Uncrewed submarines loaded with ‘multi-domain’ drones could offer a new dimension for hunting for enemy naval forces and mines, and more.
Category: drones – Page 27
How the UAE’s ‘Rain Drones’ Use Electric Shocks to Kickstart Storms
In a year of smashed global temperature records, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is turning to technology to turn the tide on the searing heat. As a report by Business Insider points out, in the city of Dubai, which reaches heats of up to 120 degrees F (48 degrees C), scientists are using a special method to make it rain.
Specifically, Dubai is using drones that fly into clouds where they then discharge electricity to kickstart rain, which reduces temperatures and provides much-needed water resources.
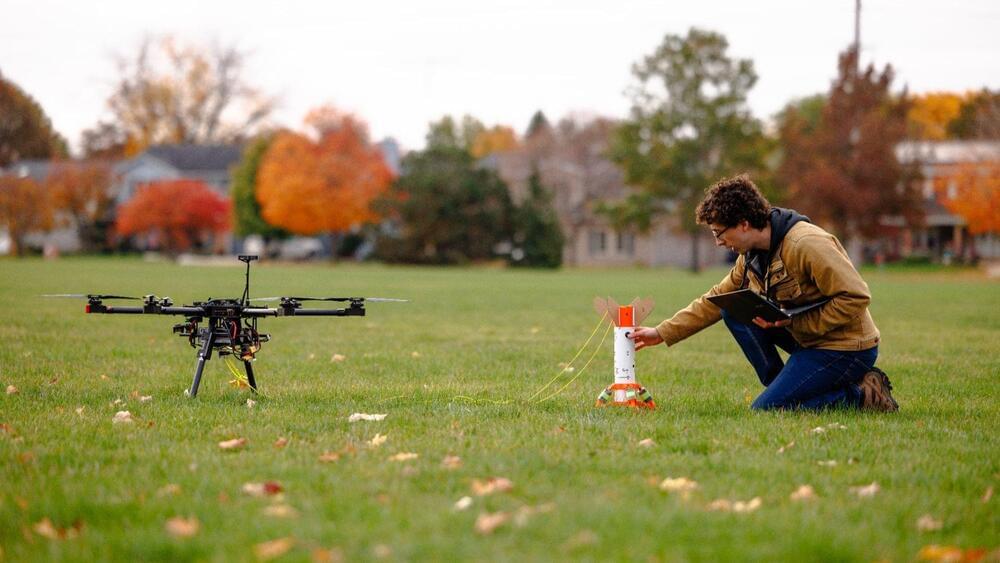


New algorithm finds failures and fixes in autonomous systems, from drone teams to power grids
From vehicle collision avoidance to airline scheduling systems to power supply grids, many of the services we rely on are managed by computers. As these autonomous systems grow in complexity and ubiquity, so too could the ways in which they fail.
Now, MIT engineers have developed an approach that can be paired with any autonomous system, to quickly identify a range of potential failures in that system before they are deployed in the real world. What’s more, the approach can find fixes to the failures, and suggest repairs to avoid system breakdowns.
The team has shown that the approach can root out failures in a variety of simulated autonomous systems, including a small and large power grid network, an aircraft collision avoidance system, a team of rescue drones, and a robotic manipulator. In each of the systems, the new approach, in the form of an automated sampling algorithm, quickly identifies a range of likely failures as well as repairs to avoid those failures.
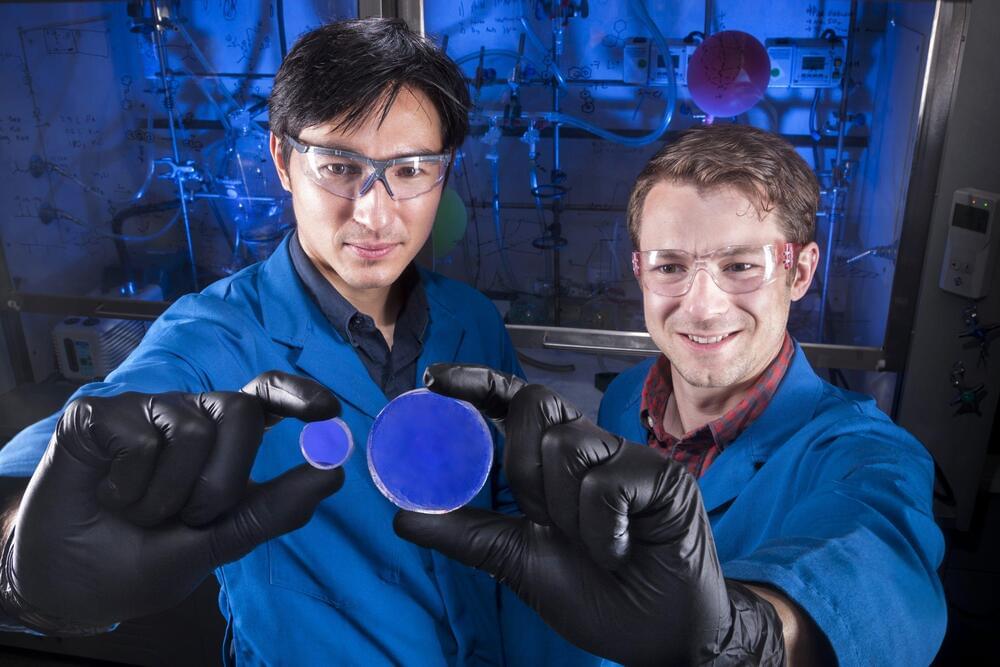
Detecting nuclear materials using light
LIVERMORE, Calif. — Blueshift Optics, owned by former Sandia employee Joey Carlson, is working to shift the way radioactive materials are detected, using technology that he helped create at Sandia National Laboratories.
Radiation detection has long been a critical aspect of national security and efforts to make the world safer.
“Agencies are trying to cast this wide net to catch nuclear smuggling, and this is one aspect of that effort,” said Sandia materials scientist Patrick Feng. “You could use this technology at a border crossing, in a handheld detector as someone enters a facility or fly it on a drone to map an area.”

