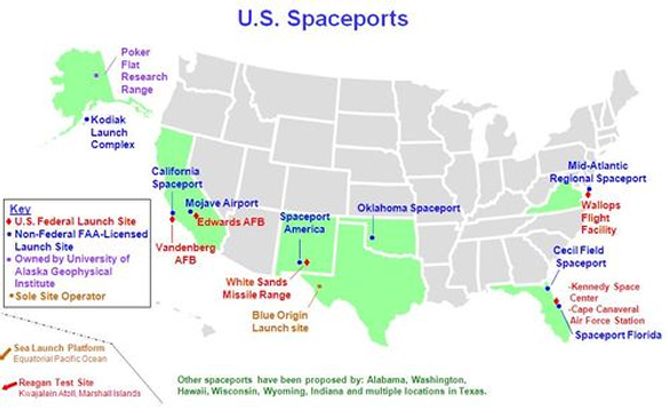
Last month a colleague of mine and I visited with Dennis Heap, Executive Director of the National Front Range Airport, at Watkins, CO, the location of the future Spaceport Colorado, and Colorado’s contribution to getting into space. Here is Part 3.
In my last post I had mentioned that there were 2 business models for spaceports. I’ll name the first Sweden-America model after spaceports Sweden & America. The second, I’ll name Colorado-Singapore model after (yet to be) spaceports Colorado & Singapore.
The Sweden-America model basic premise is that spaceport ought to be built in remote locations, and then a hinterland economy is eventually built around the spaceport. This approach was originally driven by safety concerns and the need for a rocket range or vacant land for launching rockets to crash back to.
The basic premise of the Colorado-Singapore model is that launch vehicles are safe and that spaceports ought to be built close to centers of commerce and intermodal transportation networks. That is, spaceports are to be built in an existing hinterland economy.
Spaceport Colorado is therefore tucked in close to Denver International Airport and the city of Denver. Spaceport Singapore is to be built within Changi Aiport (ranked #2 out of 388 airports in the world). Changi Airport is located on the Eastern end of the island of Singapore, with Malaysia to the North.
Note that in the case of Spaceport Singapore, the Singapore Strait to the South and East of Changi form a natural rocket range. While Spaceport Colorado has 3,000 acres (less 900 acres for the spaceport) of vacant land to develop additional revenue generating and revenue supporting facilities.
There has been debate about which is the better business model. Both models are correct. Having been Head of Corporate Planning in the early days at Westport, Malaysia, I can assure you that the key is to match your capex with revenue generation. Today the Goggle map of Westport, shows a well-developed island of Pulah Indah. When I worked there in 1995–96 the whole island was virgin and civil engineering firms were draining the swampland.
That is, if there is enough drive, ambition, and cooperation between the private and public sectors a whole island can be transformed from swampland to a world class shipping hub, commercial, industrial & residential zones in a decade. The same is true for spaceports, and for that matter, American cities.
The problem with Spaceport America is that the public sector is not willing to do enough to ensure its success. At least not what it took to ensure Westport’s long term success. New Mexico take a look at Westport and see what you will be missing 10 years from now.
I have to run now. More in the next post.
—————————————————————————————————
Benjamin T Solomon is the author & principal investigator of the 12-year study into the theoretical & technological feasibility of gravitation modification, titled An Introduction to Gravity Modification, to achieve interstellar travel in our lifetimes. For more information visit iSETI LLC, Interstellar Space Exploration Technology Initiative.
Solomon is inviting all serious participants to his LinkedIn Group Interstellar Travel & Gravity Modification.