But even Linus Torvalds says it’s not that big of a deal.



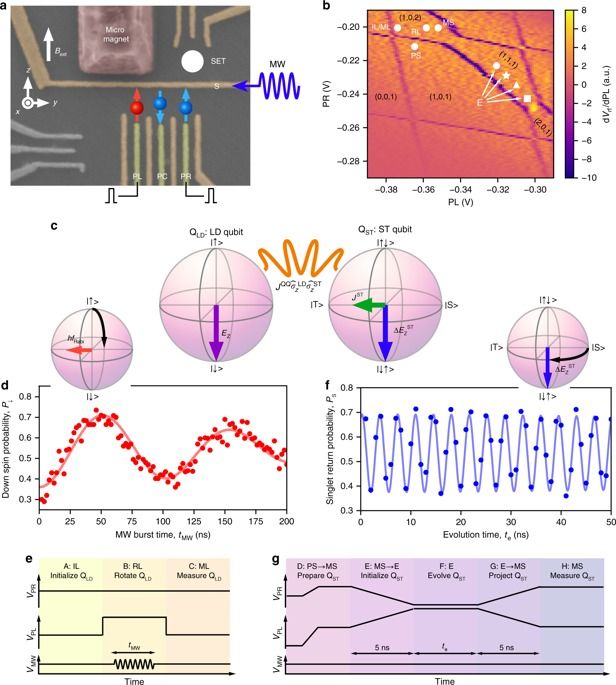
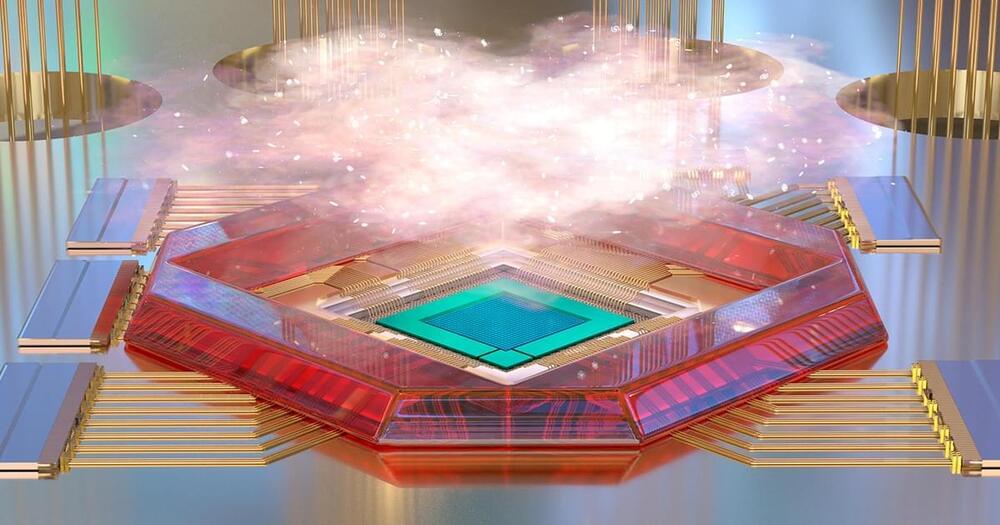
“Open Article” smile Spin-based quantum computers have the potential to tackle difficult mathematical problems that cannot be solved using ordinary computers, but many problems remain in making these machines scalable. Now, an international group of researchers led by the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science have crafted a new architecture for quantum computing. By constructing a hybrid device made from two different types of qubit—the fundamental computing element of quantum computers –they have created a device that can be quickly initialized and read out, and that simultaneously maintains high control fidelity.
Single-spin qubits in semiconductor quantum dots hold promise for universal quantum computation with demonstrations of a high single-qubit gate fidelity above 99.9% and two-qubit gates in conjunction with a long coherence time. However, initialization and readout of a qubit is orders of magnitude slower than control, which is detrimental for implementing measurement-based protocols such as error-correcting codes. In contrast, a singlet-triplet qubit, encoded in a two-spin subspace, has the virtue of fast readout with high fidelity. Here, we present a hybrid system which benefits from the different advantages of these two distinct spin-qubit implementations. A quantum interface between the two codes is realized by electrically tunable inter-qubit exchange coupling. We demonstrate a controlled-phase gate that acts within 5.5 ns, much faster than the measured dephasing time of 211 ns. The presented hybrid architecture will be useful to settle remaining key problems with building scalable spin-based quantum computers.

Qubits or quantum bits are the fundamental building block for quantum information processes. Whereas conventional computers store and process data as a series of ‘1’s and ‘0’s, quantum computers use the properties of a quantum system, such as the polarization of a photon or the spin of an electron.
Read the latest Research articles in Qubits from Nature Communications.
Get ready to get excited about excitons.
Excitons are quirky quasiparticles that exist only in semiconducting and insulating materials. Recently, a team of researchers in Lausanne, Switzerland discovered a way to control how excitons flow. Not only that, they also discovered new properties of the particles which they claim could lead to a new generation of electronic devices with transistors that lose less energy as heat. The results of their study were published this week in the journal Nature Photonics.
After developing a method to control exciton flows at room temperature, EPFL scientists have discovered new properties of these quasiparticles that can lead to more energy-efficient electronic devices.
They were the first to control exciton flows at room temperature. And now, the team of scientists from EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES) has taken their technology one step further. They have found a way to control some of the properties of excitons and change the polarization of the light they generate. This can lead to a new generation of electronic devices with transistors that undergo less energy loss and heat dissipation. The scientists’ discovery forms part of a new field of research called valleytronics and has just been published in Nature Photonics.
Excitons are created when an electron absorbs light and moves into a higher energy level, or “energy band” as they are called in solid quantum physics. This excited electron leaves behind an “electron hole” in its previous energy band. And because the electron has a negative charge and the hole a positive charge, the two are bound together by an electrostatic force called a Coulomb force. It’s this electron-electron hole pair that is referred to as an exciton.
Rice University physicists have created the world’s first laser-cooled neutral plasma, completing a 20-year quest that sets the stage for simulators that re-create exotic states of matter found inside Jupiter and white dwarf stars.
The findings are detailed this week in the journal Science and involve new techniques for laser cooling clouds of rapidly expanding plasma to temperatures about 50 times colder than deep space.
“We don’t know the practical payoff yet, but every time physicists have laser cooled a new kind of thing, it has opened a whole world of possibilities,” said lead scientist Tom Killian, professor of physics and astronomy at Rice. “Nobody predicted that laser cooling atoms and ions would lead to the world’s most accurate clocks or breakthroughs in quantum computing. We do this because it’s a frontier.”

As if battered post-Christmas finances, a looming disorderly Brexit and the prospect of a fresh nuclear arms race were not enough to dampen spirits, astronomers have declared that a nearby galaxy will slam into the Milky Way and could knock our solar system far into the cosmic void.
The unfortunate discovery was made after scientists ran computer simulations on the movement of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), one of the many satellite galaxies that orbits the Milky Way. Rather than circling at a safe distance, or breaking free of the Milky Way’s gravitational pull, the researchers found the LMC is destined to clatter into the galaxy we call home.
At the moment, the LMC is estimated to be about 163,000 light years from the Milky Way and speeding away at 250 miles per second. But simulations by astrophysicists at Durham University show that the LMC will eventually slow down and turn back towards us, ultimately smashing into the Milky Way in about 2.5 billion years’ time.
