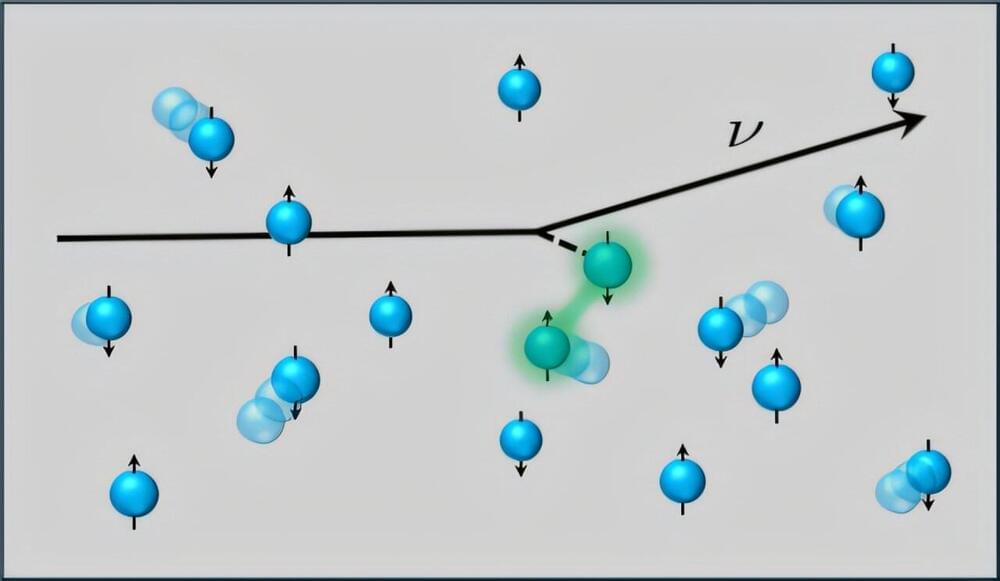
When a star dies in a supernova, one possible outcome is for the remains to become a neutron star. Inside a neutron star, the protons and electrons combine into uncharged neutrons. This substance is called neutron matter.
A team of researchers from the United States, China, Turkey, and Germany has performed ab initio (i.e., from the most fundamental principles) simulations to calculate spin and density correlations in neutron matter. They used realistic nuclear interactions at higher densities of neutrons than previously explored. Spin and density are the probability of finding a neutron in a particular position with a particular direction of spin. These correlations determine key aspects of how neutrinos scatter and heat up in a core-collapse supernova.
The research is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.