By fundamentally severing human labor and income, society can reach fourth gear capitalism, where all members of the economy will benefit.



Machines that can think, learn and adapt are coming — and that could mean that we humans will end up with significant unemployment. What should we do about it? In a straightforward talk about a controversial idea, futurist Martin Ford makes the case for separating income from traditional work and instituting a universal basic income.
About the speaker.
Robert C. W. Ettinger’s seminal work, The Prospect Of Immortality, detailed many of the scientific, moral, and economic implications of cryogenically freezing humans for later reanimation. It was after that book was published in 1962 that the idea of freezing one’s body after death began to take hold.
One of the most pressing questions is, even if we’re able to revive a person who has been cryogenically preserved, will the person’s memories and personality remain intact? Ettinger posits that long-term memory is stored in the brain as a long-lasting structural modification. Basically, those memories will remain, even if the brain’s “power is turned off”.
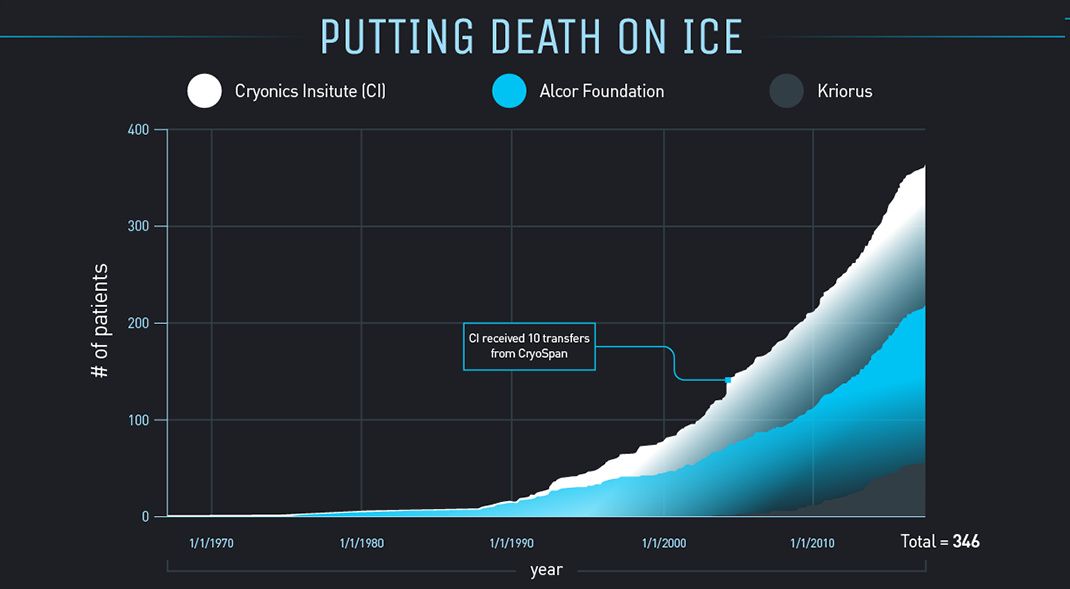
This infographic delves into the mechanics and feasibility of cryonics – a process that thousands of people are betting will give them a second shot at life.
How many individuals own at least 1 BTC?
I was asked this question today at Quora, a popular Q&A blog covering a variety of technical and economic disciplines. Under my alias “Ellery”, I am the most viewed author on Bitcoin and the blockchain.
While this question may sound like a good factoid for a trivia game, it is directly related to something with with far reaching impact on your pocketbook and your future. It goes to the heart of a debate between warring factions: In the 2nd half of this answer, I address the eternal question:
Is Bitcoin a pyramid scheme? Or are we still early on the adoption curve?
But let’s start with the question at hand…
There is no certain answer to the number of people who own Bitcoin or how many own more than 1 BTC. We know that tens of millions of wallets have been created, but this certainly doesn’t help. Although the value of every single wallet is publicly disclosed on the blockchain (most have a zero balance), there is no way to determine who owns each wallet. Some may be controlled by organizations or custodians on behalf of many individuals, while others may be just one of many wallets with a single owner.
Most of my Bitcoin is in a wallet or a vault hosted by Coinbase, the San Francisco exchange. When I log into my account to view my wallet ID, I see that I have dozens of wallets—all valid. The large number of wallets is not related to my wealth. Rather, it a byproduct of my many small transactions. Coinbase creates a new wallet each time that I buy, sell, or purchase something with my BTC. There are good reasons for this practice, but it certainly muddies the correlation between wallets and number of owners.
There are 16.6 million coins in circulation today (a bit less, since some have been irretrievably lost). That puts a cap answering the question. There cannot be more than this many people with a full BTC—currently worth about USD $5900.
But, we know that the number of individuals with a full coin is considerably less. After all, many people in my own circles own dozens of coins, and Satoshi is very likely to hold 1 million BTC. Coinbase and Bitstamp are just two of very many custodial exchanges (i.e. they offer a cloud wallet or vault service to their clients). They host many hundreds of wallets with more than 50 coins. In almost each case, the client has provided single-user taxpayer information to these services, and so it is very unlikely that a significant fraction of these wallets belong to more than a single person or family.
And, let’s not forget that a far greater fraction of exchanges fly under the covers. That is, they don’t collect taxpayer information or report the wallets that they administer to any authority—nor to analysts or journalists like me.
So, while no one can accurately estimate the number of individuals who own 1 or more BTC, the answer is very likely under 2.5 million, worldwide. 1
