AI-based model streams intelligible speech from the brain in real time
Category: cyborgs – Page 5
Major Advances in Synthetic Biology Result in Cyborg Cells and Artificial Genome
Support this channel on Patreon to help me make this a full time job: https://www.patreon.com/whatdamath (Unreleased videos, extra footage, DMs, no ads)Alter…
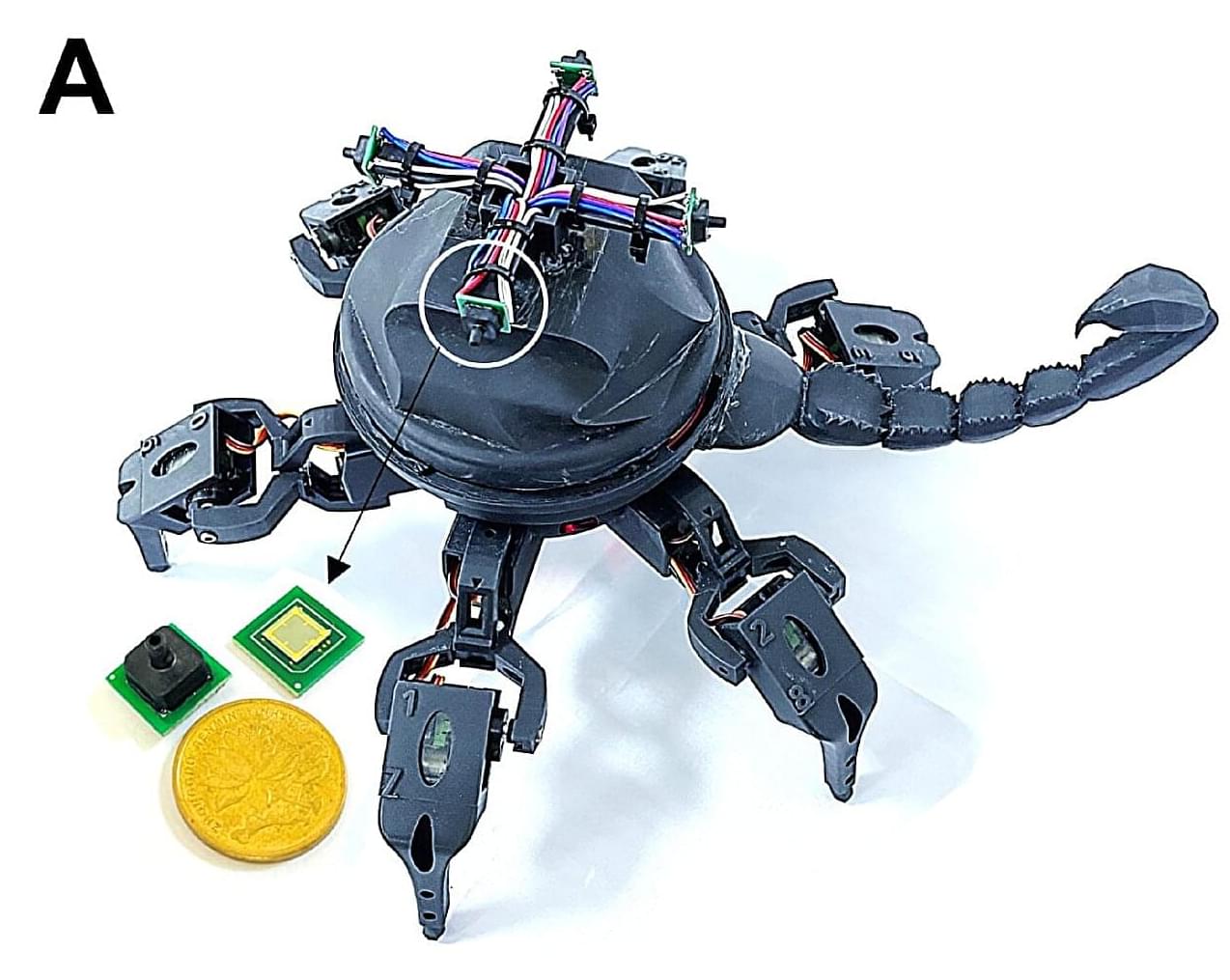

Scorpion-inspired pressure sensors let robots feel their surroundings
Nature, the master engineer, is coming to our rescue again. Inspired by scorpions, scientists have created new pressure sensors that are both highly sensitive and able to work across a wide variety of pressures.
