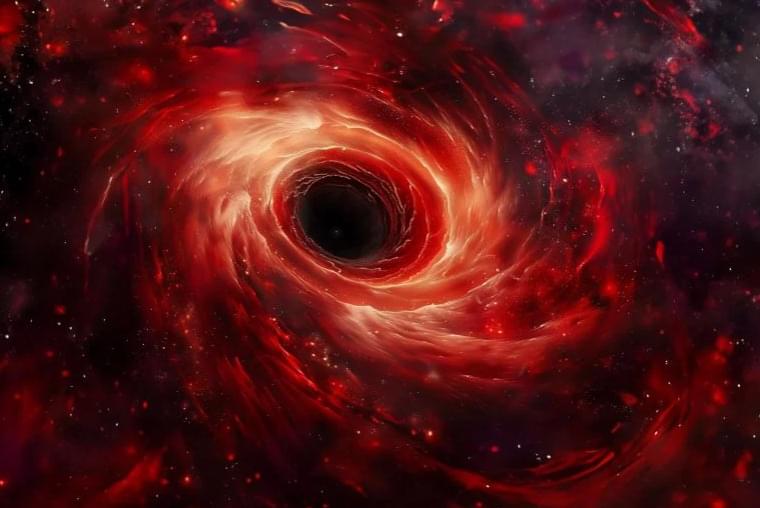
An exploration of the inverse of a black hole, a white hole and what that might mean for future physics.
The new JMG Clips channel for sleep!
• Space Facts to Fall Asleep to | John…
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
An exploration of the inverse of a black hole, a white hole and what that might mean for future physics.
The new JMG Clips channel for sleep!
• Space Facts to Fall Asleep to | John…
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:

If two points were ripped apart faster than light, they would no longer interact through any force of physics. Whereas a constant dark energy would leave behind already-intact objects, like clusters of galaxies, phantom energy could tear them apart. In a finite amount of time, billions of years from now, clusters would tear apart, followed by ever-smaller objects. Even atomic and nuclear bonds would not withstand the onslaught.
Eventually, space itself would dissolve in an event known as the Big Rip. Any two points, no matter how close, would be ripped infinitely far away from each other. The very structure of space-time, the causal foundations that make our universe work, would no longer behave. The universe would just break down.
However, luckily, most physicists do not believe this scenario can actually happen. For one, it’s unclear how this process of ripping interacts with the other laws of physics. For example, quarks cannot be torn apart — when you attempt to do so, you need so much energy that new quarks materialize out of the vacuum. So ripping apart quarks just might lead to other, interesting interactions.

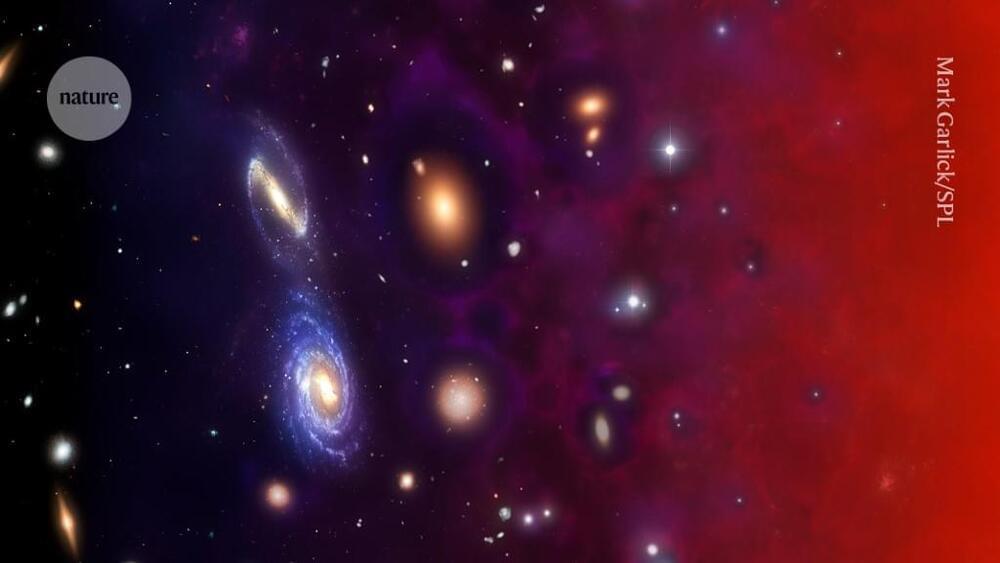
The Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences (INI) in Cambridge hosted a research programme on one of the most pressing problems in modern physics: to build a theory that can explain all the fundamental forces and particles of nature in one unifying mathematical framework. Such a theory of quantum gravity would combine two hugely successful frameworks on theoretical physics, which have so far eluded unification: quantum physics and Einstein’s theory of gravity.
The Black holes: bridges between number theory and holographic quantum information programme focusses on black holes, which play a hugely important part in this area, on something called the holographic principle, and on surprising connections to pure mathematics. This collection of articles explores the central concepts involved and gives you a gist of the cutting edge research covered by the INI programme.
Argonne’s Science 101 series takes you back to the basics, with plain-language explanations of the scientific concepts behind our pivotal discoveries and our biggest innovations.
In this Science 101 video, postdoctoral researchers Gillian Beltz-Mohrmann and Florian Kéruzoré explore two of the biggest mysteries in science: dark matter and dark energy. These strange influences seem to be stretching the universe apart and clumping stuff together in unexpected ways. Together, they make up a whopping 95% of the universe, but because we can’t see or touch them, we don’t know what they are.
Researchers around the globe, including scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, are investigating the nature of dark matter and dark energy through large cosmological surveys, particle physics experiments and advanced computing and simulation.
Find out more about Argonne Science 101 ►► https://www.anl.gov/science-101
Still haven’t subscribed to Argonne National Laboratory on YouTube? ►► http://bit.ly/2Vyzwvm.
Join us on Facebook http://bit.ly/ArgonneFacebook.


