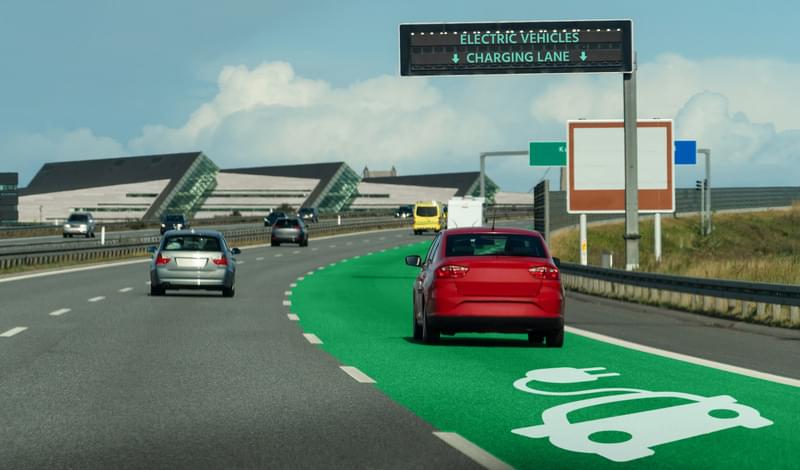
Michigan will become the first state in America to deploy inductive vehicle charging technology in roads, in an effort to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs).
Governor of Michigan, Gretchen Whitmer, made the announcement during the opening ceremony of the Motor Bella auto show on Tuesday. The Inductive Vehicle Charging Pilot is a partnership between Michigan’s Department of Transportation (MDOT) and the Office of Future Mobility and Electrification (OFME). It will deploy an electrified roadway system allowing electric cars, buses, shuttles and other vehicles to charge while driving, allowing them to operate continuously without stopping to charge. This will address range anxiety, while turning public roads into safe, sustainable, shared energy platforms.
“Michigan was home to the first mile of paved road, and now we’re paving the way for the roads of tomorrow with innovative infrastructure that will support the economy and the environment, helping us achieve our goal of carbon neutrality by 2050,” said Governor Whitmer. “This project reinforces my commitment to accelerating the deployment of electric vehicle infrastructure in Michigan and will create new opportunities for businesses and high-tech jobs amidst the transition to electric vehicles.”