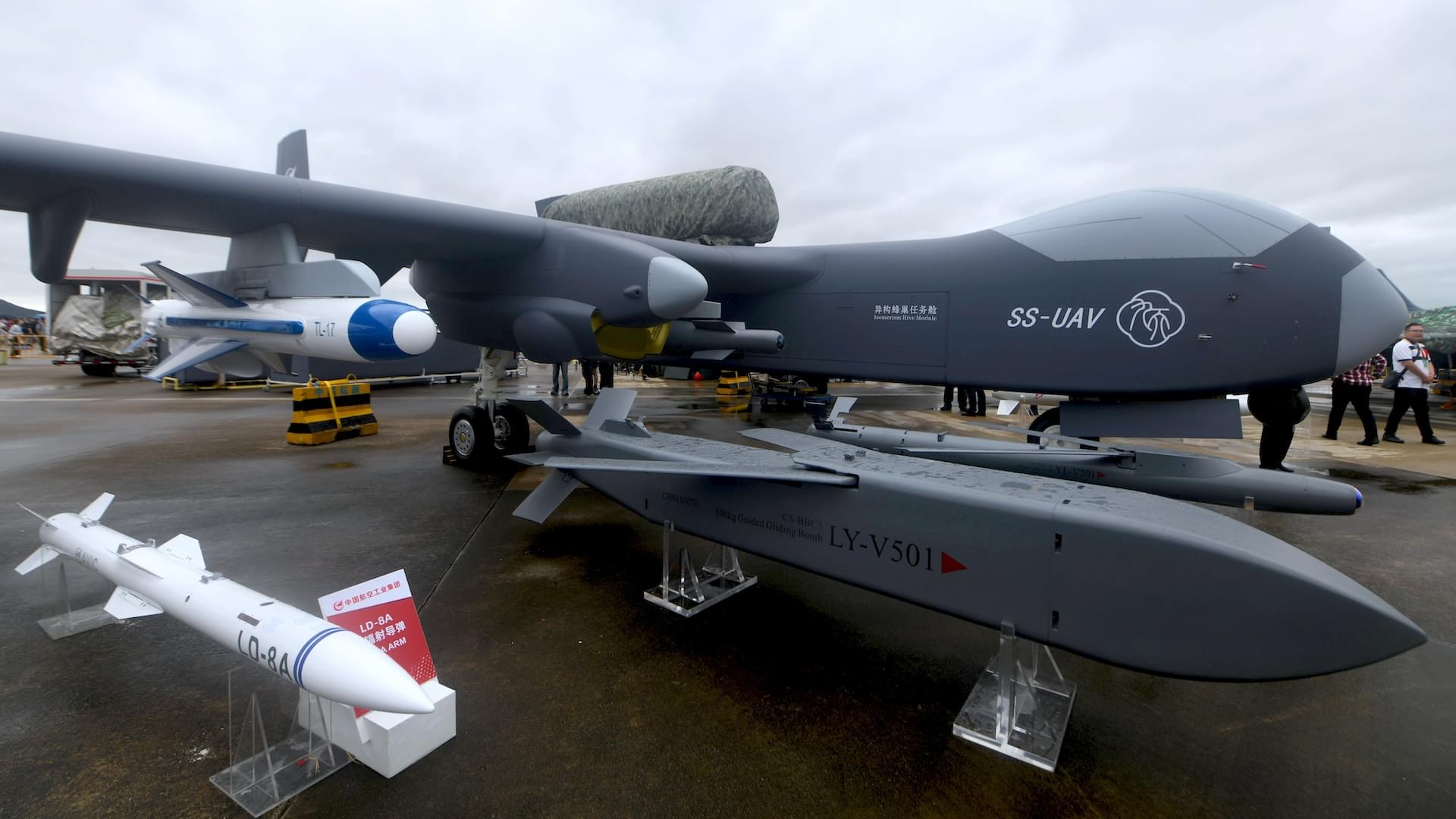
The world’s largest drone “mothership” is getting ready for deployment in June. It’s designed to carry and launch up to 100 drones in a swarm, including kamikaze drones.


