Quantum computing is still the province of specialized programmers—but that is likely to change very quickly.
Category: computing – Page 739
Rapid de novo assembly of the European eel genome from nanopore sequencing reads
Circa 2017
We have sequenced the genome of the endangered European eel using the MinION by Oxford Nanopore, and assembled these data using a novel algorithm specifically designed for large eukaryotic genomes. For this 860 Mbp genome, the entire computational process takes two days on a single CPU. The resulting genome assembly significantly improves on a previous draft based on short reads only, both in terms of contiguity (N50 1.2 Mbp) and structural quality. This combination of affordable nanopore sequencing and light weight assembly promises to make high-quality genomic resources accessible for many non-model plants and animals.

Putin orders creation of national genetic database as Russia prioritizes genetic research
The president also ordered a boost in the education of specialists in genetics and genome sequencing and the domestic production of necessary laboratory equipment, as well as tax cuts for biomedical research. Russia will also open world-class genome research centers which will, among their immediate goals, work on the development of treatments and vaccines for Covid-19.
The future database will be one of the tools that Russia hopes to use to assume a leading position in the biomedical industry. The government sees it as crucial for keeping the country competitive on the world stage going forward.
The Kurchatov Institute, which is best known for nuclear research, has been tasked with laying the foundation for the database, choosing the storage format and making tools for search and analysis. The institute has experience in the secure handling of large amounts of sensitive data and operates a number of data centers across Russia which are used for scientific collaboration projects.

Physicists entangle 15 trillion hot atoms
Physicists set a new record by linking together a hot soup of 15 trillion atoms in a bizarre phenomenon called quantum entanglement. The finding could be a major breakthrough for creating more accurate sensors to detect ripples in space-time called gravitational waves or even the elusive dark matter thought to pervade the universe.
Entanglement, a quantum phenomena Albert Einstein famously described as “spooky action at a distance,” is a process in which two or more particles become linked and any action performed on one instantaneously affects the others regardless of how far apart they are. Entanglement lies at the heart of many emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and cryptography.
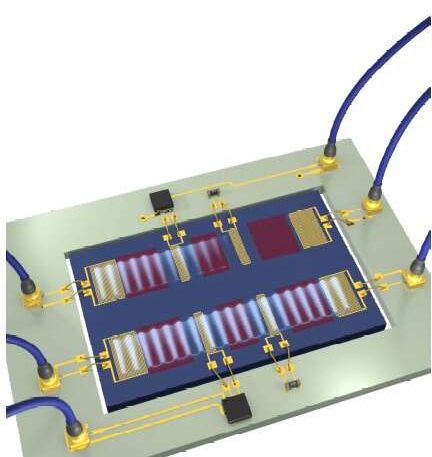
A system for the nonreciprocal transmission of microwave acoustic waves
Acoustic waves have been found to be highly versatile and promising carriers of information between chip-based electronic devices. This characteristic is ideal for the development of a number of electronic components, including microwave filters and transducers.
In the past, some researchers have tried to build devices in which waves are transmitted between two ports in a non-symmetric way. These are known as nonreciprocal devices. These devices could be particularly promising for the manipulation and routing of phonons, quasiparticles associated with acoustic waves. Building nonreciprocal devices that transmit acoustic waves, however, can be highly challenging, as acoustic systems typically transmit waves in a linear way.
Researchers at Harvard University have recently achieved the non-reciprocal transmission of non-reciprocal acoustic waves using a nonlinear parity-time symmetric system. This system, presented in a paper published in Nature Electronics, is based on two coupled acoustic resonators placed on a lithium niobate surface.

Room-temperature superconductors could revolutionize the world’s energy
· 4 hrs ·
Now that they exist it certainly will change the world.
Waste heat is all around you. On a small scale, if your phone or laptop feels warm, that’s because some of the energy powering the device is being transformed into unwanted heat.
On a larger scale, electric grids, such as high power lines, lose over 5% of their energy in the process of transmission. In an electric power industry that generated more than US$400 billion in 2018, that’s a tremendous amount of wasted money.

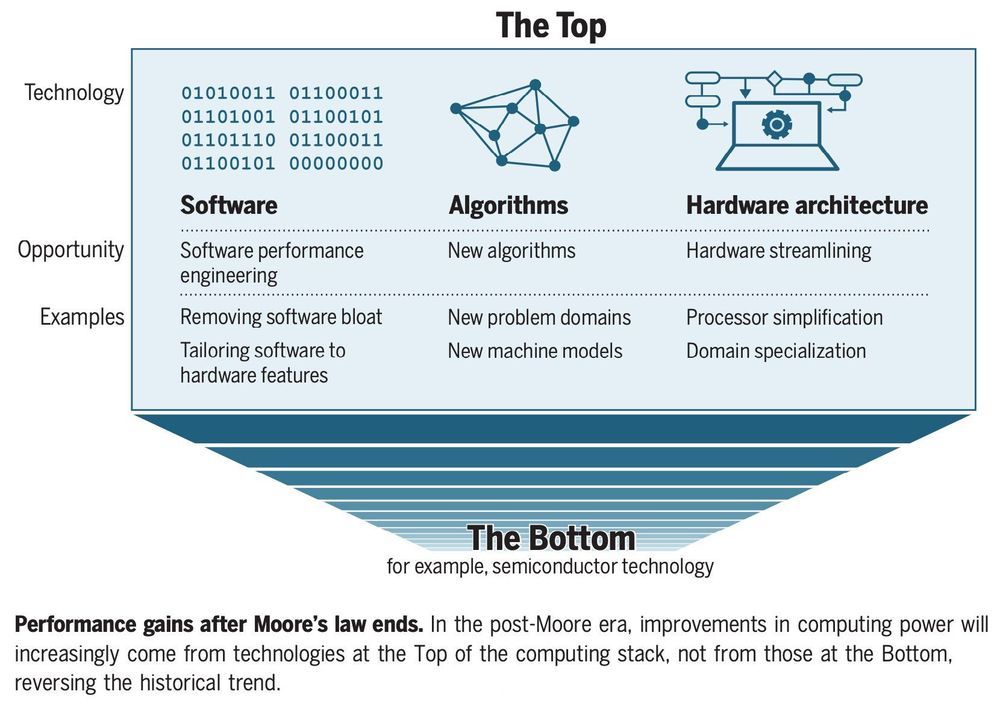
If transistors can’t get smaller, then software developers have to get smarter
In 1965, Intel co-founder Gordon Moore predicted that the number of transistors that could fit on a computer chip would grow exponentially —- and they did, doubling about every two years. For half a century Moore’s Law has endured: computers have gotten smaller, faster, cheaper and more efficient, enabling the rapid worldwide adoption of PCs, smartphones, high-speed Internet and more.
This miniaturization trend has led to silicon chips today that have almost unimaginably small circuitry. Transistors, the tiny switches that implement computer microprocessors, are so small that 1000 of them laid end-to-end are no wider than a human hair. For a long time, the smaller the transistors were, the faster they could switch.
But today, we’re approaching the limit of how small transistors can get. As a result, over the last decade researchers have been scratching their heads to find other ways to improve performance so that the computer industry can continue to innovate.
