process, an industrial technique that entails prompting a reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen at very high temperatures and pressure. Despite its widespread use, this process is known to be highly energy-intensive and is estimated to be responsible for approximately 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Researchers at Stanford University School of Engineering, Boston College and other institutes have identified new promising catalysts (i.e., materials that speed up chemical reactions) that could enable the sunlight-driven synthesis of ammonia at room temperature and under normal atmospheric pressure.
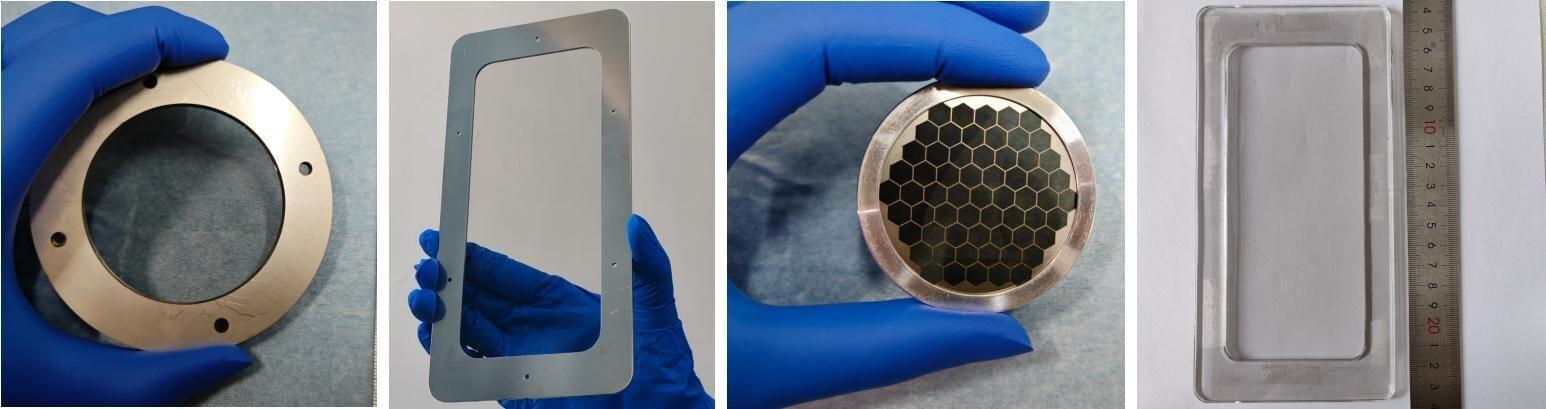
Flexible perovskite solar modules (f-PSMs) are a key innovation in current renewable energy technology, offering a pathway toward sustainable and efficient energy solutions. However, ensuring long-term operational stability without compromising efficiency or increasing material costs remains a critical challenge.
In a study published in Joule, a joint research team from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Zhengzhou University has achieved power conversion efficiency (PCE) surpassing 20% in flexible modules capable of withstanding a range of external stresses. The study highlights the use of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as window electrodes for scalable f-PSMs.
SWCNT films exhibit excellent hydrophobicity, resisting moisture-induced degradation while enhancing device stability. Their flexibility and affordability further position SWCNT-based electrodes as a practical option for sustainable energy systems, providing an ideal opportunity for buildings and infrastructure to incorporate their own power sources in support of a net-zero carbon emissions future.

A research team from NIMS, Tohoku University and AIST has developed a new technique for controlling the nanostructures and magnetic domain structures of iron-based soft amorphous ribbons, achieving more than a 50% reduction in core loss compared with the initial amorphous material.
The developed material exhibits particularly high performance in the high-frequency range of several tens of kilohertz—required for next-generation, high-frequency transformers and EV drive power supply circuits. This breakthrough is expected to contribute to the advancement of these technologies, development of more energy-efficient electric machines and progress toward carbon neutrality.
The research is published in Nature Communications.