China develops drone that ‘group chats’ battle strategy like humans
The drones utilized large language models to engage with each other and their operator.
Marking a significant leap concerning drone technology, researchers in China have enabled unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to engage in “group chats” to discuss and assign work to one another, much like human teams.
The research work accessed by South China Morning Post (SCMP) was done by a team led by Li Xuelong at the School of Artificial Intelligence, Optics and Electronics at Northwestern Polytechnical University in China. According to them, the technology might improve security patrols, disaster relief, and aerial logistics.
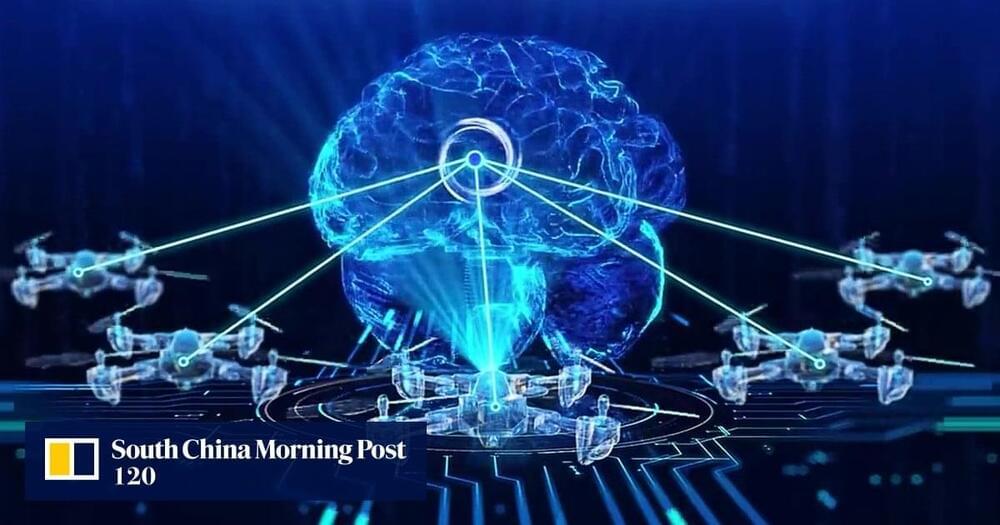
Chinese drones with ‘human brains’ tackle complex tasks through group chats
The post included a demonstration video from the researchers, showing how a team of five drones successfully located a set of keys in an outdoor park.
“The drones showcased key abilities, including humanlike dialogue interaction, proactive environmental awareness and autonomous entity control,” the WeChat report said. Autonomous entity control refers to the drone cluster’s ability to adjust flight status in real time based on environmental feedback.
The technology equips each drone with a “human brain”, allowing them to chat with each other using natural language. This ability was developed based on a Chinese open-source large language model called InternLM, according to the report.
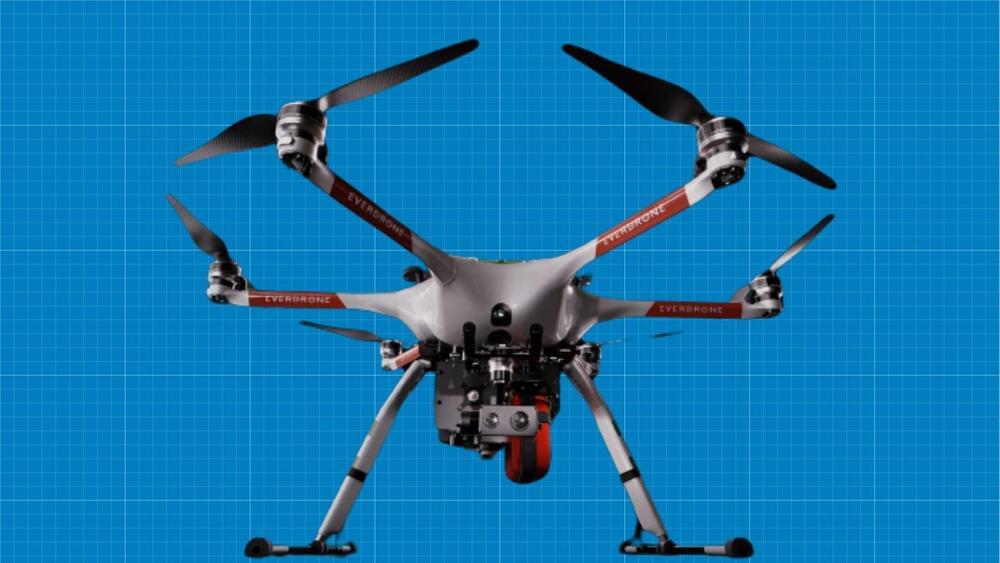

