Compromised dYdX npm and PyPI packages delivered wallet-stealing malware and a RAT via poisoned updates in a software supply chain attack.


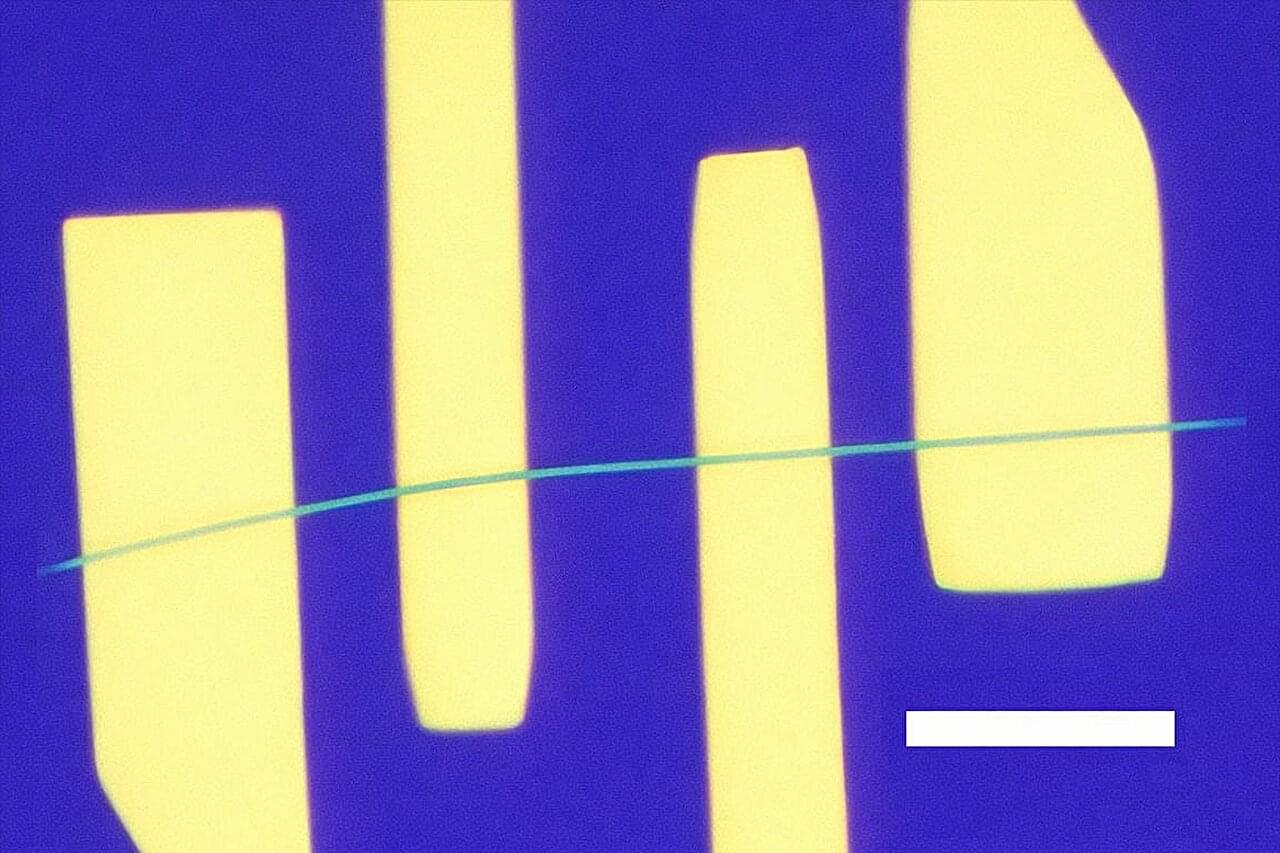
That low-frequency fuzz that can bedevil cellphone calls has to do with how electrons move through and interact in materials at the smallest scale. The electronic flicker noise is often caused by interruptions in the flow of electrons by various scattering processes in the metals that conduct them.
The same sort of noise hampers the detecting powers of advanced sensors. It also creates hurdles for the development of quantum computers—devices expected to yield unbreakable cybersecurity, process large-scale calculations and simulate nature in ways that are currently impossible.
A much quieter, brighter future may be on the way for these technologies, thanks to a new study led by UCLA. The research team demonstrated prototype devices that, above a certain voltage, conducted electricity with lower noise than the normal flow of electrons.

Multiple critical vulnerabilities in the popular n8n open-source workflow automation platform allow escaping the confines of the environment and taking complete control of the host server.
Collectively tracked as CVE-2026–25049, the issues can be exploited by any authenticated user who can create or edit workflows on the platform to perform unrestricted remote code execution on the n8n server.
Researchers at several cybersecurity companies reported the problems, which stem from n8n’s sanitization mechanism and bypass the patch for CVE-2025–68613, another critical flaw addressed on December 20.

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) ordered government agencies to patch their systems against a five-year-old GitLab vulnerability that is actively being exploited in attacks.
GitLab patched this server-side request forgery (SSRF) flaw (tracked as CVE-2021–39935) in December 2021, saying it could allow unauthenticated attackers with no privileges to access the CI Lint API, which is used to simulate pipelines and validate CI/CD configurations.
“When user registration is limited, external users that aren’t developers shouldn’t have access to the CI Lint API,” the company said at the time.

A new threat actor called Amaranth Dragon, linked to APT41 state-sponsored Chinese operations, exploited the CVE-2025–8088 vulnerability in WinRAR in espionage attacks on government and law enforcement agencies.
The hackers combined legitimate tools with the custom Amaranth Loader to deliver encrypted payloads from command-and-control (C2) servers behind Cloudflare infrastructure, for more accurate targeting and increased stealth.
According to researchers at cybersecurity company Check Point, Amaranth Dragon targeted organizations in Singapore, Thailand, Indonesia, Cambodia, Laos, and the Philippines.

According to the company’s new announcement, the earlier warning stating that March 1, 2027, would be the application’s final day should now be disregarded, as Adobe is neither discontinuing nor removing access to Adobe Animate, and there is no longer any deadline or date set for when Animate will stop being available.
Going forward, the software will remain accessible to both new and existing users, although Adobe has confirmed that users shouldn’t expect the addition of any new features. Instead, the program will remain in a perpetual “maintenance mode,” meaning Adobe will continue supporting the application and providing regular security updates and bug fixes.