The number of people who have heard of Bitcoin is growing rapidly. In the United States, fewer than one in twenty people were aware of Bitcoin just 2½ years ago (at the beginning of 2015). By September 2017, almost one in four USA adults a reasonable idea what it is—and most of them could debate their position on its future. 2
There will never be more than 21 million bitcoin. This is the mathematical upper limit. Compare this with the current US population of 323 million. So even if all Bitcoin owners were in America (they are not!) and if no one owned more than 1 BTC, fewer than 1 in 19 Americans could own a full Bitcoin today and fewer than 1 in 15 after all bitcoin are mined.
If we consider the global population of 7.6 billion, fewer than 1 in 458 people could own a full Bitcoin today. Since most early adopters have more than 1 BTC, the actual fraction is probably much smaller than 1 in 25,000 individuals.
In the introduction, above, I said that the question about how many people own more than 1 BTC leads to a more profound question. In fact, this innocent trivia question, leads to insight about adoption and the economics of investing in a deflationary instrument as it spreads throughout commerce, investors and all sorts of institutions.
Moral of the story…
The original question asks for a simple number. It doesn’t ask for editorial perspective. But it’s tough to resist. With fewer than 1 in 25 thousand people owning a bitcoin, a reasonable question is:
Will adoption increase, even if interest is limited to only one sector?
For example, what if Bitcoin falters in all but one of these venues: Bleeding edge geeks, collectors, investors, p2p payments, interbank transfer, debt settlement, or treatment in some regions as a currency.
Answer: Even if Bitcoin continues to show strength in just one of these areas, it will eventually be used or accumulated by millions of new users—even if they don’t realize it!
Do you see where I am going with this? Even if you believe that Bitcoin will…
Even if you believe in all of these limiting factors, the overall demand for Bitcoin has barely begun. We have not even started climbing the hockey-stick curve toward limited adoption as an occasional, alternative payment mechanism.
At conferences and in my own classroom, I am often asked: Should I still acquire Bitcoin? —Or is it too late? After all, it has risen from a fraction of a penny to $6,000 in just a 7 years. And from under $1000 to $6,000 this year alone!
I am not a financial advisor. I often speculate, but never offer guidance. I embrace the wisdom that past performance is never an assurance of future gains. But, I ask students to look at the assumptions and at the math: Unlike US dollars, shares in Apple, pork bellies or gold pressed latinum, Bitcoin is firmly capped. There will never be more than a paltry 21 million coins. That means that each coin absolutely, positively must increase in value with even a modest adoption scenario.
The Argument Against Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a pure supply-demand commodity. Since the supply is fixed and well understood, the only argument against acquiring Bitcoin arises from a belief that demand will dwindle. This is the argument of someone who believes that Bitcoin will fail to gain any further traction in any sector.
Perhaps you believe that something else will displace it, or that governments will find a way to effectively defeat it. If you have been reading my Blog (or my Quora answers) for more than a few months, then you already know that neither scenario is realistic.
I believe that investment in Bitcoin a speculative asset retards adoption. I defend this opinion in many interviews and articles. Although I hope for fewer speculators and more ‘legitimate’ users, I own an outsize share of the world’s future value store, transfer media and fungible, liquid asset. I am guilty of the speculation that I seek to deter.
1 & 2 CRYPSA Research, Feb 2015 and Oct 2017, Cryptocurrency Standards Association. Polls conducted at Rein’s New York Deli in Vernon CT and Spectrum Center, Irvine CA.
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, publishes Wild Duck and hosts the New York Bitcoin Event. He is on the New Money Systems board and kicks off Cryptocurrency Expo in Dubai. He frequently consults and presents.