Non contact weapon, invisible weapon, AI drone, microwave weapon, directed energy, sonic weapon, silent killer, future weapon, brain weapon, stealth tech, AI assassin, energy weapon, pulse weapon, death beam, ghost weapon, neural weapon, drone strike, mind control, lethal tech, smart weapon, AI war, kill tech, stealth drone, sound weapon, laser weapon, radiation gun, brain hack, AI killer, invisible attack, silent war, tech kill, energy beam, microwave attack, sonic attack, AI warfare, death tech, stealth kill, neural tech, drone war, mind weapon, pulse attack, ghost tech, AI death, silent strike, future kill, stealth attack, AI strike, energy kill, brain attack, tech assassin, invisible strike, AI hunter, silent beam, lethal drone, stealth beam, mind beam, death drone, AI sniper, ghost drone, pulse beam, neural beam, stealth sniper, AI pulse, silent sniper, energy sniper, brain sniper, tech sniper, invisible sniper, AI weapon, stealth weapon, mind sniper, pulse sniper, ghost sniper, AI beam, silent weapon, future sniper, stealth hunter, AI hunter drone, energy hunter, brain hunter, tech hunter, invisible hunter, AI assassin drone, silent hunter, lethal hunter, stealth assassin, mind assassin, pulse assassin, ghost assassin, AI killer drone, silent assassin, energy assassin, brain assassin, tech assassin, invisible assassin, AI death drone, stealth killer, mind killer, pulse killer, ghost killer, AI strike drone, silent killer, energy killer, brain killer, tech killer, invisible killer, AI war drone, stealth war, mind war, pulse war, ghost war, AI battle drone, silent war, energy war, brain war, tech war, invisible war, AI combat drone, stealth combat, mind combat, pulse combat, ghost combat, AI attack drone, silent combat, energy combat, brain combat, tech combat, invisible combat, AI defense drone, stealth defense, mind defense, pulse defense, ghost defense, AI security drone, silent defense, energy defense, brain defense, tech defense, invisible defense, AI surveillance drone, stealth surveillance, mind surveillance, pulse surveillance, ghost surveillance, AI recon drone, silent surveillance, energy surveillance, brain surveillance, tech surveillance, invisible surveillance, AI spy drone, stealth spy, mind spy, pulse spy, ghost spy, AI stealth drone, silent spy, energy spy, brain spy, tech spy, invisible spy, AI cloaked drone, stealth cloak, mind cloak, pulse cloak, ghost cloak, AI hidden drone, silent cloak, energy cloak, brain cloak, tech cloak, invisible cloak, AI secret drone, stealth secret, mind secret, pulse secret, ghost secret, AI covert drone, silent secret, energy secret, brain secret, tech secret, invisible secret, AI classified drone, stealth classified, mind classified, pulse classified, ghost classified, AI black ops drone, silent classified, energy classified, brain classified, tech classified, invisible classified, AI special ops drone, stealth ops, mind ops, pulse ops, ghost ops, AI tactical drone, silent ops, energy ops, brain ops, tech ops, invisible ops, AI strategic drone, stealth strategy, mind strategy, pulse strategy, ghost strategy, AI mission drone, silent strategy, energy strategy, brain strategy, tech strategy, invisible strategy, AI operation drone, stealth operation, mind operation, pulse operation, ghost operation, AI execution drone, silent operation, energy operation, brain operation, tech operation, invisible operation, AI termination drone, stealth termination, mind termination, pulse termination, ghost termination, AI elimination drone, silent termination, energy termination, brain termination, tech termination, invisible termination, AI neutralization drone, stealth neutralization, mind neutralization, pulse neutralization, ghost neutralization, AI suppression drone, silent neutralization, energy neutralization, brain neutralization, tech neutralization, invisible neutralization, AI control drone, stealth control, mind control, pulse control, energy control, brain control, tech control, invisible control, AI manipulation drone, AI persuasion drone, stealth persuasion, mind persuasion, pulse persuasion, ghost persuasion, AI coercion drone, silent persuasion, energy