Year 2018 face_with_colon_three resharing face_with_colon_three
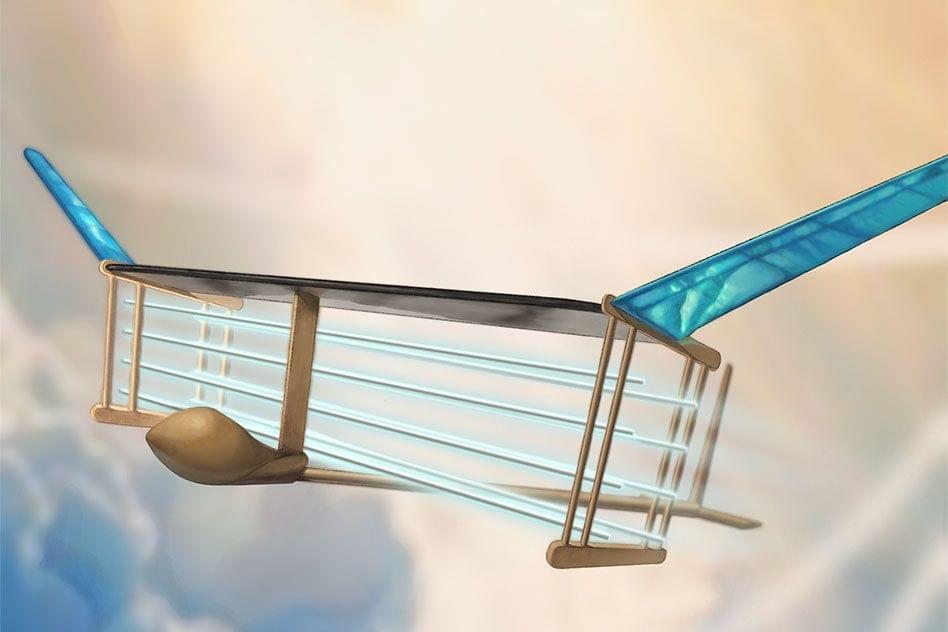
Since the first airplane took flight over 100 years ago, virtually every aircraft in the sky has flown with the help of moving parts such as propellers, turbine blades, or fans that produce a persistent, whining buzz.
Now MIT engineers have built and flown the first-ever plane with no moving parts. Instead of propellers or turbines, the light aircraft is powered by an “ionic wind” — a silent but mighty flow of ions that is produced aboard the plane, and that generates enough thrust to propel the plane over a sustained, steady flight.
Unlike turbine-powered planes, the aircraft does not depend on fossil fuels to fly. And unlike propeller-driven drones, the new design is completely silent.
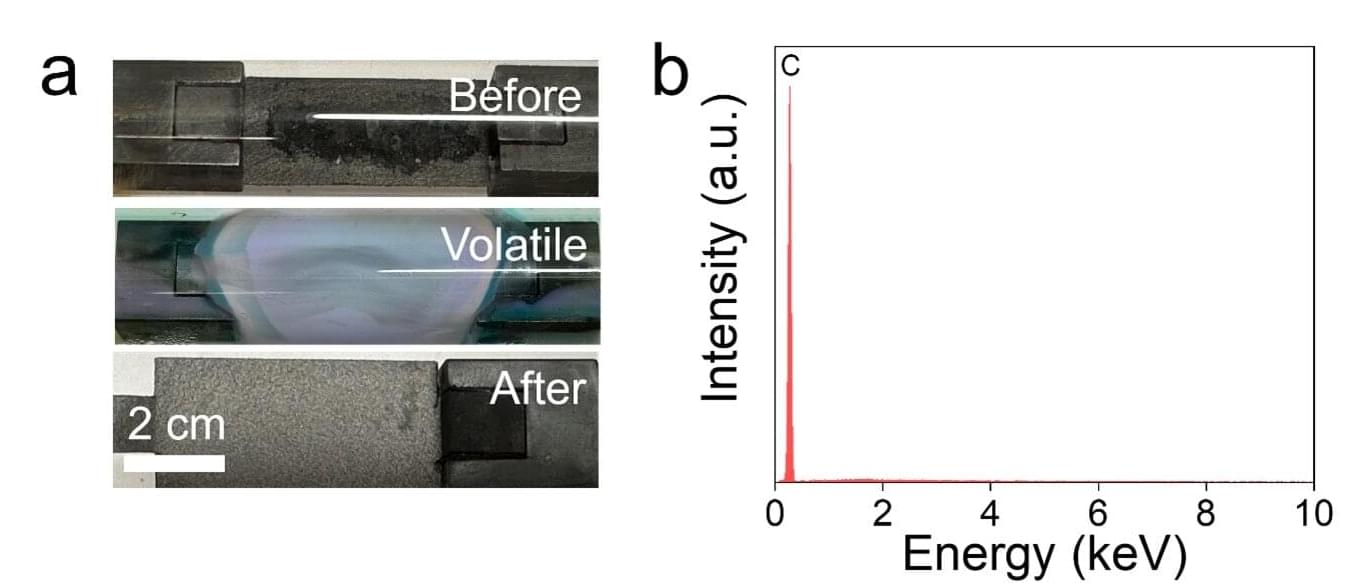
A research team at Rice University led by James Tour has developed a two-step flash Joule heating-chlorination and oxidation (FJH-ClO) process that rapidly separates lithium and transition metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. The method provides an acid-free, energy-saving alternative to conventional recycling techniques, a breakthrough that aligns with the surging global demand for batteries used in electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Published in Advanced Materials, this research could transform the recovery of critical battery materials. Traditional recycling methods are often energy intensive, generate wastewater and frequently require harsh chemicals. In contrast, the FJH-ClO process achieves high yields and purity of lithium, cobalt and graphite while reducing energy consumption, chemical usage and costs.