Pressure sensors are key components in an array of applications, from medical devices and industrial control systems to robotics and human-machine interfaces. Silicon-based piezoresistive sensors are among the most common types used today, but they have a significant limitation. They can’t be super sensitive to changes and work well across a range of pressures at the same time. Often, you have to choose one over the other.

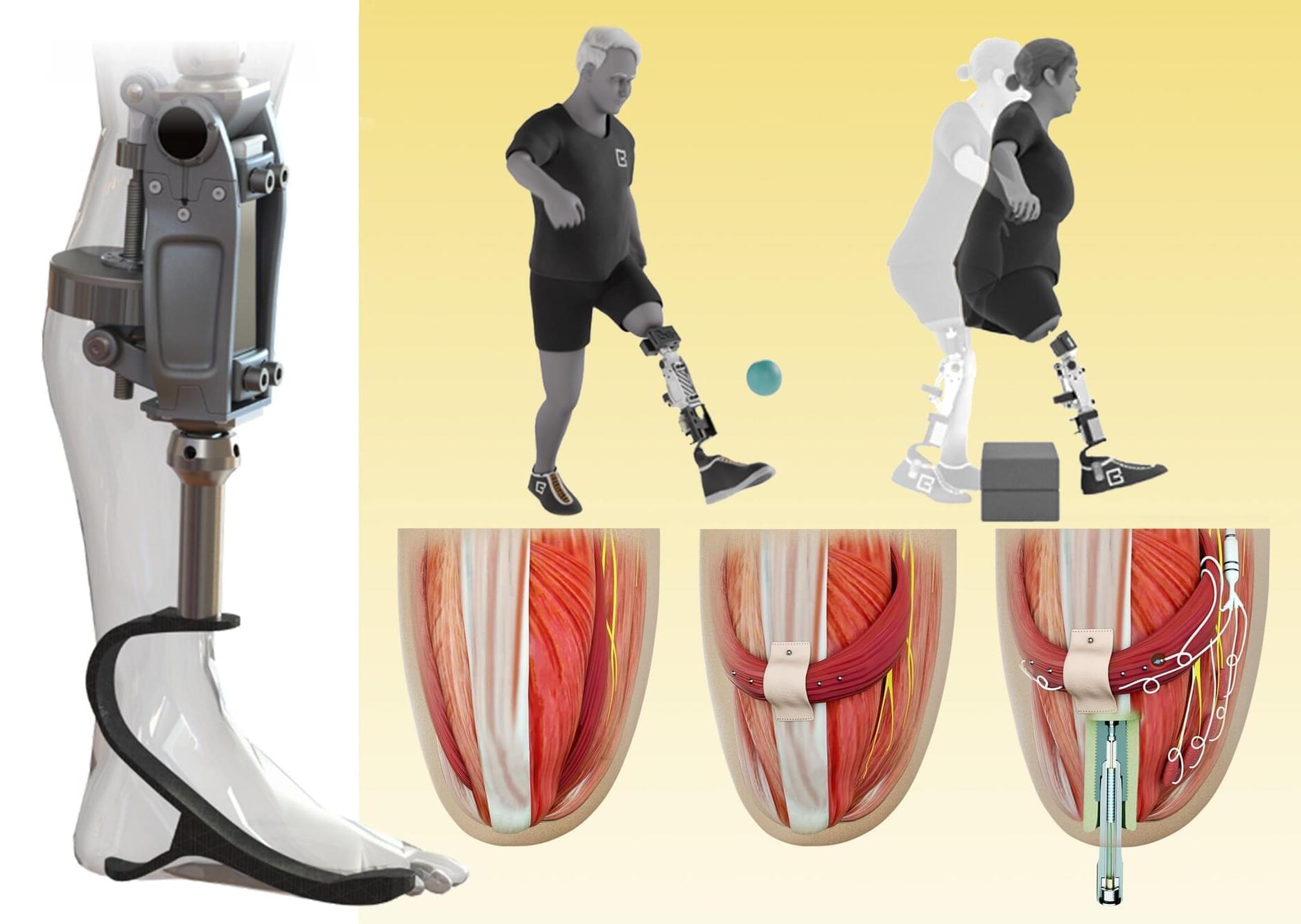
3D-Printed Exoskeleton Learns From Your Hand
3D-Printed Exoskeleton Learns From Your Hand ‘…small electric motors at the principal joints worked the prosthetic framework by means of steel cables…’ — Fritz Leiber, 1968.