persuasion, brain persuasion, tech persuasion, invisible persuasion, AI intimidation drone, stealth intimidation, mind intimidation, pulse intimidation, ghost intimidation, AI threat drone, silent intimidation, energy intimidation, brain intimidation, tech intimidation, invisible intimidation, AI fear drone, stealth fear, mind fear, pulse fear, ghost fear, AI terror drone, silent fear, energy fear, brain fear, tech fear, invisible fear, AI panic drone, stealth panic, mind panic, pulse panic, ghost panic, AI anxiety drone, silent panic, energy panic, brain panic, tech panic, invisible panic, AI stress drone, stealth stress, mind stress, stealth scar, mind scar, pulse scar, ghost scar, AI mark drone, silent scar, energy scar, brain scar, tech scar, invisible scar, AI trace drone, stealth trace, mind trace.
ASILAB is excited to introduce Asinoid – the world’s first true artificial superintelligence built on the architecture of the human brain. Designed to think, learn, and evolve autonomously like a living organism.
Learn more on our website: http://asilab.com.
Asinoid isn’t just another AI. Unlike today’s pre-trained, prompt-driven models and agents, Asinoid is a self-improving and proactive mind. It learns over time. It remembers. It sets its own goals. And it gets smarter by rewiring itself from within.
An Asinoid can power a fleet of autonomous drones. Act as the brain inside your security system. It can drive your R&D, run your meetings, become the cognitive layer behind your SaaS product or even co-found a company with you.
The possibilities are endless. And we want to explore them with you.
We’re opening access to pioneering companies, researchers, and developers who want to build with us. If you’re ready to create something groundbreaking, let’s get started.
AI surveillance, AI surveillance systems, AI surveillance technology, AI camera systems, artificial intelligence privacy, AI tracking systems, AI in public surveillance, smart city surveillance, facial recognition technology, real time surveillance ai, AI crime prediction, predictive policing, emotion detecting ai, AI facial recognition, privacy in AI era, AI and data collection, AI spying tech, surveillance capitalism, government surveillance 2025, AI monitoring tools, AI tracking devices, AI and facial data, facial emotion detection, emotion recognition ai, mass surveillance 2025, AI in smart cities, china AI surveillance, skynet china, AI scanning technology, AI crowd monitoring, AI face scanning, AI emotion scanning, AI powered cameras, smart surveillance system, AI and censorship, privacy and ai, digital surveillance, AI surveillance dangers, AI surveillance ethics, machine learning surveillance, AI powered face id, surveillance tech 2025, AI vs privacy, AI in law enforcement, AI surveillance news, smart city facial recognition, AI and security, AI privacy breach, AI threat to privacy, AI prediction tech, AI identity tracking, AI eyes everywhere, future of surveillance, AI and human rights, smart cities AI control, AI facial databases, AI surveillance control, AI emotion mapping, AI video analytics, AI data surveillance, AI scanning behavior, AI and behavior prediction, invisible surveillance, AI total control, AI police systems, AI surveillance usa, AI surveillance real time, AI security monitoring, AI surveillance 2030, AI tracking systems 2025, AI identity recognition, AI bias in surveillance, AI surveillance market growth, AI spying software, AI privacy threat, AI recognition software, AI profiling tech, AI behavior analysis, AI brain decoding, AI surveillance drones, AI privacy invasion, AI video recognition, facial recognition in cities, AI control future, AI mass monitoring, AI ethics surveillance, AI and global surveillance, AI social monitoring, surveillance without humans, AI data watch, AI neural surveillance, AI surveillance facts, AI surveillance predictions, AI smart cameras, AI surveillance networks, AI law enforcement tech, AI surveillance software 2025, AI global tracking, AI surveillance net, AI and biometric tracking, AI emotion AI detection, AI surveillance and control, real AI surveillance systems, AI surveillance internet, AI identity