“We designed the FJH-ClO process to challenge the notion that battery recycling must rely on acid leaching,” said Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor of Chemistry and professor of materials science and nanoengineering. “FJH-ClO is a fast, precise way to extract valuable materials without damaging them or harming the environment.”
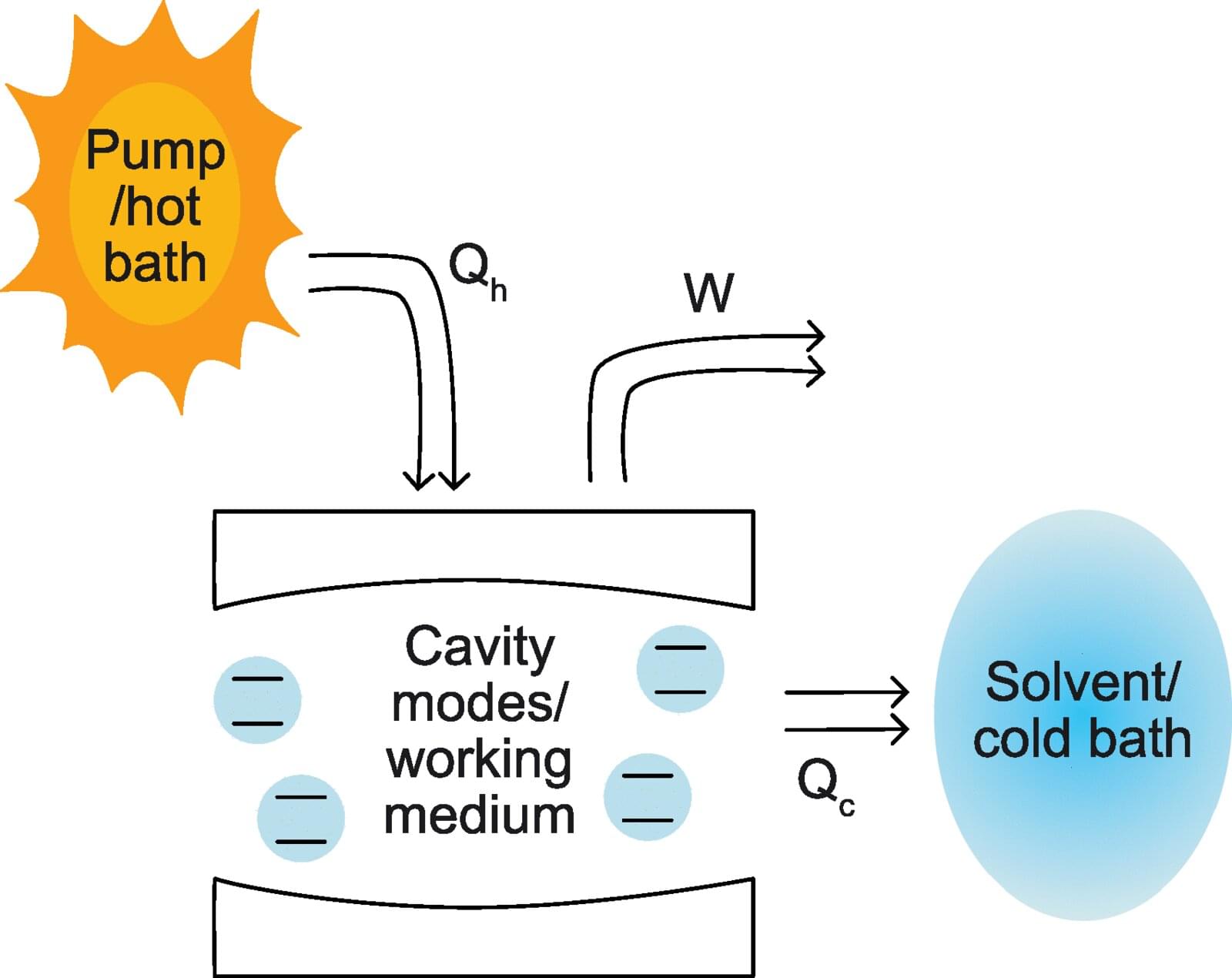
Physicists from Trinity College Dublin believe new insights into the behavior of light may offer a new means of solving one of science’s oldest challenges—how to turn heat into useful energy.
Their theoretical leap forwards, which will now be tested in the lab, could influence the development of specialized devices that would ultimately increase the amount of energy we can capture from sunlight (and lamps and LEDs) and then repurpose to perform useful tasks.
The work has just been published in the journal, Physical Review A.
Due to our ever-increasing reliance on electronics, researchers are always on the lookout for battery materials with more desirable qualities. Common battery materials, like lithium, can be prone to disadvantages like overheating and material sourcing issues, leading to safety risks and higher costs.
Now, researchers from China have revealed a new battery design that may offer a better alternative to lithium. The new study, published in Nature, describes a sodium and sulfur-based, anode-free design offering a high voltage. The sodium–sulfur (Na–S) batteries are a promising alternative to lithium-based batteries due to sodium’s abundance and potential for high energy storage.

Researchers at Princeton and North Carolina State University have developed a technique that substantially improves the ability to convert low-energy light into a high-energy version. The method has immediate applications in lighting and displays.
Their study appears in the journal Nature Photonics.

“When we see a region on the sun with an extremely complex magnetic field, we can assume that there is a large amount of energy there that will have to be released as solar storms,” said Dr. Louise Harra.
How can astronomers observe and study the Sun’s activity in the most efficient way despite the Sun and Earth orbiting each other at different speeds? This is what a recent study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated new methods for studying the Sun with the goal of better understanding its activity and how it influences Earth.
For the study, the researchers collected data from the Sun using NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory spacecraft and the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter, which orbits the Sun once every six months and is fixed on the nearside of the Sun towards Earth, respectively. The goal of the study was to observe the solar active region called NOAA 13,664, which is one of the most misunderstood and active regions observed over the last 20 years.
During the 94-day study period, lasting from April to June 2024, the researchers successfully observed a full cycle of activity from NOAA 13,664, including an initial 20-day buildup of energy, peaking approximately one month after initiation, followed by a wind-down period lasting approximately two months. These results could help scientists better understand the magnetic field activity of the Sun and predict future solar activity.