2 minute game-changer: Drone boosts advanced emergency response service
Everdrone’s advanced service promises to reduce the average response time to under 2 minutes.
Aiming to improve emergency response services, Swedish firm Everdrone has introduced a state-of-the-art drone that combines an advanced camera system as well as customizable medical kits.
Christened E2, the multi-purpose drone aims to revolutionize emergency dispatch by providing the ability to transmit live infrared and high-definition video along with emergency medical equipment supplies. Everdrone claims that E2 will help to lower average response times under two minutes.
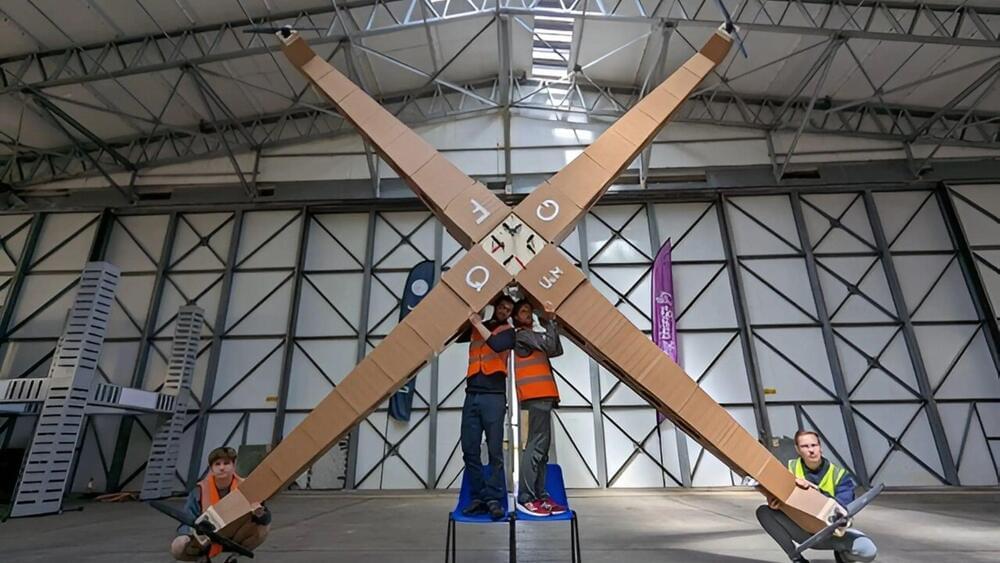

World’s largest quadcopter drone made from foamboard takes flight
A team of engineers from The University of Manchester has created and flown the world’s largest drone, made from a lightweight and eco-friendly material.
The Giant Foamboard Quadcopter (GFQ) is unlike any other drone worldwide thanks to its innovative design. It is made from foamboard, a cardboard type with a foam core and a paper skin.
A team of engineers from The University of Manchester.

AI-ready architecture doubles power with FeFETs
Hussam Amrouch has developed an AI-ready architecture that is twice as powerful as comparable in-memory computing approaches. As reported in the journal Nature Communications (“First demonstration of in-memory computing crossbar using multi-level Cell FeFET”), the professor at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) applies a new computational paradigm using special circuits known as ferroelectric field effect transistors (FeFETs). Within a few years, this could prove useful for generative AI, deep learning algorithms and robotic applications.