control, AI ethical concerns, AI powered surveillance 2025, future surveillance systems, AI surveillance in cities, AI surveillance threat, AI surveillance everywhere, AI powered recognition, AI spy systems, AI control cities, AI privacy vs safety, AI powered monitoring, AI machine surveillance, AI surveillance grid, AI digital prisons, AI digital tracking, AI surveillance videos, AI and civilian monitoring, smart surveillance future, AI and civil liberties, AI city wide tracking, AI human scanner, AI tracking with cameras, AI recognition through movement, AI awareness systems, AI cameras everywhere, AI predictive surveillance, AI spy future, AI surveillance documentary, AI urban tracking, AI public tracking, AI silent surveillance, AI surveillance myths, AI surveillance dark side, AI watching you, AI never sleeps, AI surveillance truth, AI surveillance 2025 explained, AI surveillance 2025, future of surveillance technology, smart city surveillance, emotion detecting ai, predictive AI systems, real time facial recognition, AI and privacy concerns, machine learning surveillance, AI in public safety, neural surveillance systems, AI eye tracking, surveillance without consent, AI human behavior tracking, artificial intelligence privacy threat, AI surveillance vs human rights, automated facial ID, AI security systems 2025, AI crime prediction, smart cameras ai, predictive policing technology, urban surveillance systems, AI surveillance ethics, biometric surveillance systems, AI monitoring humans, advanced AI recognition, AI watchlist systems, AI face tagging, AI emotion scanning, deep learning surveillance, AI digital footprint, surveillance capitalism, AI powered spying, next gen surveillance, AI total control, AI social monitoring, AI facial mapping, AI mind reading tech, surveillance future cities, hidden surveillance networks, AI personal data harvesting, AI truth detection, AI voice recognition monitoring, digital surveillance reality, AI spy software, AI surveillance grid, AI CCTV analysis, smart surveillance networks, AI identity tracking, AI security prediction, mass data collection ai, AI video analytics, AI security evolution, artificial intelligence surveillance tools, AI behavioral detection, AI controlled city, AI surveillance news, AI surveillance system explained, AI visual tracking, smart surveillance 2030, AI invasion of privacy, facial detection ai, AI sees you always, AI surveillance rising, future of AI spying, next level surveillance, AI technology surveillance systems, ethical issues in AI surveillance, AI surveillance future risks.
Invisibility cloak technology, real invisibility technology, military cloaking device, stealth camouflage technology, quantum stealth, cloaking device military, invisibility suit real, invisible army, military invisibility suit, DARPA cloaking tech, optical camouflage, adaptive camouflage, light bending technology, invisible tanks, real life invisibility, metamaterial invisibility, bionic camouflage, quantum invisibility cloak, future of invisibility, invisible soldier tech, battlefield invisibility, real world invisibility cloak, military stealth tech, cloaking tech 2025, thermal cloaking, active camouflage, invisibility science, invisibility suit demo, invisible armor technology, future war tech, stealth invisibility devices, camouflage that works, invisible gear military, DARPA invisibility suit, electromagnetic camouflage, AI invisibility systems, smart invisibility tech, hyperstealth material, quantum stealth suit, battlefield cloaking systems, next-gen invisibility, invisible warfare, army cloaking system, invisibility tech real, invisibility tech explained, invisibility devices 2025, invisibility war gear, invisibility prototype 2024, invisibility research military, military light bending, stealth tech evolution, invisibility in war, invisibility suit technology, military suit invisibility, invisibility fabric DARPA, smart fabric invisibility, ghost soldier tech, invisibility science real, US army invisibility trials, camouflage invisibility gear, advanced cloaking armor, invisibility cloak explained, invisibility weapons 2030, invisible battlefield weapons, stealth