The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article.
Intro
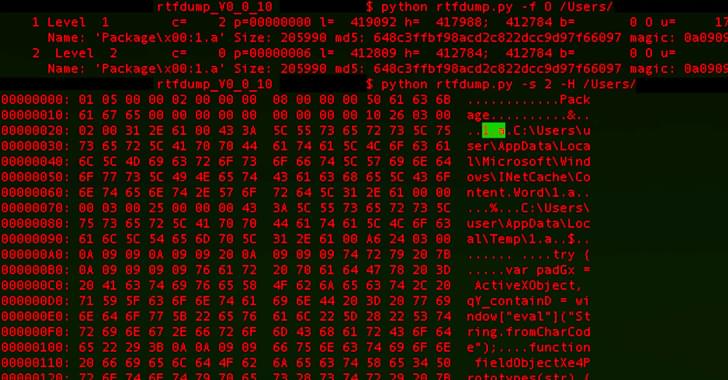
In February 2022, Microsoft disabled VBA macros on documents due to their frequent use as a malware distribution method. This move prompted malware authors to seek out new ways to distribute their payloads, resulting in an increase in the use of other infection vectors, such as password-encrypted zip files and ISO files.