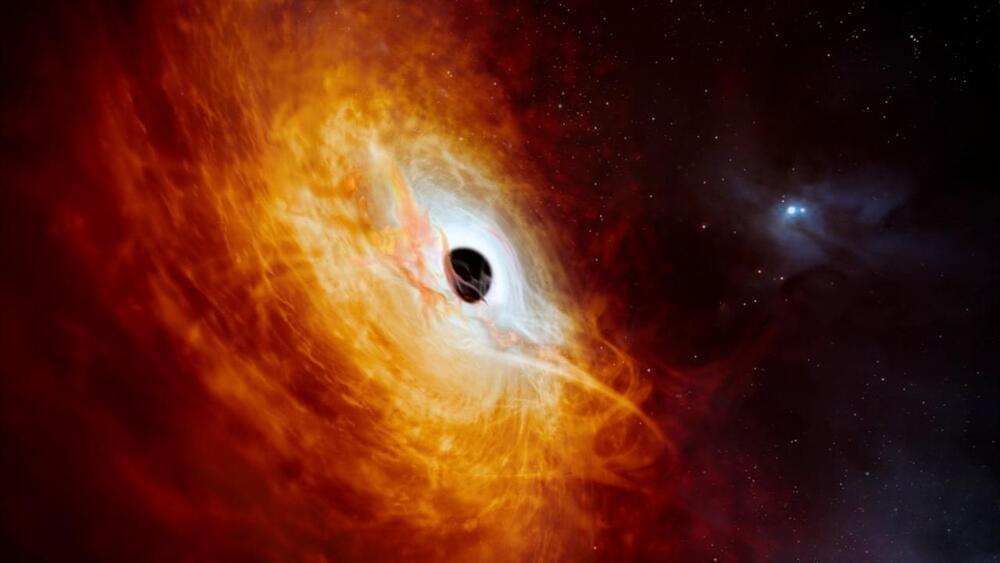
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has detected a unique and “intensely red” supermassive black hole hidden in one of the oldest part of the universe.
Scientists proposed the reddish black hole was the outcome of an enlarged universe just 700 million years following the Big Bang, as given in a paper published this month in the journal Nature. Its colors are because of a solid layer of dust compressing a lot of its light, they said.
Whereas for the first time the cosmic monster was technically invented last year, astronomers have now spotted that it is much more massive than anything else of its type in the field, making it strange discovery that could rescript the way we think how supermassive black holes increase relative to their host galaxies.
When time reaches its limits, scientists call those moments “singularities.” These can mark the start or end of time itself. The most famous singularity is the big bang, which happened around 13.7 billion years ago, kicking off the universe and time as we know it. If the universe ever stops expanding and starts collapsing, it could lead to a reverse of the big bang called the big crunch, where time would stop. As our distant descendants approach the end of time, they will face increasing challenges in a hostile universe, and their efforts will only accelerate the inevitable. We are not passive victims of time’s demise; we contribute to it. Through our existence, we convert energy into waste heat, contributing to the universe’s degeneration. Time must cease for us to continue living.

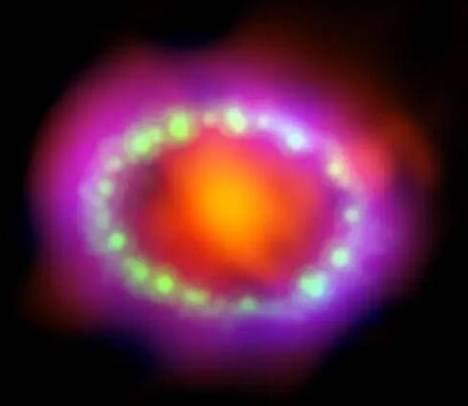
The youngest neutron star detected so far turned 37 years old last week. To celebrate, James Webb Space Telescope has finally found the most direct evidence of it, hiding among the remains of the supernova cloud it was born in.
Usually when we’re talking about the age of astronomical objects, it’s in the millions or billions of years – so finding something that’s younger than Lady Gaga feels weird. Even weirder is being able to trace its birth to a specific date – February 23, 1987, meaning it just clocked over to its 37th birthday last Friday.
The reason we can so confidently pinpoint the date is because its birth was the result of an event that only happens once every few centuries: a supernova that’s close enough to be observed from Earth with the naked eye. SN 1987A lit up the night sky for a few months in early 1987, and was quickly traced to the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way, about 168,000 light-years away. There, a blue supergiant star appeared to have collapsed and exploded, which should have left either a black hole or a neutron star.