material real, battlefield stealth cloak, future soldier invisibility, invisibility war tools, invisibility illusion tech, invisible future soldiers, invisible force field military, adaptive invisibility suit, stealth soldier tech, military suit that vanishes, invisibility clothing military, invisibility wearable tech, invisible drone tech, war invisibility device, invisibility gear real, camouflage light bending, stealth invisibility military, invisibility lab tech, hyperstealth quantum cloak, cloaking military research, invisibility science tech, invisibility defense projects, stealth invisibility real, military invisibility breakthrough, light wave bending suit, invisibility gear 2040, DARPA invisible research, invisibility gear technology, AI and invisibility, invisibility tech future army, light bending camouflage, real invisibility breakthroughs, invisible battlefield future, invisibility innovations 2024, military invisibility progress, invisibility trials real, stealth soldier gear, invisible drone camouflage, optical stealth gear, military invisibility demonstration, real life cloaking system, invisibility advances 2025, invisibility military tech, invisible warfare future, real life invisibility suit, active invisibility devices, invisibility in modern combat, military invisibility gear, invisibility armor technology, DARPA invisibility research, quantum light bending, how invisibility works, AI cloaking tech, invisibility battle gear, invisible tanks real, stealth invisibility suit, invisible combat drones, military ghost tech, invisibility light control, invisibility gear explained, see-through military suits, invisible soldiers 2040, next gen stealth military, invisible tech in war, cloaking field devices, camouflage that hides heat, battlefield invisibility tech, science of invisibility, how cloaking tech works, invisibility gear future, invisible uniforms military, real invisibility technology, stealth invisibility explained, AI-powered invisibility, invisible weapons systems, camouflage cloaking explained, invisibility for special forces, military stealth revolution, ghost soldier tech, camouflage vs invisibility, future army invisibility, invisible armor explained, tech to disappear soldiers, invisibility in action, cloaking suit 2025, invisible gear no power, invisibility that bends light, see-through cloaking explained, invisible sniper tech, cloaking helmets army, how to become invisible, invisible war technology, future stealth camouflage, invisible body armor, invisibility tech 2040, hyperstealth cloak demo, quantum stealth explained, invisibility suit prototype, optical illusion cloaking, how metamaterials hide objects, real invisibility inventions, military invisibility projects, next level stealth tech, cloak of invisibility science, invisibility tech for defense, light-bending suit, stealth invisibility reality, invisible forces military, wearable invisibility devices, adaptive camouflage tech, AI camouflage systems, invisibility war gear, real stealth invisibility, military invisibility suit 2025, advanced cloaking tech, future of optical camouflage, invisibility field generator, invisible warfare gear, cloaking tech in real life, AI invisible armor, invisibility in science today, light manipulation technology, real invisibility cloak 2025, next-gen cloaking devices, military grade invisibility, light bending.

As demand surges for batteries that store more energy and last longer—powering electric vehicles, drones, and energy storage systems—a team of South Korean researchers has introduced an approach to overcome a major limitation of conventional lithium-ion batteries (LIBs): unstable interfaces between electrodes and electrolytes.
Most of today’s consumer electronics—such as smartphones and laptops—rely on graphite-based batteries. While graphite offers long-term stability, it falls short in energy capacity.
Silicon, by contrast, can store nearly 10 times more lithium ions, making it a promising next-generation anode material. However, silicon’s main drawback is its dramatic volume expansion and contraction during charge and discharge, swelling up to three times its original size.

