O,.o Could be used to control light in electronics.


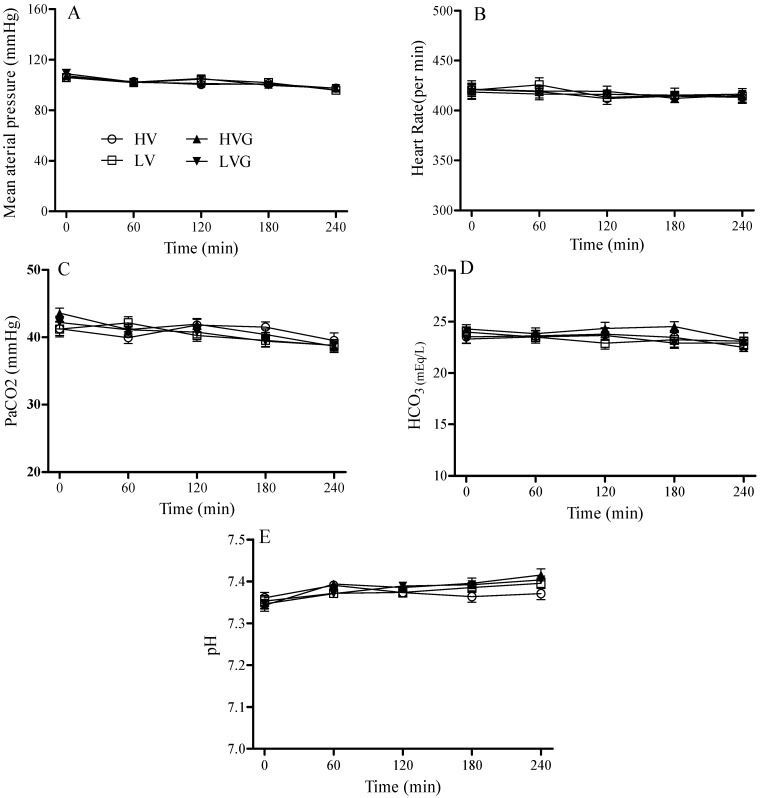
Inadequate ventilator settings may cause overwhelming inflammatory responses associated with ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Here, we examined potential benefits of glutamine (GLN) on a two-hit model for VILI after acid aspiration-induced lung injury in rats. Rats were intratracheally challenged with hydrochloric acid as a first hit to induce lung inflammation, then randomly received intravenous GLN or lactated Ringer’s solution (vehicle control) thirty min before different ventilator strategies. Rats were then randomized to receive mechanical ventilation as a second hit with a high tidal volume (TV) of 15 mL/kg and zero positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) or a low TV of 6 mL/kg with PEEP of 5 cm H2O. We evaluated lung oxygenation, inflammation, mechanics, and histology. After ventilator use for 4 h, high TV resulted in greater lung injury physiologic and biologic indices. Compared with vehicle treated rats, GLN administration attenuated lung injury, with improved oxygenation and static compliance, and decreased respiratory elastance, lung edema, extended lung destruction (lung injury scores and lung histology), neutrophil recruitment in the lung, and cytokine production. Thus, GLN administration improved the physiologic and biologic profiles of this experimental model of VILI based on the two-hit theory.
Keywords: acid aspiration, ARDS, glutamine, ventilator-induced lung injury.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a catastrophic syndrome among critically ill patients. One of its major causes is acid aspiration as an initial pneumonitis that may be complicated by subsequent bacterial pneumonia after inhaling low pH gastric fluid [1, 2, 3, 4]. Gastric fluid aspiration frequently occurs in trauma or critical patients with head trauma, alcohol or cerebrovascular accidents, and is also a complication of general anesthesia that occurs in 1 in 2000–3000 cases when anesthetics are used [3, 4].