That the surge in philanthropy is a natural consequence of the rapid wealth creation was a sentiment echoed by a number of the high-net-worth individuals speaking at the conference, including Ronnie Chan and John Long, founder and CEO of investment company Highridge Partners. China is now home to 609 billionaires, more than the 552 in the US.
Chinese entrepreneurs in China itself, Hong Kong and America are giving back to society in ways unheard of even a few years ago, with Ronnie and Gerald Chan and Li Ka-shing among the big donors.
PUBLISHED : Sunday, 08 October, 2017, 6:45pm.
UPDATED : Sunday, 08 October, 2017, 6:46pm.

Centauri Dreams returns with an essay by long-time contributor Alex Tolley. If we need to grow a much bigger economy to make starships possible one day, the best way to proceed should be through building an infrastructure starting in the inner Solar System and working outward. Alex digs into the issues here, starting with earlier conceptions of how it might be done, and the present understanding that artificial intelligence is moving at such a clip that it will affect all of our ventures as we transform into a truly space-faring species. Under the microscope here is a company called SpaceFab, as Alex explains below, and the potential of ISRU — in situ resource utilization. Emerging out of all this is a new model for expansion.
by Alex Tolley

The inclusion of technology in the leader’s most important address in an official imprimatur that underscores the continued push by China’s top leaders to identify new pillars for an economy struggling to maintain its rapid growth amid overcapacity and rising debt.
China’s State Council laid out goals in July to build a domestic artificial intelligence industry worth nearly US$150 billion in the next few years, and to make the country a “innovation centre for AI” by 2030. Xi’s speech gave the official imprimatur to the plan.
PUBLISHED : Wednesday, 18 October, 2017, 6:56pm.
UPDATED : Wednesday, 18 October, 2017, 11:42pm.

Every modern economy wants its own version of Silicon Valley and in Japan the urge to find or create one is just as strong. Although the country’s pedigree as an innovator is not in doubt, rapidly adapting to the digital age has proven challenging for its once-mighty consumer electronics companies.
Fukuoka, Kyoto and Tokyo’s Shibuya district are all staking their claim.

Sending satellites into space is going to continue to get cheaper since SpaceX proved it could reliably launch refurbished rockets. This is going to open up space exploration to more entities allowing for the continued democratization of space. Other technological advances could make a global space centered sharing economy a real possibility.
The rise of the internet and the ubiquity of mobile computing devices have changed everything from travel and shopping to politics – think Uber, Amazon, and Twitter.

China may have the clear lead in the development of artificial intelligence (AI) systems in the region, but Japan’s government, realising how vital the sector is to its economic future, has intervened in the hopes of levelling the playing field.
Japan announced in late August that it is planning to invest billions of yen to fund next-generation semiconductors and other technologies critical to AI development.
Billions of yen in public investment could help firms innovate, but analysts say the nation may never catch up with China and the US, global tech leaders that show no signs of slowing down.
By Julian Ryall
0 Share