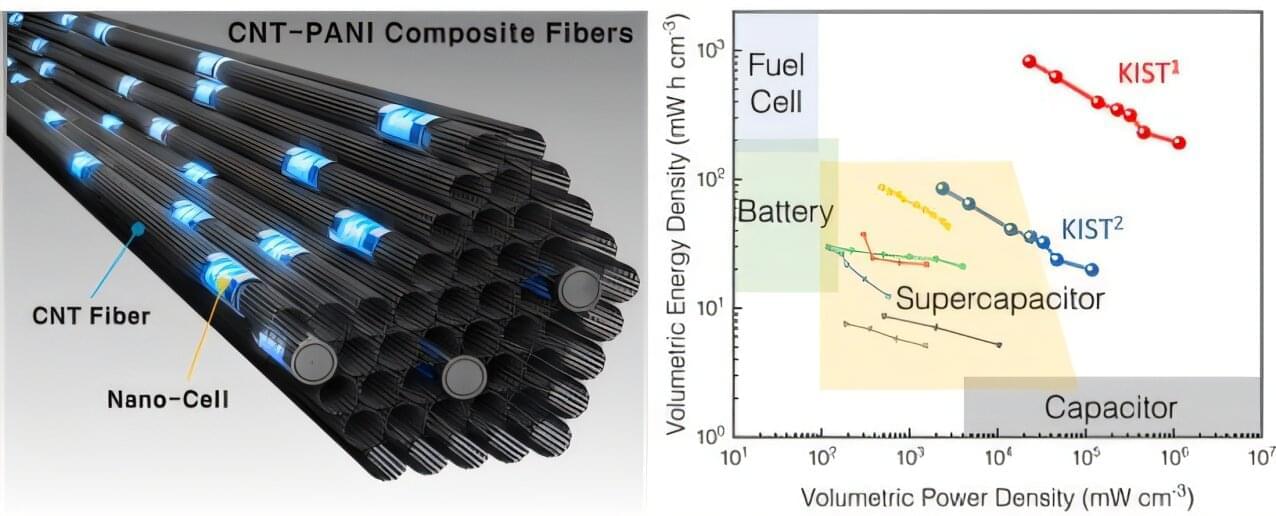
A research team has developed a high-performance supercapacitor that is expected to become the next generation of energy storage devices. With details published in the journal Composites Part B: Engineering, the technology developed by the researchers overcomes the limitations of existing supercapacitors by utilizing an innovative fiber structure composed of single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and the conductive polymer polyaniline (PANI).
Compared to conventional batteries, supercapacitors offer faster charging and higher power density, with less degradation over tens of thousands of charge and discharge cycles. However, their relatively low energy density limits their use over long periods of time, which has limited their use in practical applications such as electric vehicles and drones.
Researchers led by Dr. Bon-Cheol Ku and Dr. Seo Gyun Kim of the Carbon Composite Materials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and Professor Yuanzhe Piao of Seoul National University (SNU), uniformly chemically bonded single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which are highly conductive, with polyaniline (PANI), which is processable and inexpensive, at the nanoscale.
