With these high profile missions to the moon and Mars, sci-fi is set to become a Bollywood staple. “The Indian audience, especially the youth segment, now constantly seeks newer themes and stories,” says Vikram Malhotra, CEO of Abundantia Entertainment, one of India’s biggest production companies. “There has been so much talk and discussion about India’s space programmes and the achievements of our scientists that even the common man now wants to know more about this fascinating world. And on the big screen.”
In 2014, India sent the Mars Orbiter Mission into space, and became the first country to send a satellite to orbit the planet at its first attempt – putting its much richer regional rival China in the shade as it became the first Asian nation to get to the red planet. The project was notable for being led by a team of female scientists; as is India’s second lunar probe, Chandrayaan-2 (from the Sanskrit for “moon craft”), which was launched last month and is due to land on the moon in early September. And as the country establishes itself as a space power, Indians have developed an appetite for sci-fi themes in its cinema.
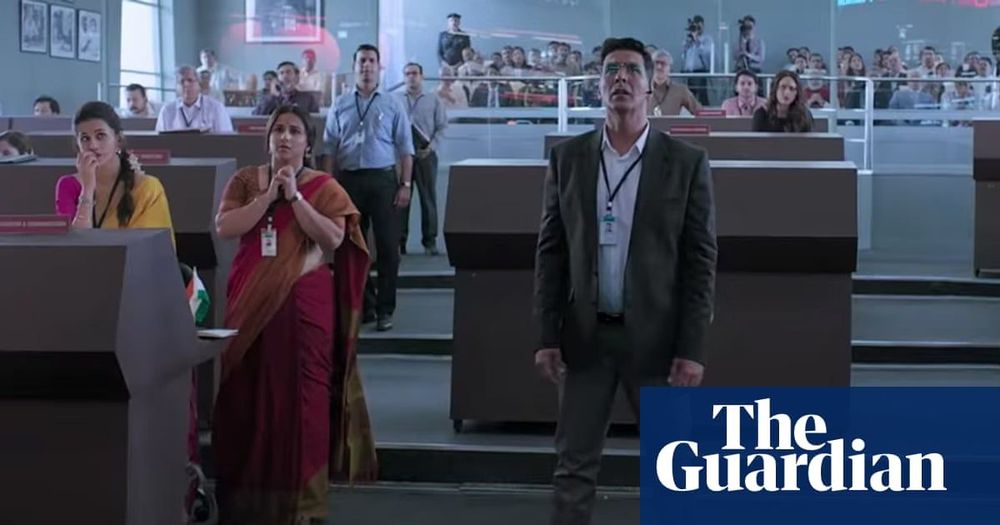
The patriotic outburst that followed the Mars mission has fuelled the latest example of Indian space cinema: Mission Mangal (Sanskrit for Mars), a fictionalised account of the Orbiter Mission. Starring and produced by Bollywood actor Akshay Kumar, it is due for release on 15 August, India’s Independence Day. “I would follow the news about India’s space missions and feel proud of what we were achieving,” says Kumar. “But through Mission Mangal I guess you could say I have an insider’s perspective.”
Kumar, one of the highest paid actors in the world, says he had long wanted to work with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Starring in a film about Mangalyaan (“Mars craft”) required him to take a crash course in astrophysics. “I now understand the amount of effort and planning it takes to successfully execute a space mission and my respect for all the scientists and engineers who work on these missions has grown immensely,” says Kumar.