Submillimeter galaxies (SMGs) are a class of the most luminous, distant, and rapidly star-forming galaxies known and can shine brighter than a trillion Suns (about one hundred times more luminous in total than the Milky Way). They are generally hard to detect in the visible, however, because most of their ultraviloet and optical light is absorbed by dust which in turn is heated and radiates at submillimeter wavelengths—the reason they are called submillimeter galaxies. The power source for these galaxies is thought to be high rates of star formation, as much as one thousand stars per year (in the Milky Way, the rate is more like one star per year). SMGs typically date from the early universe; they are so distant that their light has been traveling for over ten billion years, more than 70% of the lifetime of the universe, from the epoch about three billion years after the big bang. Because it takes time for them to have evolved, astronomers think that even a billion years earlier they probably were actively making stars and influencing their environments, but very little is known about this phase of their evolution.
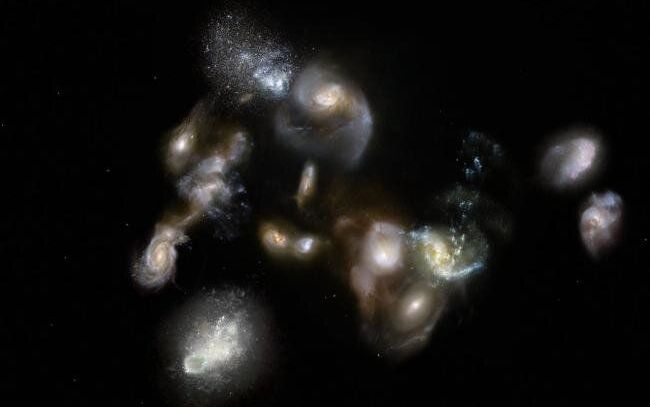
SMGs have recently been identified in galaxy protoclusters, groups of dozens of galaxies in the universe when it was less than a few billion years old. Observing massive SMGs in these distant protoclusters provides crucial details for understanding both their early evolution and that of the larger structures to which they belong. CfA astronomers Emily Pass and Matt Ashby were members of a team that used infrared and optical data from the Spitzer IRAC and Gemini-South instruments, respectively, to study a previosly identified protocluster, SPT2349-56, in the era only 1.4 billion years after the big bang. The protocluster was spotted by the South Pole Telescope millimeter wavelengths and then observed in more detail with Spitzer, Gemini, and the ALMA submillimeter array.
The protocluster contains a remarkable concentration of fourteen SMGs, nine of which were detected by these optical and infrared observations. The astronomers were then able to estimate the stellar masses, ages, and gas content in these SMGs, as well as their star formation histories, a remarkable acheievment for such distant objects. Among other properties of the protocluster, the scientists deduce that its total mass is about one trillion solar-masses, and its galaxies are making stars in a manner similar to star formation processes in the current universe. They also conclude that the whole ensemble is probably in the midst of a colossal merger.