An international team of scientists led by the University of the Witwatersrand in South Africa, has been able to reconstruct, in the smallest details, the skulls of some of the world’s oldest known dinosaur embryos in 3D, using powerful and non-destructive synchrotron techniques at the ESRF, the European Synchrotron in France. They found that the skulls develop in the same order as those of today’s crocodiles, chickens, turtles and lizards. The findings are published today in Scientific Reports.
University of the Witwatersrand scientists publish 3D reconstructions of the ~2cm-long skulls of some of the world’s oldest dinosaur embryos in an article in Scientific Reports. The embryos, found in 1976 in Golden Gate Highlands National Park (Free State Province, South Africa) belong to South Africa’s iconic dinosaur Massospondylus carinatus, a 5-meter long herbivore that nested in the Free State region 200 million years ago.
The scientific usefulness of the embryos was previously limited by their extremely fragile nature and tiny size. In 2015, scientists Kimi Chapelle and Jonah Choiniere, from the University of Witwatersrand, brought them to the European Synchrotron (ESRF) in Grenoble, France for scanning. At the ESRF, an 844 metre-ring of electrons travelling at the speed of light emits high-powered X-ray beams that can be used to non-destructively scan matter, including fossils. The embryos were scanned at an unprecedented level of detail — at the resolution of an individual bone cell. With these data in hand, and after nearly 3 years of data processing at Wits’ laboratory, the team was able to reconstruct a 3D model of the baby dinosaur skull. “No lab CT scanner in the world can generate these kinds of data,” said Vincent Fernandez, one of the co-authors and scientist at the Natural History Museum in London (UK).
This is a good one pass it on
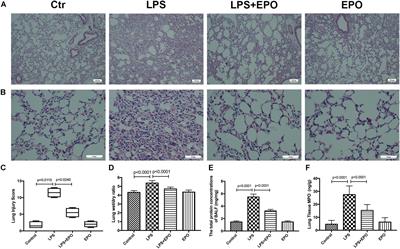
This study aimed to explore whether the therapeutic effects of EPO rely on the suppression of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the specific mechanisms in an LPS-induced ALI mouse model. ALI was induced in C57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of LPS (15 mg/kg). EPO was administered intraperitoneally at 5 U/g after LPS challenge. The mice were sacrificed 8 h later. Our findings indicated that application of EPO markedly diminished LPS-induced lung injury by restoring histopathological changes, lessened lung wet/dry (W/D) ratio, protein concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels. Meanwhile, EPO evidently decreased interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) secretion, the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome components including pro-IL-1β, NLRP3, and cleaved caspase-1 as well as phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65, which may be associated with activation of EPO receptor (EPOR), phosphorylation of Janus-tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)
Taken together, this study indicates that EPO can effectively attenuate LPS-induced lung injury in mice by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is dependent upon activation of EPOR/JAK2/STAT3 signaling and inhibition of the NF-κB pathway.
Acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are common and devastating clinical disorders with high mortality and no specific therapy. An excessive inflammatory response results in the progression of ALI/ARDS, and the NLRP3 inflammasome is a key participant in inflammation. Erythropoietin (EPO), which is clinically used for anemia, reportedly exerts pleiotropic effects in ALI. However, whether EPO could protect against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI by regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome and its underlying mechanisms remain poorly elucidated. This study aimed to explore whether the therapeutic effects of EPO rely on the suppression of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the specific mechanisms in an LPS-induced ALI mouse model. ALI was induced in C57BL/6 mice by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of LPS (15 mg/kg). EPO was administered intraperitoneally at 5 U/g after LPS challenge. The mice were sacrificed 8 h later. Our findings indicated that application of EPO markedly diminished LPS-induced lung injury by restoring histopathological changes, lessened lung wet/dry (W/D) ratio, protein concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels. Meanwhile, EPO evidently decreased interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) secretion, the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome components including pro-IL-1β, NLRP3, and cleaved caspase-1 as well as phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65, which may be associated with activation of EPO receptor (EPOR), phosphorylation of Janus-tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). However, all the beneficial effects of EPO on ALI and modulation NLRP3 inflammasome were remarkably abrogated by the inhibition of EPOR/JAK2/STAT3 pathway and knockout (KO) of NLRP3 gene. Taken together, this study indicates that EPO can effectively attenuate LPS-induced lung injury in mice by suppressing the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is dependent upon activation of EPOR/JAK2/STAT3 signaling and inhibition of the NF-κB pathway.
Acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are common life-threatening critical illnesses with substantial morbidity and mortality (ARDS Definition Task Force et al., 2012; Rezoagli et al., 2017). Despite an improved understanding of the pathophysiology of these illnesses, there are still no effective pharmacologic therapies to treat patients with ALI/ARDS, and the hospital mortality is still as high as 46.1% (ARDS Definition Task Force et al., 2012). ALI/ARDS is characterized by exaggerated lung parenchyma inflammation, which leads to massive infiltration of activated neutrophils, progressive alveolar filling, and intractable hypoxemia (Giacomo Bellani et al., 2016). Hence, preventing exuberant inflammatory responses is suggested to be a potential strategy for the prevention and treatment of ALI.
The NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a multiprotein complex consisting of the sensor protein NLRP3, the adaptor protein ASC, and the effector protein caspase-1 (Lamkanfi and Dixit, 2014). NLRP3 is a cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor (PRR) that can be activated by some pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), such as bacteria, viruses, and ATP (Swanson et al., 2019). Activation of NLRP3 leads to assembly of the adapter ASC, resulting in the autoactivation and cleavage of pro-caspase-1 into an enzymatically mature caspase-1, which further cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into mature IL-1β and IL-18, respectively (Jo et al., 2016).
If you have not seen these useless boxes, this one is the best so far! • Credit: @worldofartists • Via fxhm (youtube)… #engineer #funny #artistic #makingfactory #designer #invention #makersgonnamake #sandiego #electronics
Samsung Electronics today announced it will be introducing the first DRAM memory modules in the industry designed with cutting-edge Extreme Ultraviolet Technology (EUV).
One of the world’s leading memory manufacturers, Samsung says that response to a million evaluation units of its first line of 10nm-class DDR4 DRAM modules has been positive and that it will soon begin processing orders for worldwide distribution.
EUV technology allows memory modules to be manufactured more accurately and more quickly. It speeds up the lithography process by reducing the number of repetitive steps and facilitates the production of complex chip patterns. It means greater performance accuracy and a shortened development time.

Apple’s latest iPad — the iPad Pro — is its most-powerful and comes with several first-time features. This is the first iPad with a a dual-camera, a trackpad, a Magic keyboard and LiDAR scanner. It is the most-powerful iPad Apple has made and is set to give tough competition to a lot of Windows-powered laptops. Here are 15 things you should know about the new iPad Pro:
This could used to emp laser missiles or other targets.
The electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) generated during the interaction of a focused 1.315-μm sub-nanosecond laser pulse with a solid hydrogen ribbon were measured. The strength and temporal characteristics of EMPs were found to be dependent on the target density. If a low density target is ionized during the interaction with the laser, and the plasma does not physically touch the target holder, the EMP is weaker in strength and shorter in time duration. It is shown that during the H2 target experiment, the EMP does not strongly affect the response of fast electronic devices. The measurements of the EMP were carried out by Rohde&Schwarz B-Probes, particularly sensitive in the frequency range from 30 MHz and 1 GHz. Numerical simulations of resonant frequencies of the target chamber used in the experiment at the Prague Asterix Laser System kJ-class laser facility elucidate the peaked structure of EMP frequency spectra in the GHz domain.
Check your blood glucose without fingersticks using the FreeStyle Libre System, a continuous glucose monitoring system that includes a sensor and reader.