Smartwatch Powered By Slime Mold ‘Living protoplasm incorporated into the Ampek F-a2 recording system…’ — Philip K. Dick, 1966.
Carpentopod Walking Table ‘Twoflower’s Luggage, which was currently ambling along on its little legs…’
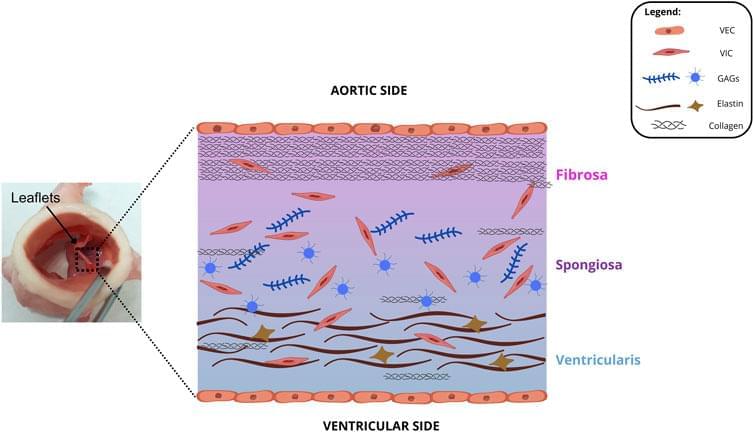
Bioengineering and Biotechnology Approaches in Cardiovascular Sciences, Volume III
Prosthetic heart valves (PHV) have been studied for around 70 years. They are the best alternative to save the life of patients with cardiac valve diseases. However, current PHVs may still cause significant disadvantages to patients. In general, native heart valves show complex structures and reproducing their functions challenges scientists. Valve repair and replacement are the options to heal heart valve diseases (VHDs), such as stenosis and regurgitation, which show high morbidity and mortality worldwide. Valve repair contributes to the performance of cardiac cycles. However, it fails to restore valve anatomy to its normal condition. On the other hand, replacement is the only alternative to treat valve degeneration. It may do so by mechanical or bioprosthetic valves. Although prostheses may restructure patients’ cardiac cycle, both prostheses may show limitations and potential disadvantages, such as mechanical valves causing thrombogenicity or bioprosthetic valves, calcification. Thus, prostheses require constant improvements to remedy these limitations. Although the design of mechanical valve structures has improved, their raw materials cause great disadvantages, and alternatives for this problem remain scarce. Cardiac valve tissue engineering emerged 30 years ago and has improved over time, e.g., xenografts and fabricated heart valves serving as scaffolds for cell seeding. Thus, this review describes cardiac valve substitutes, starting with the history of valvular prosthesis transplants and ending with some perspectives to alleviate the limitations of artificial valves.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT


Brain cells learn faster than machine learning, research reveals
Researchers have demonstrated that brain cells learn faster and carry out complex networking more effectively than machine learning by comparing how both a Synthetic Biological Intelligence (SBI) system known as “DishBrain” and state-of-the-art RL (reinforcement learning) algorithms react to certain stimuli.
The study, “Dynamic Network Plasticity and Sample Efficiency in Biological Neural Cultures: A Comparative Study with Deep Reinforcement Learning,” published in Cyborg and Bionic Systems, is the first known of its kind.
The research was led by Cortical Labs, the Melbourne-based startup which created the world’s first commercial biological computer, the CL1. The CL1, through which the research was conducted, fuses lab-cultivated neurons from human stem cells with hard silicon to create a more advanced and sustainable form of AI, known as SBI.