Autonomous battleships, autonomous defense technology, autonomous navy fleet, autonomous naval warships, autonomous patrol vessels, autonomous ship AI, autonomous warships 2025, battlefield AI systems, combat drone ships, cutting-edge naval AI, deep sea AI fleet, defense automation, drone fleet navy, drone operated ships, drone warships, future autonomous fleets, future navy AI, futuristic battle navy, ghost fleet AI, ghost fleet autonomous, ghost fleet drones, ghost naval ships, ghost warship fleet, high-tech naval fleet, military AI fleets, military autonomous ships, military drone ships, navy 2040 AI, navy AI automation, navy AI drone fleet, navy AI fleets, navy automation future, navy ghost drones, navy ghost ships, navy robotics systems, next-gen navy tech, robotic battle ships, robotic drone vessels, robotic navy future, robotic sea fleet, robotic sea patrol, robotic war navy, robotic warships AI, self-piloted navy, self-steering warships, stealth autonomous navy, stealth ghost fleet, stealth navy automation, tech navy evolution, unmanned AI navy, unmanned battle drones, unmanned combat vessels, unmanned ghost navy, unmanned military fleet, unmanned naval drones, unmanned navy boats, unmanned navy future, unmanned sea patrols, warship AI tech, warship drone AI, warship ghost fleet, warship robotics, warship self-navigation, autonomous ghost navy, AI powered navy, AI ship combat, AI ship navies, AI war vessels, AI warship combat, AI weaponized fleet, AI-controlled navy, AI-driven battle sea, AI-driven ghost fleet, AI-enabled navy future, autonomous ocean defense, autonomous war sea fleet, drone-based warships, drone-controlled navy, drone-led ghost fleet, drone-swarm navy, future military vessels, future sea combat, ghost navy technology, naval AI drones, navy AI future warfare, navy drone AI tech, navy drone patrol, navy ghost AI systems, robotic ship combat, sea battle AI systems, self-navigating warships, stealth AI navy tech, unmanned robotic ships, war automation navy, war ghost drones, war naval AI, war robot ships, weaponized drone navy, navy drone revolution, AI ocean patrols, underwater drone warfare, military ghost fleets, stealth unmanned warships, intelligent navy drones, navy robotics AI, robotic submarines AI, AI sea defense, future of naval AI, drone navy intelligence, unmanned stealth destroyers, AI-powered naval tech, smart navy ships, robotic destroyer fleet, next-gen ocean defense, deep sea robotics, drone guided torpedoes, sea AI weapons, unmanned marine fleet, combat sea robots, autonomous navy destroyers, unmanned military ocean tech, AI navy weapon systems, tech-driven warships, artificial intelligence warships, unmanned surface vessels, navy robotic patrol boats, AI-enabled destroyers, autonomous military defense, future ghost ships, navy drone control system, AI-controlled destroyers, unmanned combat surface fleet, ocean war robots, marine AI surveillance, robotic ocean patrols, future war drones, ghost ship navy, intelligent sea vessels, navy drone carriers, stealth autonomous ships, drone-enabled defense, underwater robotic navy, futuristic ocean fleet, drone-operated destroyers, AI-enabled sea robots, military robotics sea, next-gen destroyer drones, future stealth navy, navy robotics revolution, AI warfare at sea, unmanned maritime systems, AI naval monitoring, AI-controlled navy drones, autonomous destroyer squad, future naval swarms, robotic surface fleet, navy stealth AI, sea-based warbots, AI-controlled naval fleet, maritime ghost drones, automated navy systems, autonomous ship squadrons, ocean warfare automation, ghost destroyer drones, next-gen military fleets, automated sea defense, intelligent ship fleets, AI stealth destroyers, tech navy transformation, navy bots warfare, unmanned combat bots, autonomous naval innovations, AI warship patrols, automated ship navies, drone navy upgrades, future of robotic fleets, stealth robotics navy, AI ship fleets 2030, autonomous ocean warriors, naval robotics AI 2025, autonomous deep-sea ships, drone war technology, unmanned weaponized ships, futuristic ship fleets, next-gen ghost warships, ocean-based military AI, naval swarming drones, robotic future navy, navy drone revolution, AI ocean patrols, underwater drone warfare, military ghost fleets, stealth unmanned warships, intelligent navy drones, navy robotics AI, robotic submarines AI, AI sea defense, future of naval AI, drone navy intelligence, unmanned stealth destroyers, AI-powered naval tech, smart navy ships, robotic destroyer fleet, next-gen ocean defense, deep sea robotics, drone guided torpedoes, sea AI weapons, unmanned marine fleet, combat sea robots, autonomous navy destroyers, unmanned military ocean tech, AI navy weapon systems, tech-driven warships, artificial intelligence warships, unmanned surface vessels, navy robotic patrol boats, AI-enabled destroyers, autonomous military defense, future ghost ships, navy drone control system, AI-controlled destroyers.
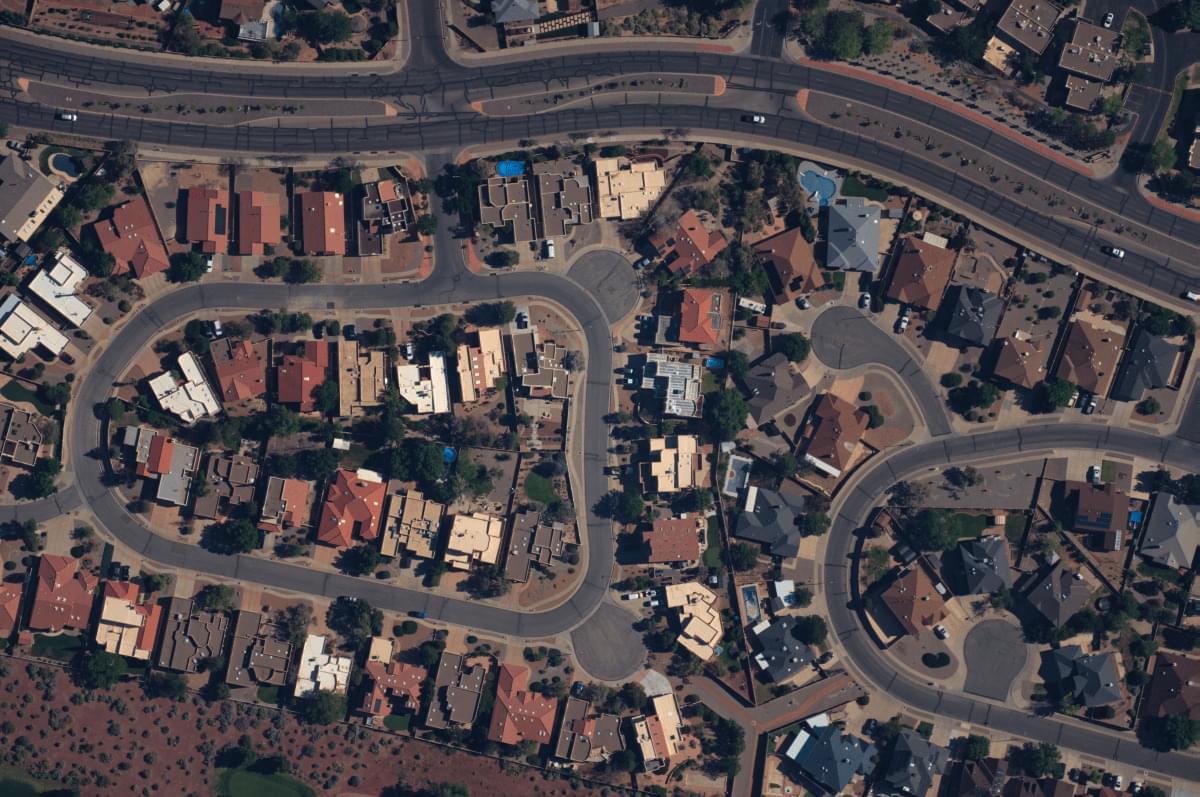

When it comes to creating images of the earth from above, satellites, drones, planes and spacecraft are what tend to come to mind. But a startup called Near Space Labs is taking a very different approach to taking high-resolution photos from up high.
Near Space Labs is building aircraft that are raised by helium balloons and then rely on air currents to stay up, move around to take pictures from the stratosphere, and eventually glide back down to earth. On the back of significant traction with customers using its images, the startup has now raised $20 million to expand its business.
Bold Capital Partners (a VC firm founded by Peter Diamandis of XPRIZE and Singularity University fame), is leading the Series B round. Strategic backer USAA (the U.S. Automobile Association) is also investing alongside Climate Capital, Gaingels, River Park Ventures, and previous backers Crosslink Capital, Third Sphere, Draper Associates, and others that are not being named. Near Space Labs has now raised over $40 million, including a $13 million Series A in 2021.